Abstract
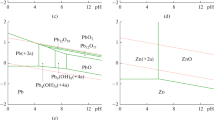
Photo-assisted electrochemical process is a promising technology for a clean ecosystem. It is largely utilized for recovering metals and oxidizing recalcitrant organic compounds. This paper aims to discuss the performance of the photo-oxidation and reduction by applying semiconductor photo-catalysis as the anode and graphite as the cathode for treating rainwater in Tehran, Iran. Organic pollutants and different metals were investigated to study the probable roles of the anodic potential, the gap between electrodes, and the concentration of electrolytes in the possible mechanisms. The laboratory experiments which lasted for 120 min exhibited that the best performance for organic, iron, manganese, and lead removal was at the anodic potential of 10 V and gap of 6 cm. But, for zinc and cadmium, the best performance occurred at the anodic potential of 5.5 V and sodium chloride of 0.65 g/L. The presented reactions and mechanisms demonstrated incidents using the treatment process. They were identical to the presented dendrogram and Pourbaix diagrams. The results of the diagrams showed iron, manganese, and lead were removed by oxidation at the photo-anode. Zinc and cadmium were mainly removed by precipitation. Chemical oxygen demand, iron, manganese, and lead were significantly related and behaved similarly in the treatment process. Their removal was controlled by all the analyzed parameters. This paper may present a cost-effective approach for removing organic and metallic pollutants by photo-assisted electrochemical process. It can be suggested for future evolution of photo-assisted electrochemical on the treatment applications of rainwater.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ab Aziz NAB, Palaniandy P, Abdul Aziz H, Aljuboury DAD (2018) Use of photocatalysis for conversion of harvested rainwater as an alternative source into drinking water. Glob Nest J 20(2):243–256
Agarwal SK (2009) Heavy metal pollution, vol 4. APH Publishing, New Delhi
ALabdeh D, Karbassi AR, Omidvar B, Sarang A (2020) Speciation of metals and metalloids in Anzali wetland, Iran. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17(3):1411–1424. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02471-8
Bakyayita GK, Norrström AC, Kulabako RN (2019) Assessment of levels, speciation, and toxicity of trace metal contaminants in selected shallow groundwater sources, surface runoff, wastewater, and surface water from designated streams in Lake Victoria Basin, Uganda. J Environ Public Health. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6734017
Barrera-Díaz C, Cañizares P, Fernández FJ, Natividad R, Rodrigo MA (2014) Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: an overview of the current applications to actual industrial effluents. J Mex Chem Soc 58(3):256–275. https://doi.org/10.29356/JMCS.V58I3.133
Bessegato GG, Cardoso JC, Zanoni MVB (2015) Enhanced photoelectrocatalytic degradation of an acid dye with boron-doped TiO2 nanotube anodes. Catal Today 240:100–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2014.03.073
Candal RJ, Zeltner WA, Anderson MA (2000) Effects of pH and applied potential on photocurrent and oxidation rate of saline solutions of formic acid in a photoelectrocatalytic reactor. Environ Sci Technol 34(16):3443–3451. https://doi.org/10.1021/es991024c
Carter DE (1995) Oxidation–reduction reactions of metal ions. Environ Health Perspect 103(1):17–19
Changanaqui K, Brillas E, Alarcón H, Sirés I (2020) ZnO/TiO2/Ag2Se nanostructures as photoelectrocatalysts for the degradation of oxytetracycline in water. Electrochim Acta 331:135194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2019.135194
Cheng L, Liu S, He G, Hu Y (2020) The simultaneous removal of heavy metals and organic contaminants over a Bi2WO6/mesoporous TiO2 nanotube composite photocatalyst. RSC Adv 10(36):21228–21237. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA03430D
Chimonyo W, Corin KC, Wiese JG, O’Connor CT (2017) Redox potential control during flotation of a sulphide mineral ore. Miner Eng 110:57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2017.04.011
