Abstract
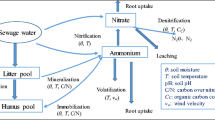
The excessive loss of soil nitrogen through drainage losses causes different environmental problems. The depth and spacing drain of drains play an important role in the quality and quantity of discharged drainage into the environment. In this paper, a simple but comprehensive model using system dynamic approach for water cycle and nitrogen dynamics was used to simulate the effect of drain depth and spacing on nitrate and ammonium losses in a sugarcane agro-industrial company. Twenty-four scenarios were modeled including the combination of four different drain depths and six drain spacing to compare the effect of drain depth and spacing on the nitrogen uptake by plant, denitrification, net mineralization, the amount of ammonium losses through runoff, nitrate and ammonium losses through drainage water, the sum of excessive water, the stress day index and the relative yield. The results indicated that optimal drainage system density is obtained in the depth of 1.1 m and spacing of 80 m, in a way that the total drainage losses would be reduced up to an acceptable level. The optimum designing of the drainage systems according to environmental criteria can control nitrogen pollution load at farm level and can therefore have appropriate results both in terms of economic and environmental considerations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi F, Sheini Dashtegol A, Salamati N (2015) Improving sugarcane water and fertilizer use efficiency in furrow fertigation. J Water Soil 29:933–942 (In Persian)
Alibakhshi H, Shahnazari A, Tahmasebi R (2013) Influence of subsurface drain depth and spacing on nitrate losses from paddy fields during canola growth season. J Water Soil Conservat 20:237–252 (In Persian)
Allam A, Tawfik A, Yoshimura C, Fleifle A (2016) Simulation-based optimization framework for reuse of agricultural drainage water in irrigation. J Environ Manag 172:82–96. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.02.022
Ayars JE, Grismer ME, Guitjens JC (1997) Water quality as design criterion in drainage water management systems. J Irrig Drain Eng ASCE 123:154–158. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9437
Ayars JE, Christen EW, Hornbuckle JW (2006) Controlled drainage for improved water management in arid regions irrigated agriculture. Agric Water Manag 86:128–139. doi:10.1016/j.agwat.2006.07.004
Bahmani O, Bromandnasab S, Behzad M, Naseri AA (2010) Evaluation of potential nitrate and ammonium accumulation in the soil profile under Irrigation and manure treatments with the LEACHM Model. Environ Sci 7:95–108 (In Persian)
Christen E, Skehan D (2001) Design and management of subsurface horizontal drainage to reduce salt loads. J Irrig Drain Eng ASCE 127:148–155. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9437
Darzi-Naftchalia A, Shahnazari A (2014) Influence of subsurface drainage on the productivity of poorly drained paddy fields. Eur J Agron 56:1–8. doi:10.1016/j.eja.2014.02.003
Darzi-Naftchalia A, Mirlatifi SA, Shahnazari A, Ejlalid F, Mahdian MH (2013) Effect of subsurface drainage on water balance and water table in poorly drained paddy fields. Agric Water Manag 130:61–68. doi:10.1016/j.agwat.2013.08.017
Forrester JW (1961) Industrial dynamics. Productivity Press, Portland
Gayle GA, Skaggs RW, Carter CE (1987) Effects of excessive soil water conditions on sugarcane yields. Trans ASAE 30:993–997. doi:10.13031/2013.30511
Groenendijk P, Kroes JG (1997) Modelling the nitrogen and phosphorus leaching to groundwater and surface water. ANIMO 3.5, Report No 144, DLO Winand Staring Centre, Wageningen, Netherlands
Hooghoudt SB (1940) Bijdragen tot de kennis van eenige natuurkundige grootheden van de grond. Verslagen Van, Landboouwkundige, Onderzoekinge 46:515–707 (in Dutch)
Kalita PK, Algoazany AS, Mitchell JK, Cooke RAC, Hirschi MC (2006) Subsurface water quality from a flat tile-drained watershed in Illinois, USA. Agric Ecosyst Environ 115:83–193. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2006.01.006
Lalehzari R, Tabatabaei SH, Kholghi M (2013) Simulation of nitrate transport and wastewater seepage in groundwater flow system. Int J Environ Sci Technol 10:1367–1376. doi:10.1007/s13762-013-0213-4
Liang XQ, Chen YX, Li H, Tian GM, Ni WZ, He MM, Zhang ZJ (2007) Modeling transport and fate of nitrogen from urea applied to a near-trench paddy field. Environ Pollut 150:313–320. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2007.02.003
