Abstract
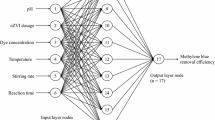
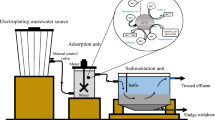
In this study, a batch-type, nanoscale, zero-valent iron process was used to treat trichloroethylene wastewater. Variations in oxidation–reduction potential (ORP) and pH in the reactor were monitored online for use in developing the model for process control. After the addition of nanoscale, zero-valent iron, the pH value increased rapidly, from 5.0–6.0 to around 8.5–9.5, whereas the ORP decreased dramatically, from around 300 mV to −700 to −800 mV. The degradation of trichloroethylene reached equilibrium at a reaction time of about 120 min. The use of a dose of 1.5 g/L to treat an influent that had a trichloroethylene concentration of 50 mg/L resulted in a removal efficiency of 94 %. Two models, i.e., a multiple regression model and an artificial neural network (ANN) model, were used to develop the control model to predict the trichloroethylene removal efficiencies. Both the regression model and the ANN model performed precise prediction results for the trichloroethylene removal efficiencies, with correlation coefficients of about 0.87 and 0.98, respectively, resulting in great potential for controlling the trichloroethylene removal.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold WA, Roberts AL (2000) Pathways and kinetics of chlorinated ethylene and chlorinated acetylene reaction with Fe(0) particles. Environ Sci Technol 34:1794–1805
Chang CN, Cheng HB, Chao AC (2004) Applying the Nernst Equation to simulate redox potential variations for biological nitrification and denitrification processes. Environ Sci Technol 38:1807–1812
Cho Y, Choi SI (2010) Degradation of PCE, TCE and 1,1,1-TCA by nanosized FePd bimetallic particles under various experimental conditions. Chemosphere 81:940–945
Crane RA, Scott TB (2012) Nanoscale zero-valent iron: future prospects for an emerging water treatment technology. J Hazard Mater 211–212:112–125
Curteanua S, Piuleaca CG, Godinib K, Azaryanc G (2011) Modeling of electrolysis process in wastewater treatment using different types of neural networks. Chem Eng J 172:267–276
Diao M, Yao M (2009) Use of zero-valent iron nanoparticles in inactivating microbes. Water Res 43:5243–5251
Dong T, Luo H, Wang Y, Hu B, Chen H (2011) Stabilization of Fe–Pd bimetallic nanoparticles with sodium carboxymethyl cellulose for catalytic reduction of para-nitrochlorobenzene in water. Desalination 271:11–19
Dua J, Lub J, Wu Q, Jing C (2012) Reduction and immobilization of chromate in chromite ore processing residue with nanoscale zero-valent iron. J Hazard Mater 215–216:152–158
Fuerhacker M, Bauer H, Ellinger R, Schmid H, Zibuschka F, Puxbaum H (2000) Approach for a novel control strategy for simultaneous nitrification/denitrification in activated sludge reactor. Water Res 34:2499–2506
Gamze TN, Mesci B, Ozgonenel O (2011) The use of artificial neural networks (ANN) for modeling of adsorption of Cu(II) from industrial leachate by pumice. Chem Eng J 171:1091–1097
Gernjak W, Fuerhacker M, Fernandez-Ibanez P, Blanco J, Malato S (2006) Solar photo-Fenton treatment—process parameters and process control. Appl Catal B Environ 64:121–130
Ghauch A, Tuqan A, Assi HA (2009) Antibiotic removal from water: elimination of amoxicillin and ampicillin by microscale and nanoscale iron particles. Environ Pollut 157:1626–1635
Haest PJ, Springael D, Seuntjens P, Smolders E (2012) Self-inhibition can limit biologically enhanced TCE dissolution from a TCE DNAPL. Chemosphere 81:1369–1375
He F, Zhao D, Liu J, Roberts CB (2007) Stabilization of Fe–Pd nanoparticles with sodium carboxymethyl cellulose for enhanced transport and dechlorination of trichloroethylene in soil and groundwater. Ind Eng Chem Res 46(1):29–34
Hua M, Zhang S, Pan B, Zhang W, Lv L, Zhang Q (2012) Heavy metal removal from water/wastewater by nanosized metal oxides: a review. J Hazard Mater 211–212:317–331
Khataeea AR, Kasiri MB (2010) Artificial neural networks modeling of contaminated water treatment processes by homogeneous and heterogeneous nanocatalysis. Mol Catal A Chem 331:86–100
Li S, Fang Y-L, Romanczuk CD, Jin Z, Li T, Wong MS (2012) Establishing the trichloroethene dechlorination rates of palladium-based catalysts and iron-based reductants. Appl Catal B Environ 125:95–102
Lin YT, Weng CH, Chen FY (2008) Effective removal of AB24 dye by nano/micro-size zero-valent iron. Sep Purif Technol 64:26–30
Lin CH, Yu RF, Cheng WP, Liu CR (2012) Monitoring and control of UV and UV-TiO2 disinfections for municipal wastewater reclamation using artificial neural networks. J Hazard Mater 209–210:348–354
Liu HB, Chen TH, Chang DY, Chen D, Liu Y, He HP, Yuan P, Frost R (2012) Nitrate reduction over nanoscale zero-valent iron prepared by hydrogen reduction of goethite. Mate Chem Phys 133:205–211
