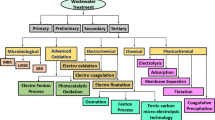
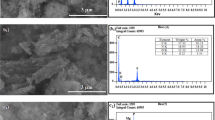
Abstract
In this study, a new type of multifunctional material PANI/NiO/MnO2 nanocomposite was first time prepared by chemical polymerisation from aniline monomer in the presence of metal oxides (NiO and MnO2) and an oxidant (ammonium persulfate) in acidic aqueous solution for the elimination of methyl orange (MO) dye from water. Herein, the PANI/NiO/MnO2 nanocomposite was found to be a favourable adsorbent for wastewater treatment due to its high adsorption and efficiency, self-regeneration, low cost and easy synthesis. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, thermo-gravimetric analysis, transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, Brunauer–Emmett–Teller analysis and Zeta potential were employed to characterise the synthesised nanocomposites. The data revealed that PANI nanocomposites doped with NiO and MnO2 nanoparticles had a higher adsorption efficiency (~ 97%) than that found in pure PANI (~ 53%). The adsorption conditions, such as pH of the medium, initial dye concentration, adsorbent dosage, and adsorption time were investigated. Various kinetic and isotherm models were used to analyse the results of the kinetics and the equilibrium adsorption and to interpret the interaction between the dye and nanocomposite adsorbents. The adsorption kinetics data for MO dye on the PANI/NiO/MnO2 were well explained based on a pseudo-second-order model while adsorption isotherm results were analysed based upon the Langmuir isotherm model. In addition, the adsorption process was an endothermic, favourable and spontaneous reaction according to thermodynamic studies. Also, the influence of matrix synthetic waste on MO dye removal was studied and found to show good results with matrix synthetic waste for both PANI/NiO/MnO2 and PANI adsorbents. The experimental adsorption capacity of the PANI/NiO/MnO2 nanocomposite (248.4 mg/g) was considerably greater than that of PANI (57.5 mg/g). The PANI/NiO/MnO2 adsorbent can be recycled up to four times and maintains a good adsorption capacity throughout.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
31 March 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03194-5
References
Ai L, Zhang C, Chen Z (2011) Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by a solvothermal-synthesized graphene/magnetite composite. J Hazard Mater 192:1515–1524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.05.070
Alabdullah SS, Ismail HK, Ryder KS, Abbott AP (2020) Evidence supporting an emulsion polymerisation mechanism for the formation of polyaniline. Electrochim Acta 354:136737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136737
Alesary HF, Ismail HK, Khudhair AF, Mohammed MQ (2018) Effects of dopant ions on the properties of polyaniline conducting polymer. Orient J Chem 34:2525. https://doi.org/10.13005/ojc/340539
Al-Ghouti MA, Da’ana DA (2020) Guidelines for the use and interpretation of adsorption isotherm models: a review. J Hazard Mater 393:122383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122383
Amir M, Julkapli N, Hamid SA (2016) Incorporation of chitosan and glass substrate for improvement in adsorption, separation, and stability of TiO2 photodegradation. Int J Environ Sci Technol 13:865–874. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-015-0914-y
Ansari R, Mosayebzadeh Z (2011) Application of polyaniline as an efficient and novel adsorbent for azo dyes removal from textile wastewaters. Chem Pap 65:1–8. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-010-0083-x
Asuha S, Zhou XG, Zhao S (2010) Adsorption of methyl orange and Cr(VI) on mesoporous TiO2 prepared by hydrothermal method. J Hazard Mater 181:204–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.04.117
Bhaumik M, McCrindle R, Maity A (2013) Efficient removal of Congo red from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto interconnected polypyrrole–polyaniline nanofibres. Chem Eng J 228:506–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.05.026
Bhaumik M, Choi HJ, McCrindle RI, Maity A (2014) Composite nanofibers prepared from metallic iron nanoparticles and polyaniline: high performance for water treatment applications. J Colloid Interface Sci 425:75–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2014.03.031
Blaisi NI, Zubair M, Ali S, Kazeem TS, Manzar MS, Al-Kutti W, Al Harthi MA (2018) Date palm ash-MgAl-layered double hydroxide composite: sustainable adsorbent for effective removal of methyl orange and eriochrome black-T from aqueous phase. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:34319–34331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3367-2
