Abstract
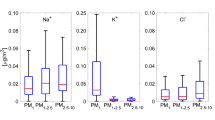
Particulate matter, the main pollutant in the atmospheric environment of the Santiago city in winter, was analyzed by means of the major water-soluble ionic species obtained under critical episodes of pollution in 2003. The particulate matter samples were collected using the Micro-Orifice uniform deposit impactors, with eight impactor stages connected in series, and the ionic species in particulate matter samples at each stage was analyzed by ion chromatography. While sulfate ion and nitrate ion showed bi-modal distributions, peaking in the fine and coarse mode, ammonium ion displayed a bi-modal size distribution, peaking in the fine and ultra fine mode. The equivalent concentration ratio of ammonium to sulfate was 2.03 ± 0.09, indicating the complete neutralization of sulfuric acid by ammonia. The excess ammonium ion was associated to nitrate ion. The study of the size distribution of water-soluble inorganic ions in particulate matter supports the notion that secondary aerosols play a significant role in the urban atmosphere.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arimoto R, Duce RA, Savoie DL, Prospero J, Talbot R, Cullen J, Tomza U, Lewis N, Ray B (1996) Relationships among aerosol constituents from Asia and the North Pacific during PEM-West A. J Geophys Res 101:2011–2023
Baek BH, Aneja VP, Tong Q (2004) Chemical coupling between ammonia, acid gases, and fine particles. Environ Pollut 129(1):89–98
Behera SN, Sharma M (2010) Investigating the potential role of ammonia in ion chemistry of fine particulate matter formation for an urban environment. Sci Total Environ 408(17):3569–3575
Brook JR, Wiebe AH, Woodhouse SA, Audette CV, Dann TF, Callaghan S, Piechowski M, Dabek-Zlotorzynska E, Dloughy JF (1997) Temporal and spatial relationships in fine particle strong acidity, sulphate, PM10 and PM2.5 across multiple Canadian locations. Atmos Environ 31(24):4223–4236
Chen Y-Q, Zhang Y, Zhang X-S (2005) Size distribution and seasonal variation of ions in aerosol at semi-urban site in Beijing. Acta Ecologica Sinica 25(12):3231–3236
Chow JC, Watson JG, Fujita EM, Lu Z, Lawson DR (1994) Temporal and spatial variations of PM2.5 and PM10 aerosol in the southern California air quality study. Atmos Environ 28(12):2061–2080
CONAMA RM (1999). Final Report Aerosol Characterization Study in Santiago de Chile-1999. Comisión Nacional del Medio Ambiente Región Metropolitana (CONAMA RM), Santiago, pp 69
Donaldson K, Li XY, MacNee W (1998) Ultrafine (nanometer) particle mediated lung injury. J Aerosol Sci 29(5–6):553–560
Du H, Kong L, Cheng T, Chen J, Yang X, Zhang R, Han Z, Yan Z, Ma Y (2010) Insights into ammonium particle-to-Gas Conversion: non-sulfate ammonium coupling with nitrate and chloride. Aerosol Air Qual Res 10(6):589–595
Hays MD, Geron CD, Linna KJ, Smith ND, Schauer JJ (2002) Speciation of gas phase and fine particle emissions from burning of foliar fuels. Environ Sci Technol 36(11):2281–2295
Krupa SV (2003) Effects of atmospheric ammonia (NH3) on terrestrial vegetation: a review. Environ Pollut 124(2):179–221
Leiva MA, Araya MC, Alvarado AM, Seguel RJ (2012) Uncertainty estimation of anions and cations measured by ion chromatography in fine urban ambient particles (PM2.5). Accredit Qual Assur 17(1):53–63
Lin CC, Chen SJ, Huang KL, Lee WJ, Lin WY, Liao CJ, Chaung HC, Chiu CH (2007) Water-soluble ions in nano/ultrafine/fine/coarse particles collected near a busy road and at a rural site. Environ Pollut 145(2):562–570
Maricq MM (2007) Chemical characterization of particulate emission from diesel engines: a review. J Aerosol Sci 38(11):1079–1118
Marple VA, Rubow KL, Behm SM (1991) A micro-orifice uniform deposit impactor (MOUDI): description, calibration and use. Aerosol Sci Tech 14(4):434–446
