Abstract
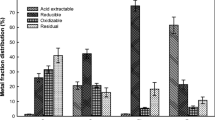
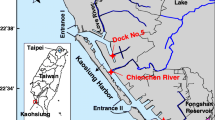
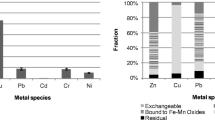
Remediation of heavy-metal-contaminated sediment is often hampered by the availability of heavy metals to the added chemical agents because the heavy metals are often shielded by the sediment matrix. Effective heavy-metal extraction technique becomes an important factor in enhancing the treatment efficiency. A novel extraction/washing technique utilizing chelating agent and elevated pressure in consecutive cycles of compression and decompression has been developed for heavy-metal-contaminated sediment washing in the presence of chelating agent. In this study, the optimal operational conditions of pressure-assisted cyclic washing of Cu-contaminated sediments (initial Cu concentration = 23.177 mg/kg) were determined in a laboratory-scale system. The control factors included applied pressure level, washing time, applied chelant [ethylenediamine-tertraacetic (EDTA)] concentration (0.01–0.5 M), pressure times, and application of consecutive batches washing. Results from the bench-scale study showed that up to 70 % of Cu can be removed from the sediments when 10 atm of pressure was applied for washing. The efficiency dropped to 55 % when the pressure dropped to 6 atm. Under the same operational conditions, the optimal cyclic washing time was 60 min. Results from the particle size analyses indicate that the mean particle size dropped from 100 to 50 μm after the pressure-assisted cyclic washing. Thus, cyclic pressure caused the fracture of sediment aggregates resulting in the exposure of Cu to chelating agents. With the assistance of pressure cyclic system, the total washing time and the amount of added chemical agent used can be significantly reduced.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abumaizar RJ, Smith EH (1999) Heavy metal contaminants removal by soil washing. J Hazard Mater 70:71–85
Akcay H, Oguz A, Karapire C (2003) Study of heavy metal pollution and speciation in BuyakMenderes and Gediz River sediments. Water Res 37:813–822
Amin B, Ismail A, Arshad A (2009) Anthropogenic impacts on heavy metal concentrations in the coastal sediments of Dumai. Indonesia Environ Monit Assess 148:291–305
Arribere MA, Ribeiro GS, Sanchez RS, Gil MI, Roman RG, Daurade LE, Fajon V, Horvat M, Alcalde R, Kestelman AJ (2002) Heavy metals in the vicinity of a chlor-alkali factory in the upper Negro river ecosystem, Northern Patagonia, Argentina. Sci Total Environ 301:187–203
Barona A, Aranguiz I, Elı′as A (2001) Metal association in soils before and after EDTA extractive decontamination: implications for the effectiveness of further clean-up procedures. Environ Pollut 113:79–85
Bermond A, Ghestem JP (2001) Kinetic study of trace metal EDTA-desorption from contaminated soils, heavy metals release in soils. In: Selim HM, Sparks DL (eds) Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, pp 131–147
Bhakta JN, Munekage Y, Ohnishi K, Jana BB (2012) Isolation and identification of cadmium- and lead-resistant lactic acid bacteria for application as metal removing probiotic. Int J Sci Technol 9:433–440
Casas JM, Rosas H, Solé M, Lao C (2003) Heavy metals and metalloids in sediments from the Llobregat basin. Spain Environ Geol 44:325–332
Cassidy DP, Irvine RL (1998) Interactions between organic contaminants and soil affecting bioavailability, bioremediation-principles and practices. Technomics Lancaster, Pennsylvania, pp 259–282
Catherine NM, Yong RN, Gibbs BF (2001) An evaluation of technologies for the heavy metal remediation of dredged sediments. J Hazard Mater 85:145–163
Chen ZY, Saito Y, Kanai Y, Wei TY, Li LQ, Yao HS (2004) Low concentration of heavy metals in the Yangtze estuarine sediments, China: a diluting setting Estuarine. Coast Shelf Sci 60:91–100
Chen CF, Chen CW, Dong CD, Kao CM (2012a) Assessment of toxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments of Kaohsiung Harbor, Taiwan. Sci Total Environ in press (available on line)
Chen CT, Chen CW, Chen CF, Dong CD, Ko MS, Kao CM (2012b) Evaluation of zinc contamination in the sediments of Salt River mouth Taiwan. Appl Mech Mater 178–181:893–896
