Abstract
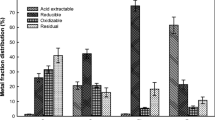
Preliminary analysis on dredged marine sediments from Benoi basin in Singapore was carried out showing elevated concentrations of Zn, Cu, Pb, Cd, Cr and Ni. Ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) thermal washing experiments were conducted for heavy metal extraction at temperature 100 °C. Results indicated the significant efficiency of thermal washing to extract Pb, Zn and Ni. However, there was little or no influence in the removal of Cu and Cr and a slight effect to Cd indicating multiple mechanisms. In addition, agitation was found to have great influence on the removal efficiency of heavy metals as experiments without agitation performed lesser or no extraction due to limited contact of the washing solution and the dredged sediment. Sequencing processes of thermal treatment followed by EDTA washing showed limited performance, likely due to thermal stabilization of the contaminants particularly at low liquid-to-soil (L/S) ratio. Furthermore, sequential extraction analysis on the metal speciation was performed before and after thermal washing. It was revealed that metals mainly extracted from fractions bound to carbonates and Fe-Mn oxides, the relative mobile fraction. On the contrary, metals in the residual fraction displayed a considerable stability.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abumaizar, R. J., & Smith, E. H. (1999). Heavy metal contaminants removal by soil washing. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B70, 71–86.
Appels, L., Degreve, J., der Bruggen, B. V., Impe, J. V., & Dewil, R. (2010). Influence of low temperature thermal pre-treatment on sludge solubilisation, heavy metal release and anaerobic digestion. Bioresource Technology, 101(15), 5743–5748.
Barona, A., Aranguiz, I., & Elías, A. (2001). Metal associations in soils before and after EDTA extractive decontamination: implications for the effectiveness of further clean-up procedures. Environmental Pollution, 113(1), 79–85.
Bayuseno, A. P., Schmahl, W. W., & Müllejans, T. (2009). Hydrothermal processing of MSWI fly ash—towards new stable minerals and fixation of heavy metals. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 167(1–3), 250–259.
Caplat, C., Texier, H., Barillier, D., & Lelievre, C. (2005). Heavy metals mobility in harbour contaminated sediments: the case of Port-en-Bessin. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50(5), 504–511.
Chen, J., Gao, J., & Wang, X. (2006). Thermal decomposition of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid in the presence of 1, 2-phenylenediamine and hydrochloric acid. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 17(5), 880–885.
Colacicco, A., De Gioannis, G., Muntoni, A., Pettinao, E., Polettini, A., & Pomi, R. (2010). Enhanced electrokinetic treatment of marine sediments contaminated by heavy metals and PAHs. Chemosphere, 81(1), 46–56.
Di Palma, L., & Mecozzi, R. (2007). Heavy metals mobilization from harbour sediments using EDTA and citric acid as chelating agents. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 147(3), 768–775.
Giannis, A., Nikolaou, A., Pentari, D., & Gidarakos, E. (2009). Chelating agent-assisted electrokinetic removal of cadmium, lead and copper from contaminated soils. Environmental Pollution, 157, 3379–3386.
Harley, N. R., Tsang, D. C. W., Olds, W. E., & Weber, P. A. (2014). Soil washing enhanced by humic substances and biodegradable chelating agents. Soil and Sediment Contamination: An International Journal, 23(6), 599–613.
Hirose, K., Dokiya, Y., & Sugimura, Y. (1982). Determination of conditional stability constants of organic copper and zinc complexes dissolved in seawater using ligand exchange method with EDTA. Marine Chemistry, 11(4), 343–354.
Howard, J. L., & Shu, J. (1996). Sequential extraction analysis of heavy metals using a chelating agent (nta) to counteract resorption. Environmental Pollution, 91(1), 89–96.
Hu, Y., Zhang, P., Chen, D., Zhou, B., Li, J., & Li, X. W. (2012). Hydrothermal treatment of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash for dioxin decomposition. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 207–208, 79–85.