Meszaros E, Barcza T, Gelencser A, Hlavay J, Kiss G, Krivacsy Z, Molnar A, Polyak K (1997) Size distributions of inorganic and organic species in the atmospheric aerosol in Hungary. J Aerosol Sci 28(7):1163–1175
Milford JB, Davidson CI (1987) The sizes of particulate sulphate and nitrate in the atmosphere. J Air Pollut Contr Assoc 37(2):125–134
Morales RGE, Leiva GMA (2006) Distribution and Critical Concentration of PM in the city of Santiago, Chile (in Spanish). In: Morales RGE (ed) Atmospheric Urban Pollution: Critical episodes of the Environmental pollution in the City of Santiago, Chile (in Spanish), 1st edn. Editorial Universitaria SA, Santiago
Morata D, Polve M, Valdes A, Belmar M, Dinator MI, Silva M, Leiva MA, Aigouy T, Morales JR (2008) Characterisation of aerosol from Santiago, Chile: an integrated PIXE-SEM-EDX study. Environ Geol 56(1):81–95
Morawska L, Ristovski Z, Jayaratne ER, Keogh DU, Ling X (2008) Ambient nano and ultrafine particles from motor vehicle emissions: characteristics, ambient processing and implications on human exposure. Atmos Environ 42(35):8113–8138
Parmar RS, Satsangi GS, Kumari M, Lakhani A, Srivastava SS, Prakash S (2001) Study of size distribution of atmospheric aerosol at Agra. Atmos Environ 35(4):693–702
Salve PR, Krupadam RJ, Wate SR (2007) A study on major inorganic ion composition of atmospheric aerosols. J Environ Biol 28(2):241–244
Seinfeld JH, Pandis SN (2006) Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change. John Wiley and Sons, Inc., Hoboken
SINCA (2011) Sistema de Información Nacional de Calidad del Aire (Information National System of Air Quality). Ministerio del Medio Ambiente, Gobierno de Chile, Chile. On line database. http://sinca.conama.cl
Toro R (2010) Secondary particulate matter formation in high pollution episodes in Santiago, Chile (In spanish) Ph.D. Disertation, Faculty of Science, University of Chile, Chile, Chile
Tsai JH, Chang KL, Lin JJ, Lin YH, Chiang HL (2005) Mass-size distributions of particulate sulfate, nitrate, and ammonium in a particulate matter nonattainment region in southern Taiwan. J Air Waste Manag 55(4):502–509
Verma SK, Deb MK, Suzuki Y, Tsai YI (2010) Ion chemistry and source identification of coarse and fine aerosols in an urban area of eastern central India. Atmos Res 95(1):65–76
Wichmann HE, Spix C, Tuch T, Wölke G, Peters A, Heinrich J, Kreyling G, Heyder J (2000) Daily mortality and fine and ultrafine particles in Erfurt, Germany. Part-I: Role of particle number and particle mass Health Effects Institute, Research report, number 98, Germany
Xiu GL, Zhang DN, Chen JZ, Huang XJ, Chen ZX, Guo HL, Pan JF (2004) Characterization of major water-soluble inorganic ions in size-fractionated particulate matters in Shanghai campus ambient air. Atmos Environ 38(2):227–236
Zhang WJ, Zhuang GS, Guo JH, Xu DQ, Wang W, Baumgardner D, Wu ZY, Yang W (2010) Sources of aerosol as determined from elemental composition and size distributions in Beijing. Atmos Res 95(2–3):197–209
Zhao JP, Zhang FW, Xu Y, Chen JS (2011) Characterization of water-soluble inorganic ions in size-segregated aerosols in coastal city Xiamen. Atmos Res 99(3–4):546–562
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Centro Nacional del Medio Ambiente (CENMA) for providing the MOUDI equipment. They would like to thank the anonymous referees for providing us with constructive comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leiva G., M.A., Toro, R., Morales, R.G.E. et al. A study of water-soluble inorganic ions in size-segregated aerosols in atmospheric pollution episode. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 11, 437–448 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0221-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0221-4