Daghrir R, Drogui P, El Khakani MA (2013) Photoelectrocatalytic oxidation of chlortetracycline using Ti/TiO2 photo-anode with simultaneous H2O2 production. Electrochim Acta 87:18–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2012.09.020
Davranche M, Bollinger JC, Bril H (2003) Effect of reductive conditions on metal mobility from wasteland solids: an example from the Mortagne-du-Nord site (France). Appl Geochem 18(3):383–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00075-6
De Brito JF, Bessegato GG, Viana TS, de Oliveira DP, Martínez-Huitle CA, Zanoni MVB (2019) Combination of photoelectrocatalysis and ozonation as a good strategy for organics oxidation and decreased toxicity in oil-produced water. J Electrochem Soc 166(5):H3231. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0331905jes
Egerton TA, Christensen PA, Kosa SAM, Onoka B, Harper JC, Tinlin JR (2006) Photoelectrocatalysis by titanium dioxide for water treatment. Int J Environ Pollut 27(1–3):2–19. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJEP.2006.010450
Etacheri V, Di Valentin C, Schneider J, Bahnemann D, Pillai SC (2015) Visible-light activation of TiO2 photocatalysts: advances in theory and experiments. J Photochem Photobiol C 25:1–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochemrev.2015.08.003
Farajnejad H, Karbassi AR, Heidari M (2017) Fate of toxic metals during estuarine mixing of fresh water with saline water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(35):27430–27435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0329-z
Feng Y, Yang L, Liu J, Logan BE (2016) Electrochemical technologies for wastewater treatment and resource reclamation. Environ Sci Water Res Technol 2(5):800–831. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5EW00289C
Ferniza-García F, Amaya-Chávez A, Roa-Morales G, Barrera-Díaz CE (2017) Removal of Pb, Cu, Cd, and Zn present in aqueous solution using coupled electrocoagulation-phytoremediation treatment. Int J Electrochem. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7681451
Ghimire U, Jang M, Jung SP, Park D, Park SJ, Yu H, Oh SE (2019) Electrochemical removal of ammonium nitrogen and cod of domestic wastewater using platinum coated titanium as an anode electrode. Energies 12(5):883. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12050883
Goncharuk VV, Bagrii VA, Mel’nik LA, Chebotareva RD, Bashtan SY (2010) The use of redox potential in water treatment processes. J Water Chem Technol 32(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.3103/S1063455X10010017
Hassani S, Karbassi AR, Ardestani M (2017) Role of estuarine natural flocculation process in removal of Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn. Glob J Environ Sci Manag 3(2):187–196. https://doi.org/10.22034/gjesm.2017.03.02.007
Jia M, Yang Z, Xu H, Song P, Xiong W, Cao J, Yang Y (2020) Integrating N and F co-doped TiO2 nanotubes with ZIF-8 as photoelectrode for enhanced photo-electrocatalytic degradation of sulfamethazine. Chem Eng J 388:124388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124388
Jin P, Chang R, Liu D, Zhao K, Zhang L, Ouyang Y (2014) Phenol degradation in an electrochemical system with TiO2/activated carbon fiber as electrode. J Environ Chem Eng 2(2):1040–1047. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2014.03.023
Keith L, Telliard W (1979) EST special report: priority pollutants: Ia perspective view. Environ Sci Technol 13(4):416–423. https://doi.org/10.1021/es60152a601
Kim J, Bae S (2019) Fabrication of Ti/Ir–Ru electrode by spin coating method for electrochemical removal of copper. Environ Eng Res 24(4):646–653. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2018.229
Komtchou S, Delegan N, Dirany A, Drogui P, Robert D, El Khakani MA (2020) Photo-electrocatalytic oxidation of atrazine using sputtured deposited TiO2: WN photoanodes under UV/visible light. Catal Today 340:323–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2019.04.067
Kruthika NL, Karthika S, Raju GB, Prabhakar S (2013) Efficacy of electrocoagulation and electrooxidation for the purification of wastewater generated from gelatin production plant. J Environ Chem Eng 1(3):183–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2013.04.017