Chiu YM, Huang CH, Chang FC, Kang HY, Wang HP (2011) Recovery of copper from a wastewater for preparation of Cu nanoparticles sustain. Environ Res 21:279–282
Demirak A, Yilmaz F, Tuna AL, Ozdemir N (2006) Heavy metals in water, sediment and tissues of Leuciscus cephalus from a stream in southwestern Turkey. Chemosphere 63:1451–1458
ECB, European Chemical Bureau (2004) European union risk assessment report on Na4EDTA, Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, Italy
Elliott HA, Shastri L (1999) Extractive decontamination of metal-polluted soils using oxalate. Water Air Soil Pollut 110:335–346
Fischer K, Bipp HP, Riemschneider P, Leidmann P, Bieniek D, Kettrup A (1998) Utilization of biomass residues for the remediation of metal-polluted soils. Environ Sci Technol 32:2154–2161
Gao P, Feng YJ, Zhang ZH, Liu JF, Ren NQ (2012) Effect of heavy metals and surfactants on the adsorption of phenolic compounds on sediment. Int J Sci Technol 9:671–682
Ghrefat H, Yusuf N (2006) Assessing Mn, Fe, Cu, Zn, and Cd pollution in bottom sediments of Wadi Al-Arab Dam, Jordan. Chemosphere 65:2114–2121
Gundersen P, Steinnes E (2003) Influence of pH and TOC concentration on Cu, Zn, Cd, and Al speciation in rivers. Water Res 37:307–318
Gustavon K, Burton GA, Francingues NR, Reible D, Vorhees DJ, Wolfe JR (2008) Evaluating the effectiveness of contaminated-sediment dredging. Environ Sci Technol 42:5042–5047
Harikumar PS, Nasir UP (2010) Ecotoxicological impact assessment of heavy metal in core sediments of a tropical estuary. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:1742–1747
Hong PAK, Li C, Banerji SK, Regmi T (1999) Extraction, recovery, and biostability of EDTA for remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil. J Soil Contam 8:81–103
Hong PAK, Cai X, Cha Z (2008) Pressure-assisted chelation extraction of lead from contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 153:14–21
Jayawardana DT, Ishiga H, Pitawala HMTGA (2012) Geochemistry of surface sediments in tsunami-affected Sri Lankan lagoons regarding environmental implications. Int J Environ Sci Technol 9:41–55
Juang RS, Wang SW (2000) Metal recovery and EDTA recycling from simulated washing effluents of metal-contaminated soils. Water Res 34:3795–3803
Khaled A, Nemr AE, Sikaily AE (2006) An assessment of heavy-metal contamination in surface sediments of the Suez Gulf using geoaccumulation indexes and statistical analysis. Chem Ecol 22:239–252
Lee CS (2003) Fractionation and extractability of copper, zinc, and lead in contaminated soils, Ph.D. dissertation, National Cheng Kung University, Taiwan
Liaghati T, Preda M, Cox M (2003) Heavy metal distribution and controlling factors within coastal plain sediments, bells creek catchment, southeast Queensland Australia. Environ Int 29:935–948
Liang JR, Huang SC (2012) Kinetic model for sulfate/hydroxyl radical oxidation of methylene blue in a thermally-activated persulfate system at various pH and temperatures sustain. Environ Res 22:199–208
Lim TT, Tay JH, Wang JY (2004) Chelating-agent-enhanced heavy metal extraction from a contaminated acidic soil. J Environ Eng 130:59–66
Lin CE, Chen CT, Kao CM, Hong A, Wu CY (2011) Development of the sediment and water quality management strategies for the Salt-water River Taiwan. Marine Pollut Bull 63:528–534
Liu JY, Cheng SF (2007) Effect of soil particle fractionation on removal efficiency of heavy metals in soils. Department of environmental engineering and management Chaoyang University of Technology, MS Thesis
Martinez CE (2000) Solubility of lead, zinc and copper added to mineral soils. Environ Pollut 107:153–158
Moreda-Pineiro J, Alonso-Rodriguez E, Lopez-Barrerra P (2006) As, Cd, Cr, Ni and Pb pressurized liquid extraction with acetic acid from marine sediment and soil samples. Spectrochim Acta Part B At Spectrosc 61:1304–1309
Mwamburi J (2003) Variations in trace elements in bottom sediments of major rivers in Lake Victoria’s basin, Kenya. Lakes Reserv Res Manag 8:5–13
NIEA (2003) Method of soil quality extraction of heavy metals, NIEA S321.63B