Cai X, Cui X, Zu L, Zhang Y, Gao X, Lian H (2017) Ultra high electrical performance of nano nickel oxide and polyaniline composite materials. Polymers 9:288. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9070288
Chen Z, Xu L, Li W, Waje M, Yan Y (2006) Polyaniline nanofibre supported platinum nanoelectrocatalysts for direct methanol fuel cells. Nanotechnology 17:5254. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/17/20/035
Chen W, Lu W, Yao Y, Xu M (2007) Highly efficient decomposition of organic dyes by aqueous-fiber phase transfer and in situ catalytic oxidation using fiber-supported cobalt phthalocyanine. Environ Sci Technol 41:6240–6245. https://doi.org/10.1021/es070002k
Dahri MK, Kooh MRR, Lim LB (2015) Application of Casuarina equisetifolia needle for the removal of methylene blue and malachite green dyes from aqueous solution. Alex Eng J 54:1253–1263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2015.07.005
Darwish A, Rashad M, Al-Aoh HA (2019) Methyl orange adsorption comparison on nanoparticles: isotherm, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies. Dyes Pigment 160:563–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2018.08.045
Das SK, Khan MMR, Parandhaman T, Laffir F, Guha AK, Sekaran G, Mandal AB (2013) Nano-silica fabricated with silver nanoparticles: antifouling adsorbent for efficient dye removal, effective water disinfection and biofouling control. Nanoscale 5:5549–5560. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3nr00856h
Duhan M, Kaur R (2019) Adsorptive removal of methyl orange with polyaniline nanofibers: an unconventional adsorbent for water treatment. Environ Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2019.1593511
Eftekhari A (2011) Nanostructured conductive polymers. Wiley, New York. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470661338
Elwakeel KZ (2009) Removal of Reactive Black 5 from aqueous solutions using magnetic chitosan resins. J Hazard Mater 167:383–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.01.051
Elwakeel KZ, Abd El-Ghaffar M, El-Kousy SM, El-Shorbagy HG (2013) Enhanced remediation of Reactive Black 5 from aqueous media using new chitosan ion exchangers. J Dispers Sci Technol 34:1008–1019. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2012.695943
Elwakeel K, El-Bindary A, Ismail A, Morshidy A (2017a) Magnetic chitosan grafted with polymerized thiourea for remazol brilliant blue R recovery: effects of uptake conditions. J Dispers Sci Technol 38:943–952. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2016.1216436
Elwakeel KZ, El-Bindary A, El-Sonbati A, Hawas AR (2017b) Magnetic alginate beads with high basic dye removal potential and excellent regeneration ability. Can J Chem 95:807–815. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjc-2016-0641
Elwakeel KZ, Elgarahy AM, Mohammad SH (2017c) Use of beach bivalve shells located at Port Said coast (Egypt) as a green approach for methylene blue removal. J Environ Chem Eng 5:578–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.12.032
Ge F, Ye H, Li MM, Zhao BX (2012) Efficient removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution by polymer-modified magnetic nanoparticles. Chem Eng J 198–199:11–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.05.074
Ghasemian E, Palizban Z (2016) Comparisons of azo dye adsorptions onto activated carbon and silicon carbide nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon. Int J Environ Sci Technol 13:501–512. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-015-0875-1
Gil A, Assis FCC, Albeniz S, Korili SA (2011) Removal of dyes from wastewaters by adsorption on pillared clays. Chem Eng J 168:1032–1040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.01.078
Gong R, Li M, Yang C, Sun Y, Chen J (2005) Removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution by adsorption on peanut hull. J Hazard Mater 121:247–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.01.029
Gutiérrez MC, Pepió M, Crespi M (2002) Electrochemical oxidation of reactive dyes method validation and application. Color Technol 118:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1478-4408.2002.tb00129.x
Hemmati M, Rajabi M, Asghari A (2018) Magnetic nanoparticle based solid-phase extraction of heavy metal ions: a review on recent advances. Microchim Acta 185:160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2670-4
Hillman AR, Ryder KS, Ismail HK, Unal A, Voorhaar A (2017) Fundamental aspects of electrochemically controlled wetting of nanoscale composite materials. Faraday Discuss 199:75–99. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7fd00060j
