Abstract
Nowadays, the widespread application of formate fluids in petroleum industries due to its feasibility and its high potential to have more compatibility with the several formation characteristics would become a revolution to control the drilling inefficiencies and provide lower drilling expenditures. Formate fluids have the ability to maintain the property of drilling fluid on the high temperatures and high pressures, reduce the resistance of hydraulic flow, and decrease the rate of corrosion rate for the contact of drilling pipe with drilling fluid. The objective of this comprehensive study is to investigate the visual laboratory measurements of rheological characteristics, consider the profound impact of different types of pollutants on the rheological property, pore pressure transmission (henceforth; PPT) tests to measure formation pressure, and analyze the different concentration of salts for each drilling fluid. The drilling fluids are utilized in this study are silicate muds, glycol muds, sodium and potassium formate muds, and base muds. Consequently, regarding the results of this investigation, it is clarified that NaoH has performed the least impact on the rheological properties of formate fluids and sodium/potassium formate fluids has the minimum formation pressure (PPT tests) which leads to be operated as the best choice in drilling operations. Moreover, the more concentration of salts in the drilling fluid would be a weakening point which indicated that formate fluids would not be appropriate in higher salts concentration.

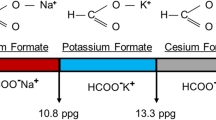
(Reproduced with permission from Caenn et al. 2017)

(Reproduced with permission from Caenn et al. 2017)

(Reproduced with permission from Caenn et al. 2017)

(Reproduced with permission from Caenn et al. 2017)


(Reproduced with permission from Caenn et al. 2017)




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Busch A, Islam A, Martins DW et al (2018) Cuttings-transport modeling–part 1: specification of benchmark parameters with a Norwegian-continental-shelf perspective. In: SPE Drilling and Completion
Caenn R, Chillingar GV (1996) Drilling fluids: state of the art. J Pet Sci Eng 14:221–230
Caenn R, Darley HC, Gray GR (2011) Composition and properties of drilling and completion fluids. Gulf Professional Publishing, Boston
Caenn R, Darley HCH, Gray GR (2017) Chapter 11—completion, workover, packer, and reservoir drilling fluids. Composition and properties of drilling and completion fluids, 7th edn. Gulf Professional Publishing, Boston, pp 461–519
Chao S (2017) Application of fitting progressively filling model in drilling fluids of the permeability reservoirs. Energy 1:029
Cutillas V, Galera MM, Rajski Ł et al (2018) Evaluation of supercritical fluid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry for pesticide residues in food. J Chromatogr A 1545:67–74
Davarpanah A (2018) The integrated feasibility analysis of water reuse management in the petroleum exploration performances of unconventional shale reservoirs. Appl Water Sci 8:75
Davarpanah A, Mirshekari B, Behbahani TJ et al (2018) Integrated production logging tools approach for convenient experimental individual layer permeability measurements in a multi-layered fractured reservoir. J Pet Explor Prod Technol 1:1–9
Downs J, Fleming N (2018) Evaluating formation damage predictions drawn from HPHT core flooding tests on brent group sandstone reservoir cores with heavy formate drill-in fluids: a case study from the huldra field. In: SPE international conference and exhibition on formation damage control. Society of Petroleum Engineers
Downs J, Howard S, Anderson Z (2018) Rates of permeability restoration in tight gas-bearing sandstone cores following long-duration exposure to cesium formate fluids under HPHT conditions—a detailed laboratory investigation. In: SPE international conference and exhibition on formation damage control. Society of Petroleum Engineers
Javora PH, Ke M, Stevens RF et al (2003) The chemistry of formate brines at downhole conditions. In: International symposium on oilfield chemistry. Society of Petroleum Engineers
Jøntvedt E, Fjeldheim M, Løchen J et al (2018) Deployment of cesium formate drill-in and openhole completion fluid in the martin linge high pressure, high permeability gas reservoir enhances total’s operational efficiency and radically improves well performance. In: SPE international conference and exhibition on formation damage control. Society of Petroleum Engineers
Kakoli M, Davarpanah A, Ahmadi A et al (2016) Recommendations for compatibility of different types of polymers with potassium/sodium formate-based fluids for drilling operations: an experimental comparative analysis. J Mater Sci Eng 6(2169–0022):1000311
Karimi S, Goudarzi B, Moezzi A et al (2015) Documenting water (fluid) from dewatering process as the most strategic product in drilling operations in order to make fluid and improve its rheological properties in line with environmental standards for reuse of wastewater. Environ Conserv J 16:503–508
Lan P, Polycarpou AA (2017) High temperature and high pressure tribological experiments of advanced polymeric coatings in the presence of drilling mud for oil and gas applications. Tribol Int 61:1
Li Y, Feng Y, Sun X et al (2017) Inside cover: a sodium-ion-conducting direct formate fuel cell: generating electricity and producing base. Angew Chem Int Ed 56:5634
Long L, Da Y, Lei L et al (2018) Application of innovative high density high-performance water-based drilling fluid technology in the efficient development and production of ultra-deep complicated formations in the Tian mountain front block in China. In: Offshore technology conference Asia
Lowry E, Sedghi M, Goual L (2016) Novel dispersant for formation damage prevention in CO2: a molecular dynamics study. Energy Fuels 30:7187–7195
Mazarei M, Davarpanah A, Ebadati A et al (2018) The feasibility analysis of underground gas storage during an integration of improved condensate recovery processes. J Pet Explor Prod Technol 1:1–12
Pickup A, Mahoney M, Kelly J (2017) Cesium formate as a dense medium liquid for laboratory coal washability testing. Int J Coal Prep Util 1:1–13
Rabbani E, Davarpanah A, Memariani M (2018) An experimental study of acidizing operation performances on the wellbore productivity index enhancement. J Pet Explor Prod Technol 1:1–11
Redburn M, Heath G (2017) Improved fluid characteristics with clear calcium chloride brine drilling fluid. In: Offshore mediterranean conference and exhibition
Sukhoboka O (2017) Drilling fluid rheology under high pressure high temperature conditions and its impact on the rate of penetration. In: SPE Bergen one day seminar. Society of Petroleum Engineers
Topçuoğlu BD, Meydan C, Orellana R et al (2018) Formate hydrogenlyase and formate secretion ameliorate H2 inhibition in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus paralvinellae. Environ Microbiol 20:949–957
Van Oort E (2018) How to test for compatibility between fluids and shales. In: IADC/SPE drilling conference and exhibition. Society of Petroleum Engineers
van Oort E, Pasturel C, Bryla J et al (2017) Improved wellbore stability in tor/ekofisk wells through shale-fluid compatibility optimization. In: SPE/IADC drilling conference and exhibition. Society of Petroleum Engineers
Yu B, Goodman A, Hayes B et al (2017) From laboratory high-pressure, high-temperature technology to field success: a case study on new anti-balling coating development. In: SPE/IADC drilling conference and exhibition. Society of Petroleum Engineers
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank my supervisor Dr. Behnam Mirshekari for his guidance and support throughout this research. Thanks also to my dear friends Afshin Hosseini Hemat and so on who make my life full of fun and make me brave to face difficulty. I will always remember the days together with them.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript don’t have any conflict of interests.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: M. Abbaspour.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davarpanah, A. The feasible visual laboratory investigation of formate fluids on the rheological properties of a shale formation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 4783–4792 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1877-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1877-6