Le AT, Pung SY, Sreekantan S, Matsuda A (2019) Mechanisms of removal of heavy metal ions by ZnO particles. Heliyon 5(4):1440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01440
Leng WH, Zhu WC, Ni J, Zhang Z, Zhang JQ, Cao CN (2006) Photoelectrocatalytic destruction of organics using TiO2 as photoanode with simultaneous production of H2O2 at the cathode. Appl Catal A Gen 300(1):24–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2005.10.053
Li XZ, Li FB, Fan CM, Sun YP (2002) Photoelectrocatalytic degradation of humic acid in aqueous solution using a Ti/TiO2 mesh photoelectrode. Water Res 36(9):2215–2224. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00440-7
Li XZ, Zhao BX, Wang P (2007) Degradation of 2, 4-dichlorophenol in aqueous solution by a hybrid oxidation process. J Hazard Mater 147(1–2):281–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.12.077
Lim J, Hoffmann MR (2019) Substrate oxidation enhances the electrochemical production of hydrogen peroxide. Chem Eng J 374:958–964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.05.165
Litter MI (2015) Mechanisms of removal of heavy metals and arsenic from water by TiO2-heterogeneous photocatalysis. Pure Appl Chem 87(6):557–567. https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2014-0710
Liu L, Li R, Liu Y, Zhang J (2016) Simultaneous degradation of ofloxacin and recovery of Cu(II) by photoelectrocatalysis with highly ordered TiO2 nanotubes. J Hazard Mater 308:264–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.01.046
Liu Y, Lai M, Long L, Zhang Y, Luo L, Shen F, Chen X (2020) Photonic TiO2 photoelectrodes for environmental protections: can color be used as a quick selection indicator for photoelectrocatalytic performance. J Hazard Mater 398:122867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122867
Mais L, Mascia M, Palmas S, Vacca A (2019) Photoelectrochemical oxidation of phenol with nanostructured TiO2-PANI electrodes under solar light irradiation. Sep Purif Technol 208:153–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.03.074
Maksimenko O, Pancheva H, Madzhd S, Pysanko Y, Briankin O, Tykhomyrova T, Hrebeniuk T (2018) Examining the efficiency of electrochemical purification of storm wastewater at machine-building enterprises. East Eur J Enterp Technol 6(10):21–27. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2018.150088
Mieluch J, Sadkowski A, Wild J, Zoltowski P (1975) Electrochemical oxidation of phenol compounds in aqueous-solutions. Przemysl Chem 54(9):513–516
Mishra S, Kumar A, Yadav S, Singhal MK (2018) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in water of Kali River using principle component and cluster analysis, India. Sustain Water Resour Manag 4(3):573–581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-017-0141-4
Montenegro-Ayo R, Morales-Gomero JC, Alarcon H, Cotillas S, Westerhoff P, Garcia-Segura S (2019) Scaling up photoelectrocatalytic reactors: a TiO2 nanotube-coated disc compound reactor effectively degrades acetaminophen. Water 11(12):2522. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122522
Moreno CHA, Cocke DL, Gomes JA, Morkovsky P, Parga JR, Peterson E, Garcia C (2009) Electrochemical reactions for electrocoagulation using iron electrodes. Ind Eng Chem Res 48(4):2275–2282. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie8013007
Ndjomgoue-Yossa AC, Nanseu-Njiki CP, Kengne IM, Ngameni E (2015) Effect of electrode material and supporting electrolyte on the treatment of water containing Escherichia coli by electrocoagulation. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12(6):2103–2110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-014-0609-9
Nwoke OO, Ezema IF, Chigor VN, Anoliefo EC, Mbajiorgu CC (2018) Disinfection of a farmstead roof harvested rainwater for potable purposes using an automated solar photocatalytic reactor. Agric Eng Int CIGR J 20(3):52–60
Ojani R, Raoof JB, Zarei E (2012) Electrochemical monitoring of photoelectrocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B using TiO2 thin film modified graphite electrode. J Solid State Electrochem 16(6):2143–2149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-011-1634-y