James, B. R. (1996). The challenge of remediating chromium-contaminated soil. Environmental Science and Technology, 30(6), 248A–251A.
Jin, Y. Q., Ma, X. J., Jiang, X. G., Liu, H. M., Li, X. D., Yan, J. H., et al. (2012). Effects of hydrothermal treatment on the major heavy metals in fly ash from municipal solid waste incineration. Energy & Fuels, 27(1), 394–400.
Jing, Z., Ran, X., Jin, F., & Ishida, E. H. (2010). Hydrothermal solidification of municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash with slag addition. Waste Management, 30(8–9), 1521–1527.
Kim, C., Lee, Y., & Ong, S. K. (2003). Factors affecting EDTA extraction of lead from lead-contaminated soils. Chemosphere, 51(9), 845–853.
Leštan, D., Luo, C., & Li, X. (2008). The use of chelating agents in the remediation of metal-contaminated soils: a review. Environmental Pollution, 153(1), 3–13.
Li, W., Peters, R. W., Brewster, M. D., & Miller, G. A. (1995, June 18–23). Sequential extraction evaluation of heavy-metal contaminated soil: how clean is clean. Proceedings of the 88th Annual Meeting and Exhibition on Air and Waste Management Association, San Antonio, TX.
Lo, I. M. C., & Yang, X. Y. (1998). Removal and redistribution of metals from contaminated soils by a sequential extraction method. Waste Management, 18(1), 1–7.
Lo, I. M. C., Tsang, D. C. W., Yip, T. C. M., Wang, F., & Zhang, W. (2011). Significance of metal exchange in EDDS-flushing column experiments. Chemosphere, 83(1), 7–13.
Meegoda, J. N., & Perera, R. (2001). Ultrasound to decontaminate heavy metals in dredged sediments. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 85, 73–89.
Mulligan, C. N., Yong, R. N., & Gibbs, B. F. (2001). An evaluation of technologies for the heavy metal remediation of dredged sediments. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 85, 145–163.
Ndiba, P., Axe, L., & Boonfueng, T. (2008). Heavy metal immobilization through phosphate and thermal treatment of dredged sediments. Environmental Science and Technology, 42(3), 920–926.
Nowack, B., Kari, F. G., & Kruger, H. G. (2001). The remobilization of metals from iron oxides and sediments by metal-edta complexes. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 125, 243–257.
Obrador, A., Rico, M. I., Alvarez, J. M., & Novillo, J. (2001). Influence of thermal treatment on sequential extraction and leaching behaviour of trace metals in a contaminated sewage sludge. Bioresource Technology, 76(3), 259–264.
Peng, J. F., Song, Y. H., Yuan, P., Cui, X. Y., & Qiu, G. L. (2009). The remediation of heavy metals contaminated sediment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 161(2–3), 633–640.
Peters, R. W. (1999). Chelant extraction of heavy metals from contaminated soils. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 66(1–2), 151–210.
Pinto, I., Neto, I., & Soares, H. (2013). Biodegradable chelating agents for industrial, domestic and agricultural applications-a review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, Proceedings of the 14th Euchems International Conference on Chemistry and the Environment. Barcelona, June 25–28, 2013.
Polettini, A., Pomi, R., Rolle, E., Ceremigna, D., De Propris, L., Gabellini, M., et al. (2006). A kinetic study of chelant-assisted remediation of contaminated dredged sediment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 137(3), 1458–1465.
Polettini, A., Pomi, R., & Calcagnoli, G. (2009). Assisted washing for heavy metal and metalloid removal from contaminated dredged materials. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 196(1–4), 183–198.
Shahid, M., Austruy, A., Echevarria, G., Arshad, M., Sanaullah, M., Aslam, M., et al. (2013). EDTA-enhanced phytoremediation of heavy metals: a review. Soil and Sediment Contamination: An International Journal, 23(4), 389–416.
Singer, A., & Berkgaut, V. (1995). Cation exchange properties of hydrothermally treated coal fly ash. Environmental Science and Technology, 29(7), 1748–1753.