NIEA (2005) Method of soil pH analysis, NIEA S410.61C
Palma LD, Mecozzi R (2007) Heavy metal mobilization from harbor sediments using EDTA and citric acid as chelating agents. J Hazard Mater 147:768–775
Peng JF, Song YH, Yuan P, Cui XY, Qiu GL (2009) The remediation of heavy metals contaminated sediment. J Hazard Mater 161:633–640
Polettini A, Pomi R, Calcagnoli G (2009) Assisted washing for heavy metal and metalloid removal from contaminated dredged materials. Water Air Soil Pollut 196:183–198
Reed BE, Carriere PC, Moore R (1996) Flushing of a Pb(II) contaminated soil using HCl, EDTA and CaCl2. J Environ Eng 122:48–50
Reimann C, de Caritat P (2005) Distinguishing between natural and anthropogenic sources for elements in the environment: regional geochemical surveys versus enrichment factors. Sci Total Environ 337:91–107
Shiue A, Ma CM, Ruan RT, Chang CT (2012) Adsorption kinetics and isotherms for the removal methyl orange from wastewaters using copper oxide catalyst prepared by the waste printed circuit boards sustain. Environ Res 22:209–215
Singh KP, Mohan D, Singh VK, Malik A (2005) Studies on distribution and fractionation of heavy metals in Gomti river sediments-a tributary of the Ganges. J Hydrol 312:14–27
Susana OR, Daniel DLR, Lazaro L, David WG, Katia DA, Jorge B, Francisco M (2005) Assessment of heavy metal levels in Almendares River sediments—Havana city Cuba. Water Res 39:3945–3953
Tandy S, Bossart K, Mueller R, Ritschel J, Hauser L, Schulin R, Nowack B (2004) Extraction of heavy metals from soils using biodegradable chelating agents. Environ Sci Technol 38:937–944
TEPA, Taiwan Environmental Protection Administration (2012) Taiwan soil and groundwater remediation act web, http://sgw.epa.gov.tw/public/En/Default.aspx
Theofanis ZU, Astrid S, Lidia G, Calmano WG (2001) Contaminants in sediments: remobilisation and demobilization. Sci Total Environ 266:195–202
Tsai TT, Kao CM, Surampalli RY, Liang SH (2009) Treatment of fuel-oil contaminated soils by biodegradable surfactant washing followed by Fenton-like oxidation. J Environ Eng 135:1015–1024
Uta K, Jens W (2006) Long-term effects of the Aznalcóllar mine spill—heavy metal content and mobility in soils and sediments of the Guadiamar River valley (SW Spain). Sci Total Environ 367:855–871
Voglar D, Lestan D (2010) Electrochemical separation and reuse of EDTA after extraction of Cu contaminated soil. J Hazard Mater 180:152–157
Wanekaya AK, Myung S, Sadik QA (2002) Pressure assisted chelating extraction: a novel technique for digesting metals in solid matrices. Analyst 127:1272–1276
Wasay SA, Barrington SF, Tokunaga S (2001) Organic acids for the in situ remediation of soils polluted by metals: soil flushing in columns. Water Air Soil Pollut 127:301–314
Xia W, Gao H, Wang X, Zhou C, Liu Y, Fam T, Wang X (2009) Application of EDTA decontamination on soil affected by mining activities and impact of treatment on the geochemical partition of metal contaminants. J Hazard Mater 163:936–940
Yang Y, He Z, Lin Y, Phlips E, Stoffella PJ, Powell CA (2009) Temporal and spatial variations of copper, cadmium, lead, and zinc in Ten Mile Creek in South Florida USA. Water Environ Res 81:40–50
Zhang WH, Lo IMC (2006) EDTA-enhanced washing for remediation of Pb and/or Zn-contaminated soils. J Environ Eng 132:1282–1288
Zou Z, Qiu R, Zhang W, Dong H, Zhao Z, Zhang T, Wei X, Cai X (2009) The study of operating variables in soil washing with EDTA. Environ Pollut 157:229–236
Acknowledgments
This project was funded in part by Taiwan National Science Council (Grant No. NSC99-2221-E-110-027-MY3). Additional thanks are extended to the personnel at China Steel Co., Taiwan and Kaohsiung Environmental Protection Bureau, Kaohsiung, Taiwan for their assistance and support throughout this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, C.E., Hong, P.K.A., Chiu, H.Y. et al. Pressure-assisted cyclic washing of heavy-metal-contaminated sediments. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 11, 1017–1026 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0304-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0304-2