Abstract
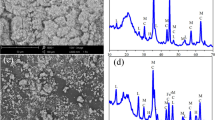
In this study, agar-stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron (A-nZVI) was synthesized using a rheological phase reaction method. The structure and morphology of A-nZVI particles were investigated by X-ray powder diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy and Fourier-transform infrared spectrometry. Batch removal experiments showed that the pH value of solution, hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)]/A-nZVI mass ratio and reaction time have significant effects on the removal of Cr(VI). A 100 % removal of Cr(VI) was achieved when applying 50 mg L−1 of Cr(VI) at the optimal pH value of 3 and the Cr(VI)/A-nZVI molar ratio of 0.025 with the reaction time of 2 h at room temperature. The removal rates of Cr(VI) were fitted to the modified pseudo-first-order kinetic equations with respect to Cr(VI) concentrations.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alidokht L, Khataee AR, Reyhanitabar A, Oustan S (2011) Reductive removal of Cr(VI) by starch-stabilized Fe0 nanoparticles in aqueous solution. Desalination 270:105–110
Andrade AL, Souza DM, Pereira MC, Fabris JD, Domingues RZ (2009) Synthesis and characterization of magnetic nanoparticles coated with silica through a sol–gel approach. Cerâmica 55:420–424
Bezbaruah AN, Krajangpan S, Chisholm BJ, Khan E, Bermudez JJ (2009) Entrapment of iron nanoparticles in calcium alginate beads for groundwater remediation applications. J Hazard Mater 166:1339–1343
Choi H, Agarwal S, Al-Abed SR (2009) Adsorption and simultaneous dechlorination of PCBs on GAC/Fe/Pd: mechanistic aspects and reactive capping barrier concept. Environ Sci Technol 43:488–493
Cirtiu CM, Raychoudhury T, Ghoshal S (2011) Systematic comparison of the size, surface characteristics and colloidal stability of zero valent iron nanoparticles pre- and post-grafted with common polymers. Colloid Surface A 39:95–104
Crane RA, Scott TB (2012) Nanoscale zero-valent iron: future prospects for emerging water treatment technology. J Hazard Mater 211–212:122–125
Elliott DW, Lien HL, Zhang WX (2009) Degradation of lindane by zero-valent iron nanoparticles. J Environ Energy 135:317–324
Flury B, Eggenberger U, Mader U (2009) First results of operating and monitoring an innovative design of a permeable reactive barrier for the remediation of chromate contaminated groundwater. Appl Geochem 24:687–696
Franco DV, Silva LMD, Jardim WF (2009) Reduction of hexavalent chromium in soil and ground water using zero-valent iron under batch and semi-batch conditions. Water Air Soil Pollut 197:49–60
Gheju M (2011) Hexavalent chromium reduction with zero-valent iron (ZVI) in aquatic systems. Water Air Soil Pollut 222(1):103–148
Gotic M, Music S (2007) Mössbauer, FT-IR and FE SEM investigation of iron oxides precipitated from FeSO4 solutions. J Mol Struct 834–836:445–453
He F, Zhao D (2005) Preparation and characterization of a new class of starch-stabilized bimetallic nanoparticles for degradation of chlorinated hydrocarbons in water. Environ Sci Technol 39:3314–3320
He F, Zhao D, Liu J, Roberts CB (2007) Stabilization of Fe/pd bimetallic nanoparticles with sodium carboxymethyl cellulose to facilitate dechlorination of trichloroethene and soil transportability. Ind Eng Chem Res 46:29–34
Ho YS, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465
Hoch LB, Mack EJ, Hydutsky BW, Hershman JM, Skluzacek JM, Mallouk TE (2008) Carbothermal synthesis of carbon-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron particles for the remediation of hexavalent chromium. Environ Sci Technol 42:2600–2605
Huang QG, Shi XY, Pinto RA, Petersen EJ, Weber WJ (2008) Tunable synthesis and immobilization of zero-valent iron nanoparticles for environmental applications. Environ Sci Technol 42:8884–8889
Jiang J, Li L, Xu F, Xie Y (2007) Preparation and magnetic properties of Zn–Cu–Cr–Sm ferrite via a rheological phase reaction method. Mater Sci Eng B Adv 137:166–169
Lai KCK, Lo IMC (2008) Removal of chromium(VI) by acid washed zero-valent iron under various groundwater geochemistry conditions. Environ Sci Technol 42:1238–1244
Legrand L, Figuigui EA, Mercier F, Chausse A (2004) Reduction of aqueous chromate by Fe(II)/Fe(III) carbonate green rust: kinetic and mechanistic studies. Environ Sci Technol 38:4587–4595
Liu T, Tsang DCW, Lo IMC (2008) Chromium (VI) reduction kinetics by zero-valent iron in moderately hard water with humic acid: iron dissolution and humic acid adsorption. Environ Sci Technol 42:2092–2098
Manning BA, Kiser JR, Kwon H, Kanels SR (2007) Spectroscopic investigation of Cr(III)-and Cr(VI)-treated nanoscale zerovalent iron. Environ Sci Technol 41:586–592
Norziah MH, Foo SL, Karim AA (2006) Rheological studies on mixtures of agar (Gracilaria changii) and κ-carrageenan. Food Hydrocolloid 20:204–217