Lookman R, Bastiaens L, Borremans B, Maesen M, Gemoets J, Diels L (2004) Batch-test study on the dechlorination of 1,1,1-trichloroethane in contaminated aquifer material by zero-valent iron. J Contam Hydrol 74:133–144
Lucas MS, Peres JA (2009) Removal of COD from olive mill wastewater by Fenton’s reagent: KINETIC study. J Hazard Mater 168:1253–1259
Martin de la Vega PT, Martinez de Salazar E, Jaramillo MA, Cros J (2012) New contributions to the ORP & DO time profile characterization to improve biological nutrient removal. Bioresour Technol 114:160–167
Matheson LJ, Tratnyek PG (1994) Reductive dehalogenation of chlorinated methanes by iron metal. Environ Sci Technol 28:2045–2053
Moon BH, Park YB, Park KH (2011) Fenton oxidation of Orange II by pre-reduction using nanoscale zero-valent iron. Desalination 268:249–252
Olsson G (2012) ICA and me—a subjective review. Water Res 46:1585–1624
Ortega-Gomez E, Ubeda JCM, Hervas JDA, Lopez JLC, Jorda LS-J, Perez JAS (2012) Automatic dosage of hydrogen peroxide in solar photo-Fenton plants: development of a control strategy for efficiency enhancement. J Hazard Mater 237–238:223–230
Roberts AL, Totten LA, Arnold WA, Burris DR, Campbell TJ (1996) Reductive elimination of chlorinated ethylenes by zero-valent metals. Environ Sci Technol 30:2654–2659
Ryu A, Jeong SW, Jang A, Choi H (2011) Reduction of highly concentrated nitrate using nanoscale zero-valent iron: effects of aggregation and catalyst on reactivity. Appl Catal B Environ 105:128–135
Saby S, Djafer M, Chen GH (2003) Effect of low ORP in anoxic sludge zone on excess sludge production in oxic-settling-anoxic activated sludge process. Water Res 37:11–20
Shi LN, Zhang X, Chen ZL (2010) Removal of Chromium (VI) from wastewater using bentonite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. Water Res 45:886–892
Shu HY, Chang MC, Yu HH, Chen WH (2007) Reduction of an azo dye Acid Black 24 solution using synthesized nanoscale zerovalent iron particles. J Colloid Inter Sci 314:89–97
Shu HY, Chang MC, Chen CC, Chen PE (2010) Using resin supported nano zero-valent iron particles for decoloration of Acid Blue 113 azo dye solution. J Hazard Mater 184:499–505
Smuleac V, Varma R, Sikdar S, Bhattacharyya D (2011) Green synthesis of Fe and Fe/Pd bimetallic nanoparticles in membranes for reductive degradation of chlorinated organics. J Membrane Sci 379:131–137
Uzuma C, Shahwan T, Eroglu AE, Lieberwirth I, Scott TB, Hallam KR (2008) Application of zero-valent iron nanoparticles for the removal of aqueous Co2+ ions under various experimental conditions. Chem Eng J 144:213–220
Wang Q, Jeong S-W, Choi H (2012) Removal of trichloroethylene DNAPL trapped in porous media using nanoscale zerovalent iron and bimetallic nanoparticles: direct observation and quantification. J Hazard Mater 213–214:299–310
West MR, Grant GP, Gerhard JI, Kueper BH (2008) The influence of precipitate formation on the chemical oxidation of TCE DNAPL with potassium permanganate. Adv Water Res 31:324–338
Won SG, Ra CS (2011) Biological nitrogen removal with a real-time control strategy using moving slope changes of pH(mV)- and ORP-time profiles. Water Res 45:171–178
Yu RF, Liaw SL, Cheng WY, Chang CN (2000) Performance enhancement of SBR applying real-time control. J Environ Eng ASCE 126:943–948
Yu RF, Chen HW, Cheng WP, Shen YC (2009a) Application of pH-ORP titration to dynamically control the chlorination and dechlorination for wastewater reclamation. Desalination 244:164–176
Yu RF, Chen HW, Cheng WP, Hsieh PH (2009b) Dosage control of Fenton process for color removal of textile wastewater applying ORP monitoring and artificial neural network. J Environ Eng ASCE 135:325–332
Zanetti L, Frison N, Nota E, Tomizioli M, Bolzonella D, Fatone F (2012) Progress in real-time control applied to biological nitrogen removal from wastewater. A short-review. Desalination 286:1–7
Zhang X, Lin S, Lu XQ, Chen ZL (2010) Removal of Pb(II) from water using synthesized kaolin supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. Chem Eng J 163:243–248
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the National Science Council of the Republic of China, Taiwan, for financially supporting this research under Contract No. NSC 100-2221-E-239-006-MY2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, RF., Chi, FH., Cheng, WP. et al. Online monitoring of the nanoscale zero-valent iron process for trichloroethylene wastewater treatment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 12, 1647–1656 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-014-0567-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-014-0567-2