Matinzadeh MM, Abedi Koupai J, Sadeghi Lari A, Nozari H, Shayannejad M (2016) Modeling of nitrogen fertilization management in sugarcane farmlands with drainage system using system dynamics approach. J Water Soil Sci 20:189–205 (In Persian)
Neuwirth C, Peck A, Simonovic SP (2015) Modeling structural change in spatial system dynamics: a Daisyworld example. Environ Model Softw 65:30–40. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2014.11.026
Nozari H, Liaghat AM (2014) Simulation of drainage water quantity and quality using system dynamics. J Irrig Drain Eng ASCE 140:05014007. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)IR.1943-4774
Rijtema PE, Kroes GJ (1991) Some results of nitrogen simulations with the model ANIMO. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 27:189–198. doi:10.1007/bf01051127
Sadeghi L, Abadi K, Shamsai A, Goharnejad H (2015) An Analysis of the sustainability of basin water resources using Vensim Model. KSCE J Civ Eng 19:1941–1949. doi:10.1007/s12205-014-0570-7
Sahin O, Siems RS, Stewart RA, Porter MG (2016) Paradigm shift to enhanced water supply planning through augmented grids, scarcity pricing and adaptive factory water: a system dynamics approach. Environ Model Softw 75:348–361. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2014.05.018
Shaffer MJ, Liwang MA, Hansen S (2001) Modeling carbon and nitrogen dynamics for soil management. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton. doi:10.1201/9781420032635.ch8
Shariati-Rad M, Irandoust M, Haghighi M (2015) Introduction of a spectrophotometric method for simultaneous determination of nitrite and nitrate in water samples using partial least squares. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:3837–3842. doi:10.1007/s13762-015-0846-6
Simonovic SP (2000) Tools for water management: one view of the future. Water Int 25:76–88. doi:10.1080/02508060008686799
Simunek J, Sejna M, van Genuchten MT (1999) The HYDRUS-2D software package for simulating two-dimensional movement of water, heat, and multiple solutes in variable saturated media. Version 2.0. IGWMCTPS-53, International Ground Water Modeling Center, Colorado School of Mines, Golden, Colorado
Skaggs RW (1999) Water table management: sub irrigation and controlled drainage. In: Skaggs RW, Van Schilfgaarde J (eds) Agricultural drainage. Number 38 in the series Agronomy. Madison, Wisconsin, The United States of America, America Soil Science Society of America
Sterman JD (2000) Business dynamics: systems thinking and modeling for a complex world. McGraw-Hill, New York
Van Genuchten MT, Davidson JM, Wierenga PJ (1974) An evaluation of kinetic and equilibrium equations for the prediction of pesticide movement in porous media. Soil Sci Soc Am J 39:29–35. doi:10.2136/sssaj1974.03615995003800010016x
Wagenet RJ, Hutson AJ (1989) LEACHM: Leaching estimation and chemistry model—a process based model of water and solute movement, transformations, plant uptake and chemical reactions in the unsaturated zone. Water resources Institute, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York
Xin P, Dan H, Zhou T, Lu CH, Kong J, Li L (2016a) An analytical solution for predicting the transient seepage from a subsurface drainage system. Adv Water Resour 91:1–10. doi:10.1016/j.advwatres.2016.03.006
Xin P, Yu X, Lu C, Li L (2016b) Effects of macro-pores on water flow in coastal subsurface drainage systems. Adv Water Resour 87:56–67. doi:10.1016/j.advwatres.2015.11.007
Youssef MA, Skaggs RW, Chescheir GM, Gilliam JW (2005) The nitrogen simulation model, DRAINMOD-NII. Am Soc Agric Eng 48:611–625. doi:10.13031/2013.18335
Zucker LA, Brown LC (1998) Agricultural drainage: water quality impacts and subsurface drainage studies in the Midwest extension Bulletin 871. Ohio State University, the United States of America
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to offer their thanks and appreciations to Imam agro-industrial Company for providing facility to collect data from the field.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: M. Abbaspour.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matinzadeh, M.M., Abedi Koupai, J., Sadeghi-Lari, A. et al. System dynamic modeling to assess the effect of subsurface drain spacing and depth on minimizing the environmental impacts. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 14, 563–576 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1262-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1262-x