Ola O, Maroto-Valer MM (2015) Review of material design and reactor engineering on TiO2 photocatalysis for CO2 reduction. J Photochem Photobiol C 24:16–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochemrev.2015.06.001
Osugi ME, Umbuzeiro GA, Anderson MA, Zanoni MVB (2005) Degradation of metallophtalocyanine dye by combined processes of electrochemistry and photoelectrochemistry. Electrochim Acta 50(25–26):5261–5269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2005.01.058
Papagiannis I, Koutsikou G, Frontistis Z, Konstantinou I, Avgouropoulos G, Mantzavinos D, Lianos P (2018) Photoelectrocatalytic vs. photocatalytic degradation of organic water born pollutants. Catalysts 8(10):455. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8100455
Paschoal FM, Anderson MA, Zanoni MVB (2008) Photoeletrocatalytic oxidation of anionic surfactant used in leather industry on nanoporous Ti/TiO2 eletrodes. J Braz Chem Soc 19(4):803–810. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-50532008000400027
Qiu L, Wang Q, Liu Z, Zhao Q, Tian X, Li H, Gao S (2018) Preparation of 3D TiO2 nanotube arrays photoelectrode on Ti mesh for photoelectric conversion and photoelectrocatalytic removal of pollutant. Sep Purif Technol 207:206–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.06.050
Rajkumar D, Palanivelu K, Mohan N (2001) Electrochemical oxidation of resorcinol for wastewater treatment using Ti/TiO2–RuO2–IrO2 electrode. J Environ Sci Health A 36(10):1997–2010. https://doi.org/10.1081/ESE-100107443
Robertson PK, Robertson JM, Bahnemann DW (2012) Removal of microorganisms and their chemical metabolites from water using semiconductor photocatalysis. J Hazard Mater 211:161–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.11.058
Rodríguez A, Rosal R, Perdigón-Melón JA, Mezcua M, Agüera A, Hernando MD, García-Calvo E (2008) Ozone-based technologies in water and wastewater treatment. Handb Environ Chem 5:127–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/698_5_103
Sazakli E, Alexopoulos A, Leotsinidis M (2007) Rainwater harvesting, quality assessment and utilization in Kefalonia Island, Greece. Water Res 41(9):2039–2047. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.01.037
Sharififard H, Ghorbanpour M, Hosseinirad S (2018) Cadmium removal from wastewater using nano-clay/TiO2 composite: kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamic study. Adv Environ Technol 4(4):203–209. https://doi.org/10.22104/AET.2019.3029.1149
Su X, Kushima A, Halliday C, Zhou J, Li J, Hatton TA (2018) Electrochemically-mediated selective capture of heavy metal chromium and arsenic oxyanions from water. Nat Commun 9(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07159-0
Subramaniam MN, Goh PS, Lau WJ, Ismail AF (2019) The roles of nanomaterials in conventional and emerging technologies for heavy metal removal: a state-of-the-art review. Nanomaterials 9(4):625. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9040625
Szögi AA, Hunt PG, Sadler EJ, Evans DE (2004) Characterization of oxidation-reduction processes in constructed wetlands for swine wastewater treatment. Appl Eng Agric 20(2):189. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.15891
Tien TT, Luu TL (2019) Electrooxidation of tannery wastewater with continuous flow system: role of electrode materials. Environ Eng Res 25(3):324–334. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2018.349
Wahyuni ET, Aprilita NH, Hatimah H, Wulandari AM, Mudasir M (2015) Removal of toxic metal ions in water by photocatalytic method. Chem Sci Int J 5(2):194–201. https://doi.org/10.9734/ACSJ/2015/13807
Wahyuni ET, Siswanta D, Kunarti ES, Supraba D, Budiraharjo S (2019) Removal of Pb(II) ions in the aqueous solution by photo-Fenton method. Glob Nest J 21(2):180–186. https://doi.org/10.30955/gnj.002936
Wang Q, Shang J, Zhu T, Zhao F (2011) Efficient photoelectrocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI) using TiO2 nanotube arrays as the photoanode and a large-area titanium mesh as the photocathode. J Mol Catal A Chem 335(1–2):242–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2010.11.040
