Abstract
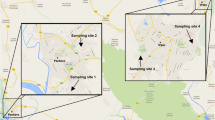
Honeybees are great bioindicators because they cover wide areas during their foraging activity. Our study included industrial, urban and rural region, where samples were taken in July and September. Industrial region with three apiaries in the area covered two thermal power plants, Kostolac A and B. Two apiaries covered a wide urban region of Belgrade, and the rural region consisting of mainly agricultural–woodland area near village Mesić was covered with one apiary. Aim of this study was to investigate the capability of bees as bioindicators to detect different concentrations of metals in foraging regions, during two sampling periods, and to compare concentrations of Al, Ba, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Li, Mn, Na, Ni, Pb, Sr and Zn found in their bodies. Significant differences were detected for Al, Ba, Cr, Cu, Fe, Li, and Ni between at least two analyzed regions. Significant differences in concentrations between sampling dates were found for Al, Ba, Co, Cr and Fe in at least one of the locations. For Cd, Mn, Na, Pb, Sr and Zn, no significant differences were found between locations or sampling dates, suggesting equal and stable levels of concentration for these elements in the environment.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akguc N, Ozyigit II, Yasar U, Leblebici Z, Yarci C (2010) Use of pyracantha coccinea Roem. as a possible biomonitor for the selected heavy metals. Int J Environ Sci Technol 7(3):427–434
Alcon MP, Arola L, Mas A (1991) Response to acute nickel toxicity in rats as a function of sex. Biol Met 4(3):136–140
Bencko V, Wagner V, Wagnerova M, Zavazal V (1986) Human exposure to nickel and cobalt: biological monitoring and immunobiological response. Environ Res 40:399–410
Berg D, Gerlach M, Youdim MB, Double KL, Zecca L, Riederer P, Becker G (2001) Brain iron pathways and their relevance to Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 79:225–236
Black J (2006) Review of honeybee nutrition research and practices. Rural Industries Research and Development Corporation, Australia, pp 32–35
Bromenshenk JJ, Carlson SR, Simpson JC, Thomas JM (1985) Pollution monitoring of Puget Sound with honeybees. Science 227(4687):632–634
Burge PS, Scott JA, McCoach J (2000) Occupational asthma caused by aluminum. Allergy 55(8):779–780
Christoforidis A, Stamatis N (2009) Heavy metal contamination in street dust and roadside soil along the major national road in Kavala’s region, Greece. Geoderma 151(3–4):257–263
Conti ME, Botré F (2001) Honeybees and their products as potential bio-indicators of heavy metal contamination. Environ Monit Assess 69(3):267–282
Cordell D, Rosemarin A, Schröder JJ, Smit AL (2011) Towards global phosphorus security: a systems framework for phosphorus recovery and reuse options. Chemosphere 84(6):747–758
Crane E (1984) Bees, honey and pollen as indicators of metals in the environment. Bee World 65(1):47–49
Davison RL, Natusch DFS, Wallace JR, Evans CA Jr (1974) Trace elements in fly ash dependence of concentration on particle size. Environ Sci Technol 8(13):1107–1113
de Dorlodot S, Lutts S, Bertin P (2005) Effects of ferrous iron toxicity on the growth and mineral composition of an inter specific rice. J Plant Nutr 28:1–20
Diels L, Van Der Lelie N, Bastiaens L (2002) New developments in treatment of heavy metal contaminated soils. Environ Sci Biotechnol 1(1):75–82
Ebbs SD, Kochian LV (1997) Toxicity of zinc and copper to Brassica species: implications for phytoremediation. J Environ Qual 26:776–781
Fakhimzadeh K, Lodenius M (2000) Heavy metals in Finnish honey, pollen and honey bees. Apiacta 35:85–95
Fargasova A (2001) Phytotoxic effects of Cd, Zn, Pb, Cu and Fe on Sinapis alba L. seedling and their accumulation in roots and shoots. Biol Plant 44:471–473
Formicki G, Greń A, Stawarz R, Zyśk B, Gał A (2013) Metal content in honey, propolis, wax, and bee pollen and implications for metal pollution monitoring. Pol J Environ Stud 22(1):99–106
Foy CD, Fleming AL, Burns GR, Armiger WH (1967) Characterization of differential aluminum tolerance among varieties of wheat and barley. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 31:513–521
Fraga CG (2005) Relevance, essentiality and toxicity of trace elements in human health. Mol Aspects Med 25(4–5):235–244