Ibrahim RK, El-Shafie A, Hin LS, Mohd NSB, Aljumaily MM, Ibraim S, AlSaadi MA (2019) A clean approach for functionalized carbon nanotubes by deep eutectic solvents and their performance in the adsorption of methyl orange from aqueous solution. J Environ Manag 235:521–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.01.070
Inzelt G (2012) Conducting polymers: a new era in electrochemistry. Springer, Berlin. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-75930-0
Ismail HK, Alesary HF, Al-Murshedi AYM, Kareem JH (2019a) Ion and solvent transfer of polyaniline films electrodeposited from deep eutectic solvents via EQCM. J Solid State Electrochem 23:3107–3121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-019-04415-1
Ismail HK, Alesary HF, Mohammed MQ (2019b) Synthesis and characterisation of polyaniline and/or MoO2/graphite composites from deep eutectic solvents via chemical polymerisation. J Polym Res 26:65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1732-6
Iwuoha EI, Mavundla SE, Somerset VS, Petrik LF, Klink MJ, Sekota M, Bakers P (2006) Electrochemical and spectroscopic properties of fly ash–polyaniline matrix nanorod composites. Microchim Acta 155:453–458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-006-0584-z
Janaki V, Oh BT, Shanthi K, Lee KJ, Ramasamy AK, Kamala-Kannan S (2012a) Polyaniline/chitosan composite: an eco-friendly polymer for enhanced removal of dyes from aqueous solution. Synth Met 162:974–980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2012.04.015
Janaki V, Vijayaraghavan K, Oh BT, Lee KJ, Muthuchelian K, Ramasamy AK, Kamala-Kannan S (2012b) Starch/polyaniline nanocomposite for enhanced removal of reactive dyes from synthetic effluent. Carbohydr Polym 90:1437–1444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.07.012
Jawad AH, Mamat NH, Hameed B, Ismail K (2019) Biofilm of cross-linked chitosan-ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether for removal of reactive red 120 and methyl orange: adsorption and mechanism studies. J Environ Chem Eng 7:102965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.102965
Jianjun H, Yuping D, Jia Z, Hui J, Shunhua L, Weiping L (2011) γ-MnO2–polyaniline composites preparation, characterization, and applications in microwave absorption. Phys B Condens Matter 406:1950–1955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2011.02.063
Kannusamy P, Sivalingam T (2013) Chitosan–ZnO/polyaniline hybrid composites: polymerization of aniline with chitosan–ZnO for better thermal and electrical property. Polym Degrad Stab 98:988–996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2013.02.015
Karri RR, Tanzifi M, Tavakkoli Yaraki M, Sahu JN (2018) Optimization and modeling of methyl orange adsorption onto polyaniline nano-adsorbent through response surface methodology and differential evolution embedded neural network. J Environ Manag 223:517–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.06.027
Kim KN, Jung HR, Lee WJ (2016) Hollow cobalt ferrite–polyaniline nanofibers as magnetically separable visible-light photocatalyst for photodegradation of methyl orange. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 321:257–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2016.02.007
Lian Z, Wang J (2012) Molecularly imprinted polymer for selective extraction of malachite green from seawater and seafood coupled with high-performance liquid chromatographic determination. Mar Pollut Bull 64:2656–2662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.10.011
Lima EC, Hosseini-Bandegharaei A, Moreno-Piraján JC, Anastopoulos I (2019) A critical review of the estimation of the thermodynamic parameters on adsorption equilibria. Wrong use of equilibrium constant in the Van’t Hoof equation for calculation of thermodynamic parameters of adsorption. J Mol Liq 273:425–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.10.048
Lu L, Zhao M, Liang SC, Zhao LY, Li DB, Zhang BB (2009) Production and synthetic dyes decolourization capacity of a recombinant laccase from Pichia pastoris. J Appl Microbiol 107:1149–1156. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04291.x
Lv SW, Liu JM, Ma H, Wang ZH, Li CY, Zhao N, Wang S (2019) Simultaneous adsorption of methyl orange and methylene blue from aqueous solution using amino functionalized Zr-based MOFs. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 282:179–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2019.03.017