O’Carroll D, Sleep B, Krol M, Boparai H, Kocur C (2013) Nanoscale zero valent iron and bimetallic particles for contaminated site remediation. Adv Water Resour 51:104–122
Owlad M, Kheireddine MA, Daud WAW, Baroutian S (2009) Removal of hexavalent chromium contaminated water and wastewater: a review. Water Air Soil Pollut 200:59–77
Park D, Yun YS, Ahn CK, Park JM (2007) Kinetics of the reduction of hexavalent chromium with the brown seaweed ecklonia biomass. Chemosphere 66:939–946
Ponder SM, Darab JG, Mallouk TE (2000) Remediation of Cr(VI) and Pb(II) aqueous solutions using supported, nano-scale zero-valent iron. Environ Sci Technol 34:2564–2569
Ponder SM, Darab JG, Bucher J, Caulder D, Craig I, Davis L, Edelstein N, Lukens W, Nitsche H, Rao L, Shuh DK, Mallouk TE (2001) Surface chemistry and electrochemistry of supported zerovalent iron nanoparticles in the remediation of aqueous metal contaminants. Chem Mater 13:479–486
Portilla VI (1976) The nature of hydrogen bonds and water in legrandite by IR spectroscopy. Am Mineral 61:95–99
Pourjavadi A, Farhadpour B, Seidi F (2009) Synthesis and investigation of swelling behavior of new agar based superabsorbent hydrogel as a candidate for agrochemical delivery. J Polym Res 16:655–665
Powell RM, Puls RW, Hightower SK, Sabatini DA (1995) Coupled iron corrosion and chromate reduction: mechanism of subsurface remediation. Environ Sci Technol 29(8):1913–1922
Prabhakaran SK, Vijayaraghavan K, Balasubramanian R (2009) Removal of ions by spent tea and coffee dusts: reduction to Cr(III) and biosorption. Ind Eng Chem Res 48:2113–2117
Pratt AR, Blowes DW, Ptacek CJ (1997) Products of chromate reduction on proposed subsurface remediation material. Environ Sci Technol 31:2492–2498
Sass BM, Rai D (1987) Solubility of amorphous chromium (III)–iron (III) hydroxide solid solutions. Inorg Chem 26:2228–2232
Schrick B, Hydutsky BW, Blough JL, Mallouk TE (2004) Delivery vehicles for zerovalent metal nanoparticles in soil and groundwater. Chem Mater 16:2187–2193
Shi LN, Lin YM, Zhang X (2011) Synthesis, characterization and kinetics of bentonite supported nZVI for the removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 171:612–617
Shukla MK, Singh RP, Reddy CRK (2012) Synthesis and characterization of agar-based silver nanoparticles and nanocomposite film with antibacterial applications. Bioresour Technol 107:295–300
Singh R, Misra V, Singh RP (2011) Synthesis, characterization and role of zero-valent iron nanoparticle in removal of hexavalent chromium from chromium-spiked soil. J Nanpart Res 13:4063–4073
Weckhuysen BM, Wachs IE, Schoonheydt RA (1996) Surface chemistry and spectroscopy of chromium in inorganic oxides. Chem Rev 96:3327–3349
Yuan P, Fan M, Yang D, He H, Liu D, Yuan A, Zhu J, Chen T (2009) Montmorillonite-supported magnetite nanoparticles for the removal of hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)] from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 166:821–829
Zhang H, Jin Z, Han L, Qin C (2006) Synthesis of nanoscale zero-valent iron supported on exfoliated graphite for removal of nitrate. Trans Nonferr Metals Soc China 16:345–349
Zhang X, Lin Y, Chen Z (2009) 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene reduction kinetics in aqueous solution using nanoscale zero-valent iron. J Hazard Mater 165:923–927
Zhang X, Lin S, Lu XQ, Chen ZL (2010) Removal of Pb(II) from water using natural kaolin loaded with synthesized nanoscale zero-valent iron. Chem Eng J 163:243–248
Zhang X, Lin S, Chen Z, Megharaj M, Naidu R (2011) Kaolinite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron for removal of Pb2+ from aqueous solution: reactivity, characterization and mechanism. Water Res 45:3481–3488
Zhu BW, Lim TT, Feng J (2006) Reductive dechlorination of 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene with palladized nanoscale Fe0 particles supported on chitosan and silica. Chemosphere 65:1137–1145
Acknowledgments
This work has been funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51268018), supported by the Open Funds from Key Laboratory of Jiangsu Province for Chemical Pollution Control and Resources Reuse (Nanjing University of Science and Technology), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 30920130122007), and Jingdezhen Science and Technology Bureau (No.701301257). The authors are grateful to National Engineering Research Center for Domestic and Building Ceramics, JCU for the assistance in analytical measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiao, C., Cheng, Y., Fan, W. et al. Synthesis of agar-stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron particles and removal study of hexavalent chromium. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 12, 1603–1612 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-014-0524-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-014-0524-0