Free JB, Williams IH, Pinset RJFH, Townshend A, Basi MS, Graham CL (1983) Using foraging honeybees to sample an area for trace metals. Environ Int 9(1):9–12
García-Hernández J, Hurtado LA, Leyva-García G, Güido-Moreno A, Aguilera-Márquez D, Mazzei V, Ferrante M (2015) Isopods of the genus Ligia as potential biomonitors of trace metals from the Gulf of California and pacific coast of the Baja California peninsula. Ecotox Environ Safe 112:177–185
Gonnelli C, Renella G (2013) Chromium and nickel. In: Alloway BJ (ed) Heavy metals in soils, 22. Springer, Netherlands, pp 313–333
Gonnelli C, Galardi F, Gabbrielli R (2001) Nickel and copper tolerance in three Tuscan populations of Silene paradoxa. Physiol Planta 113:507–514
Goodarzi F (2006) Characteristics and composition of fly ash from Canadian coal-fired power plants. Fuel 85(10–11):1418–1427
Hänsch R, Mendel RR (2009) Physiological functions of mineral micronutrients (Cu, Zn, Mn, Fe, Ni, Mo, B, Cl). Curr Opin Plant Biol 12(3):259–266
Ho YB, Tai KM (1988) Elevated levels of lead and other metals in roadside soil and grass and their use to monitor aerial metal depositions in Hong Kong. Environ Pollut 49(1):37–51
Hower JC, Robertson JD, Thomas GA, Wong AS, Schram WH, Graham UM, Rathbone RF, Robl TL (1996) Characterization of fly ash from Kentucky power plants. Fuel 75(4):403–411
Iregren A, Sjogren B, Gustafsson K, Hagman M, Nylén L, Frech W, Andersson M, Ljunggren KG, Wennberg A (2001) Effect on the nervous system in different groups of workers exposed to aluminum. Occup Environ Med 58(7):453–460
Junninen H, Mønster J, Rey M, Cancelinha J, Douglas K, Duane M, Forcina V, Müller A, Lagler F, Marelli L, Borowiak A, Niedzialek J, Paradiz B, Mira-Salama D, Jimenez J, Hansen U, Astorga C, Stanczyk K, Viana M, Querol X, Duvall RM, Norris GA, Tsakovski S, Wåhlin P, Hoŕak J, Larsen BR (2009) Quantifying the impact of residential heating on the urban air quality in a typical European coal combustion region. Environ Sci Technol 43(20):7964–7970
Kaonga CC, Kumwenda J, Mapoma HT (2010) Accumulation of lead, cadmium, manganese, copper and zinc by sludge worms; Tubifex tubifex in sewage sludge. Int J Environ Sci Technol 7(1):119–126
Kauffeld NM (1980) Seasonal cycle of activities in honey bee colonies. Beekeeping in the United States, agriculture handbook 335. USDA, Washington DC, pp 30–32
Lee CR, Yoo CI, Lee JH, Kang SK (2002) Nasal septum perforation of welders. Ind Health 40:286–289
Leita L, Muhlbachova G, Cesco S, Barbattini R, Mondini C (1996) Investigation on the use of honeybees and honeybee products to assess heavy metals contamination. Environ Monit Assess 43(1):1–9
Li X, Poon C, Liu PS (2001) Heavy metal contamination of urban soils and street dusts in Hong Kong. Appl Geochem 16(11–12):1361–1368
Meij R (1994) Trace element behavior in coal-fired power plants. Fuel Process Technol 39(1–3):199–217
Meij R, Te Winkel H (2007) The emissions of heavy metals and persistent organic pollutants from modern coal-fired power stations. Atmos Environ 41(40):9262–9272
Meister RT (2004) Crop protection handbook. Meister Media Worldwide, Willoughby
Migula P, Kafel A, Kedziorski A, Marczak G, Nakonieczny M (1991) Heavy metals in nectar flows, products and bees’ tissues from industrialized regions. XXVIIIth Scientific Apicultural Conference, Puławy
Mortvedt JJ (1996) Heavy metal contaminants in inorganic and organic fertilizers. Fert Res 43(1–3):55–61
Park RM, Stayner LT (2006) A search for thresholds and other nonlinearities in the relationship between hexavalent chromium and lung cancer. Risk Anal 26(1):79–88
Pavageau M-P, Pécheyran C, Krupp EM, Morin A, Donard OFX (2002) Volatile metal species in coal combustion flue gas. Environ Sci Technol 36(7):1561–1573
Perugini M, Manera M, Grotta L, Abete MC, Tarasco R (2011) Heavy metal (Hg, Cr, Cd, and Pb) contamination in urban areas and wildlife reserves: honeybees as bioindicators. Biol Trace Elem Res 140(2):170–176
Popović A, Đorđević D, Relić D, Mihajlidi-Zelić A (2011) Speciation of trace and major elements from coal combustion products of serbian power plants (I)—“Kostolac A” power plant. Energy Sources Part A 33:1960–1968