Mahanta D, Madras G, Radhakrishnan S, Patil S (2008) Adsorption of sulfonated dyes by polyaniline emeraldine salt and its kinetics. J Phys Chem B 112:10153–10157. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp803903x
Mallakpour S, Hatami M (2019) An effective, low-cost and recyclable bio-adsorbent having amino acid intercalated LDH@Fe3O4/PVA magnetic nanocomposites for removal of methyl orange from aqueous solution. Appl Clay Sci 174:127–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2019.03.026
Manchaiah A, Badalamoole V (2019) Novel heterocyclic chitosan-based Schiff base: evaluation as adsorbent for removal of methyl orange from aqueous solution. Water Environ J. https://doi.org/10.1111/wej.12470
Manzar MS, Waheed A, Qazi IW, Blaisi NI, Ullah N (2019) Synthesis of a novel epibromohydrin modified crosslinked polyamine resin for highly efficient removal of methyl orange and eriochrome black T. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 97:424–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2019.01.027
Mohammadi N, Khani H, Gupta VK, Amereh E, Agarwal S (2011) Adsorption process of methyl orange dye onto mesoporous carbon material-kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J Colloid Interface Sci 362:457–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2011.06.067
Nasar A, Mashkoor F (2019) Application of polyaniline-based adsorbents for dye removal from water and wastewater—a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:5333–5356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3990-y
Nasir AM, Goh PS, Abdullah MS, Cheer NB, Ismail AF (2019) Adsorptive nanocomposite membranes for heavy metal remediation: recent progresses and challenges. Chemosphere 232:96–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.174
Rahman N, Dafader NC, Miah AR, Shahnaz S (2019) Efficient removal of methyl orange from aqueous solution using amidoxime adsorbent. Int J Environ Stud 76:594–607. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207233.2018.1494930
Rondina DJG, Ymbong DV, Cadutdut MJM, Nalasa JRS, Paradero JB, Mabayo VIF, Arazo RO (2019) Utilization of a novel activated carbon adsorbent from press mud of sugarcane industry for the optimized removal of methyl orange dye in aqueous solution. Appl Water Sci 9:181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-1063-0
Sarma GK, Gupta SS, Bhattacharyya KG (2019) Nanomaterials as versatile adsorbents for heavy metal ions in water: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:6245–6278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-04093-y
Shahabuddin S, Sarih N, Afzal Kamboh M, Rashidi Nodeh H, Mohamad S (2016a) Synthesis of polyaniline-coated graphene oxide@SrTiO3 nanocube nanocomposites for enhanced removal of carcinogenic dyes from aqueous solution. Polymers 8:305. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8090305
Shahabuddin S, Sarih NM, Mohamad S, Baharin SNA (2016b) Synthesis and characterization of Co3O4 nanocube-doped polyaniline nanocomposites with enhanced methyl orange adsorption from aqueous solution. RSC Adv 6:43388–43400. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra04757b
Shambharkar B, Umare S (2011) Synthesis and characterization of polyaniline/NiO nanocomposite. J Appl Polym Sci 122:1905–1912. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.34286
Shariati S, Faraji M, Yamini Y, Rajabi AA (2011) Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles modified with sodium dodecyl sulfate for removal of safranin O dye from aqueous solutions. Desalination 270:160–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.11.040
Sharifpour E, Alipanahpour Dil E, Asfaram A, Ghaedi M, Goudarzi A (2019) Optimizing adsorptive removal of malachite green and methyl orange dyes from simulated wastewater by Mn-doped CuO-Nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon using CCD-RSM: mechanism, regeneration, isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. Appl Organomet Chem 33:e4768. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.4768
Shukla AK, Alam J, Rahaman M, Alrehaili A, Alhoshan M, Aldalbahi A (2020) A facile approach for elimination of electroneutral/anionic organic dyes from water using a developed carbon-based polymer nanocomposite membrane. Water Air Soil Pollut 231:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04483-4
Tao X, Wu Y, Cha L (2019) Shaddock peels-based activated carbon as cost-saving adsorbents for efficient removal of Cr(VI) and methyl orange. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:19828–19842. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05322-8