Smith, R. M., & Martell, A. E. (1987). Critical stability constants, enthalpies and entropies for the formation of metal complexes of aminopolycarboxylic acids and carboxylic acids. The Science of the Total Environment, 64, 125–147.
Sørensen, M. A., Koch, C. B., Stackpoole, M. M., Bordia, R. K., Benjamin, M. M., & Christensen, T. H. (2000). Effects of thermal treatment on mineralogy and heavy metal behavior in iron oxide stabilized air pollution control residues. Environmental Science and Technology, 34(21), 4620–4627.
Tandy, S., Bossart, K., Mueller, R., Ritschel, J., Hauser, L., Schulin, R., et al. (2004). Extraction of heavy metals from soils using biodegradable chelating agents. Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 937–944.
Tessier, A., Campbell, P. G. C., & Bisson, M. (1979). Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Analytical Chemistry, 51, 844–851.
Tiedje, J. M. (1975). Microbial degradation of ethylenediaminetetraacetate in soils and sediments. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 30(2), 327–329.
Tsang, D. C. W., Zhang, W., & Lo, I. M. C. (2007). Copper extraction effectiveness and soil dissolution issues of EDTA-flushing of artificially contaminated soils. Chemosphere, 68, 234–243.
Tsang, D. C. W., Lo, I. M. C., & Surampalli, R. Y. (Eds.). (2012). Chelating agents for land decontamination technologies. Virginia: American Society of Civil Engineers.
Vallet, V., Wahlgren, U., & Grenthe, I. (2003). Chelate effect and thermodynamics of metal complex formation in solution: a quantum chemical study. Journal of American Chemical Society, 125, 14941–14950.
Vandevivere, P., Hammes, F., Verstraete, W., Feijtel, T., & Schowanek, D. (2001a). Metal decontamination of soil, sediment, and sewage sludge by means of transition metal chelant [S, S]-EDDS. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 127(9), 802–811.
Vandevivere, P., Saveyn, H., Verstraete, W., Feijtel, W., & Schowanck, D. (2001b). Biodegradation of metal-[s, s]-EDDS complexes. Environmental Science and Technology, 35, 1765–1770.
Vulava, V. M., & Seaman, J. C. (2000). Mobilization of lead from highly weathered porous material by extracting agents. Environmental Science and Technology, 34, 4828–4834.
Vuyyuru, K. R., Pant, K. K., Krishnan, V. V., & Nigam, K. D. P. (2010). Recovery of Nickel from spent industrial catalysts using chelating agents. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 49(5), 2014–2024.
Yip, T. C. M., Tsang, D. C. W., Ng, K. T. W., & Lo, I. M. C. (2009). Kinetic interactions of EDDS with soils: 1. Metal re-sorption and competition under EDDS deficiency. Environmental Science and Technology, 43(3), 831–836.
Yong Do, N., & Park, H. I. (2011). A study on adsorption of Pb, Cu, Zn and Cd onto natural clay. International Journal on Environmental Research, 5(2), 413–424.
Yuan, S., Wu, X., Wan, J., Long, H., Lu, X., Wu, X. (2010). Enhanced washing of HCB and Zn from aged sediments by TX-100 and EDTA mixed solutions. Geoderma, 156(3-4), 119-125.
Zhang, F. S., & Itoh, H. (2006). Extraction of metals from municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash by hydrothermal process. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 136(3), 663–670.
Zhang, W., Tong, L., Yuan, Y., Liu, Z., Huang, H., Tan, F., et al. (2010). Influence of soil washing with a chelator on subsequent chemical immobilization of heavy metals in a contaminated soil. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 178, 578–587.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Singapore for providing financial support under account M060380007 for this research study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 45 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, K., Giannis, A., Wong, A.S.Y. et al. EDTA-Enhanced Thermal Washing of Contaminated Dredged Marine Sediments for Heavy Metal Removal. Water Air Soil Pollut 225, 2024 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2024-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2024-8