Porrini C, Ghini S, Girotti S, Sabatini AG, Gattavecchia E, Celli G (2002) Use of honeybees as bioindicators of environmental pollution in Italy. In: Deville’s J, Pham-Delegate MH (eds) Honey bees: estimating the environmental impact of chemicals. Taylor & Francis, London, New York, pp 186–247
Porrini C, Sabatini AG, Girotti S, Ghini S, Medrzycki P, Grillenzoni F, Bortolotti L, Gattavecchia E, Celli G (2003) Honeybees and bee products as monitors of the environmental contamination. Apiacta 38:63–70
Pudasainee D, Kim J-H, Lee S-H, Park J-M, Jang H-N, Song G-J, Seo Y-C (2010) Hazardous air pollutants emission from coal and oil-fired power plants. Asia-Pac J Chem Eng 5(2):299–303
Raes H, Cornelis R, Rzeznik U (1992) Distribution, accumulation and depuration of administered lead in adult honeybees. Sci Total Environ 113(3):269–279
Rahman H, Sabreen S, Alam S, Kawai S (2005) Effects of nickel on growth and composition of metal micronutrients in barley plants grown in nutrient solution. J Plant Nutri 28:393–404
Rakić T, Ilijević K, Lazarević M, Gržetić I, Stevanović V, Stevanović B (2013) The resurrection flowering plant Ramonda nathaliae on serpentine soil–coping with extreme mineral element stress. Flora 208(10–12):618–625
Roman A (2005) The influence of environment on accumulation of toxic elements in honey bees’ body. Proc Int Congr Anim Hyg ISAH 2:423–426
Roman A (2010) Levels of copper, selenium, lead, and cadmium in forager bees. Pol J Environ Stud 19(3):663–669
Sadeghi A, Mozafari A-A, Bahmani R, Shokri K (2013) Use of honeybees as bio-indicators of environmental pollution in the Kurdistan Province of Iran. J Agric Sci 56(2):83–88
Shanker AK, Cervantes C, Loza-Tavera H, Avudainayagam S (2005) Chromium toxicity in plants. Environ Int 31(5):739–753
Silva LT, Pinho JL, Nurusman H (2014) Traffic air pollution monitoring based on an air–water pollutants deposition device. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11(8):2307–2318
Sinha S, Guptha M, Chandra P (1997) Oxidative Stress induced by iron in Hydrilla verticillata (i.f) Royle: response of antioxidants. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 38:286–291
Smolders E, Mertens J (2013) Cadmium. In: Alloway BJ (ed) Heavy metals in soils, 22. Springer, Netherlands, pp 283–311
Tong SSC, Morse RA, Bache CA, Lisk DJ (1975) Elemental analysis of honey as an indicator of pollution. Arch Environ Health 30(7):329–332
Ugulu I, Dogan Y, Baslar S, Varol O (2012) Biomonitoring of trace element accumulation in plants growing at Murat Mountain. Int J Environ Sci Technol 9(3):527–534
Van Der Steen JJM, de Kraker J, Grotenhuis T (2012) Spatial and temporal variation of metal concentrations in adult honeybees (Apis mellifera L.). Environ Monit Assess 184(7):4119–4126
Walker EMJ, Walker SM (2000) Effects of iron overload on the immune system. Ann Clin Lab Sci 30:354–365
Wallwork-Barber MK, Ferenbaugh RW, Gladney ES (1982) The use of honeybees as monitors of environmental pollution. Am Bee J 122:770–772
Wang YM, Chen TC, Yeh KJ, Shue MF (2001) Stabilization of an elevated heavy metal contaminated site. J Hazard Mater 88(1):63–74
Westfall DG, Mortvedt JJ, Peterson GA, Gangloff WJ (2005) Efficient and environmentally safe use of micronutrients in agriculture. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 36(1–3):169–182
Whiley AJ (2011) Copper and zinc loading associated with automotive brake-pad and tire wear, water quality program. Washington State Department of Ecology Olympia, Washington
Wilkinson H (1996) Haemochromatosis associated with arthritis and hypopituitarism. Ann Clin Biochem 333:171–173
Zhelyazkova I, Atanasova S, Barakova V, Mihaylova G (2010) Content of heavy metals and metalloids in bees and bee products from areas with different degree of anthropogenic impact. J Agr Sci Technol 3(1):136–142
Acknowledgments
This paper was realized as part of project No. 176006, which was financed by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zarić, N.M., Ilijević, K., Stanisavljević, L. et al. Metal concentrations around thermal power plants, rural and urban areas using honeybees (Apis mellifera L.) as bioindicators. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 13, 413–422 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-015-0895-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-015-0895-x