Taty-Costodes VC, Fauduet H, Porte C, Delacroix A (2003) Removal of Cd (II) and Pb(II) ions, from aqueous solutions, by adsorption onto sawdust of Pinus sylvestris. J Hazard Mater 105:121–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2003.07.009
Tony M (2020) Zeolite-based adsorbent from alum sludge residue for textile wastewater treatment. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17:2485–2498. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02646-8
Türkeş E, Açıkel YS (2020) Synthesis and characterization of magnetic halloysite–chitosan nanocomposites: use in the removal of methylene blue in wastewaters. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17:1281–1294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02550-w
Vidya J, Bosco AJ, Haribaaskar K, Balamurugan P (2019) Polyaniline–BiVO4 nanocomposite as an efficient adsorbent for the removal of methyl orange from aqueous solution. Mater Sci Semicond Process 103:104645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2019.104645
Wang J, Guo X (2020) Adsorption kinetic models: physical meanings, applications, and solving methods. J Hazard Mater 390:122156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122156
Wang L, Zhao X, Zhang J, Xiong Z (2017) Selective adsorption of Pb(II) over the zinc-based MOFs in aqueous solution-kinetics, isotherms, and the ion exchange mechanism. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:14198–14206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9002-9
Wu TM, Lin YW, Liao CS (2005) Preparation and characterization of polyaniline/multi-walled carbon nanotube composites. Carbon 43:734–740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2004.10.043
Xu H, Zhang J, Chen Y, Lu H, Zhuang J, Li J (2014) Synthesis of polyaniline-modified MnO2 composite nanorods and their photocatalytic application. Mater Lett 117:21–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2013.11.089
Yang L, Gao J, Liu Y, Zhang Z, Zou M, Liao Q, Shang J (2018) Removal of methyl orange from water using sulfur-modified nZVI supported on biochar composite. Water Air Soil Pollut 229:355. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3992-x
Yang XJ, Zhang P, Li P, Li Z, Xia W, Zhang H et al (2019) Layered double hydroxide/polyacrylamide nanocomposite hydrogels: green preparation, rheology and application in methyl orange removal from aqueous solution. J Mol Liq 280:128–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.02.033
Yang X, Xiong Z, Meng X, Zhu H, Xia Y (2020) Broad-spectrum adsorption property of Chondrus crispus activated carbon for ionic and solvent dyes. Water Air Soil Pollut 231:64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-4442-0
Zare EN, Motahari A, Sillanpaa M (2018) Nanoadsorbents based on conducting polymer nanocomposites with main focus on polyaniline and its derivatives for removal of heavy metal ions/dyes: a review. Environ Res 162:173–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2017.12.025
Zeng A, Zeng A (2017) Synthesis of a quaternized beta cyclodextrin–montmorillonite composite and its adsorption capacity for Cr(VI), methyl orange, and p-nitrophenol. Water Air Soil Pollut 228:278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3461-y
Zhang Z, Zhang J, Liu J, Xiong Z, Chen X (2016) Selective and competitive adsorption of azo dyes on the metal–organic framework ZIF-67. Water Air Soil Pollut 227:471. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3166-7
Zhang M, Yu Z, Yu H (2019) Adsorption of Eosin Y, methyl orange and brilliant green from aqueous solution using ferroferric oxide/polypyrrole magnetic composite. Polym Bull 77:1049–1066. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-02792-1
Zhao Y, Chen H, Li J, Chen C (2015) Hierarchical MWCNTs/Fe3O4/PANI magnetic composite as adsorbent for methyl orange removal. J Colloid Interface Sci 450:189–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.03.015
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge the Universities of Koya and Kerbala for providing the required materials and instruments for this work. They would also like to thank Dr. Mark Watkins from university of Leicester (UK) for proofreading the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Abhishek RoyChowdhury.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, L.I.A., Ismail, H.K., Alesary, H.F. et al. A nanocomposite based on polyaniline, nickel and manganese oxides for dye removal from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 18, 2031–2050 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02961-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02961-0