Wang D, Li Y, Puma GL, Lianos P, Wang C, Wang P (2017) Photoelectrochemical cell for simultaneous electricity generation and heavy metals recovery from wastewater. J Hazard Mater 323:681–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.10.037
Waso M, Khan S, Singh A, Mcmichael S, Ahmed W, Fernandez-Ibanez P, Khan W (2020) Predatory bacteria in combination with solar disinfection and solar photocatalysis for the treatment of rainwater. Water Res 169:115281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.115281
Williams JL (2006) An electrolytic technique to study the mobility of inorganic constituents in soils and waste materials. Dissertation, University of Vanderbilt
Wriedt HA (1988) The O–Pb (Oxygen–Lead) system. J Phase Equilibria 9(2):106–127
Xie YB, Li XZ (2006) Interactive oxidation of photoelectrocatalysis and electro-Fenton for azo dye degradation using TiO2–Ti mesh and reticulated vitreous carbon electrodes. Mater Chem Phys 95(1):39–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2005.05.048
Yao J, Mei Y, Xia G, Lu Y, Xu D, Sun N, Chen J (2019) Process optimization of electrochemical oxidation of ammonia to nitrogen for actual dyeing wastewater treatment. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16(16):2931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16162931
Yuan N, Jiang Q, Li J, Tang J (2020) A review on non-noble metal based electrocatalysis for the oxygen evolution reaction. Arab J Chem 13(2):4294–4309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2019.08.006
Yurdakal S, Çetinkaya S, Şarlak MB, Özcan L, Loddo V, Palmisano L (2020) Photoelectrocatalytic oxidation of 3-pyridinemethanol to 3-pyridinemethanal and vitamin B 3 by TiO2 nanotubes. Catal Sci Technol 10(1):124–137. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CY01583C
Zanoni MVB, Sene JJ, Anderson MA (2003) Photoelectrocatalytic degradation of Remazol Brilliant Orange 3R on titanium dioxide thin-film electrodes. J Photochem Photobiol A 157(1):55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1010-6030(02)00320-9
Zarei E (2019) A strategy for degradation of 2, 5-dichlorophenol using its photoelectrocatalytic oxidation on the TiO2/Ti thin film electrode. Iran J Catal 9(2):99–108
Zarei E, Ojani R (2017) Fundamentals and some applications of photoelectrocatalysis and effective factors on its efficiency: a review. J Solid State Electrochem 21(2):305–336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-016-3385-2
Zhao X, Guo L, Zhang B, Liu H, Qu J (2013) Photoelectrocatalytic oxidation of Cu(II)–EDTA at the TiO2 electrode and simultaneous recovery of Cu(II) by electrodeposition. Environ Sci Technol 47(9):4480–4488. https://doi.org/10.1021/es3046982
Zhao X, Guo L, Hu C, Liu H, Qu J (2014) Simultaneous destruction of Nickel(II)-EDTA with TiO2/Ti film anode and electrodeposition of nickel ions on the cathode. Appl Catal B 144:478–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.07.038
Zhou X, Zheng Y, Zhou J, Zhou S (2015) Degradation kinetics of photoelectrocatalysis on landfill leachate using codoped TiO2/Ti photoelectrodes. J Nanomater. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/810579
Acknowledgements
The present research was sponsored by Ministry of Higher Education, Syria. We also thank University of Tehran for providing us with the electro-flocculation laboratory to carry out the analyses.
Funding
The present research is supported by Syrian Ministry of Education (Fund No. 46/B/4/103626)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is not any conflict of interest regarding the publication of this manuscript. In addition, the ethical issues, including plagiarism, informed consent, misconduct, data fabrication and/or falsification, double publication and/or submission, and redundancy have been completely observed by the authors.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Samareh Mirkia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ebraheim, G., Karbassi, A.R. & Mehrdadi, N. Employing speciation of metals to assess photo-assisted electrochemical efficiency for improving rainwater quality in Tehran, Iran. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19, 261–280 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03127-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03127-2