Abstract
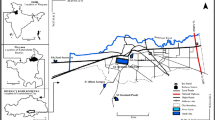
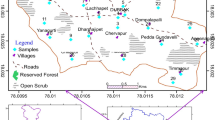
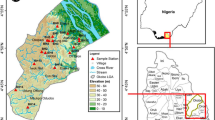
Ground water of the farm settlements in the bitumen deposit area of Western Nigeria were tested for pH, conductivity, turbidity, total dissolved solid, sulphate, phosphate, nitrogen nitrate, chloride, alkalinity, total hardness, calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium and total coliform in the dry season (March) and rainy season (August) of years 2008 and 2009 using atomic absorption spectrometer and standard analytical methods. Conductivity, pH, turbidity, phosphate ions and total coliform values obtained in some of the wells were out of the recommended range for drinking water. Water quality index analysis was carried out using information entropy method. Water quality index of the wells when compared with the permissible limits of international standards, ranked the bore hole as ‘excellent’ in the dry season of year 2009 and just ‘good’ in the rainy season of the same year. Ground water sampling stations were ranked extremely poor at least once out of the four seasons considered. Water quality index ranking also showed that the quality of the wells declined over the years. The correlation coefficient matrix (p < 0.05) of water quality index and the parameters showed significant relationships between water quality index and total coliform (0.99), total dissolved solids and conductivity (0.96), hardness and Ca2+ (0.68), hardness and Mg2+ (0.75). Water quality index also showed moderate significant relationship with total dissolved solid, conductivity and N–NO3 −. High concentration of total coliform in most of the shallow wells in the environment, due to bitumen deposit, renders them unfit for human consumption unless properly treated.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abulude FO, Obidiran GO, Orungbemi S (2007) Determination of physico-chemical parameter and trace metal contents of drinking water samples in Akure Nigeria. Electronic J of Environ, Agric and food Chem 6(8):2297–2303
Adebiyi FM, Asubiojo OI, Ajayi TR (2006) Multi-elemental analysis of Nigerian bitumen by TXRF spectrometry and the physical constants characterization of its hydrocarbon content. Fuel 85(3):396–400
Adegoke OS, Ibe EC (1982) The tar sand and heavy crude resources of Nigeria. Proc 2nd Intern Conf on heavy crude and Tarsands, Caracas, Venezuela, chapter 32, 280–285
Adewole MO (2010) Environmental implications of bitumen seep induced pollution in parts of Ogun state, southwestern Nigeria. Environ Earth Sci 59:1507–1514
Akinmosin A, Osinowo OO, Oladunjoye MA (2009) Radiogenic components of the Nigeria Tarsand deposits. Earth Sci Res J 13(1):64–73
American Public Health Association—APHA (1985) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, Washington. http://www.h2oc.com/pdfs/Kinetics-Figures.pdf. Accessed 12/July/2010
Asonye CC, Okolie NP, Okenwa EE, Iwuanyanwu UG (2007) Some physico-chemical characteristics and heavy metal profiles of Nigerian rivers, streams and waterways. Afr J Biotechnol 6(5):617–624
Atulegwu PU, Njoku JD (2004) The impact of biocides on the water quality. Int Res J Eng Sci Technol 1:47–52
Ayotamuno MJ, Akor AJ, Igho TJ (2002) Effluent quality and wastes from petroleum drilling operations in the Niger Delta Nigeria. J Environ Manag Health 13(2):207–216
Bali G, Ramamurthi RS, Sullia SB, Shivalipour A, Kastury S (2002) Environmental Biotechnology, ISBN 8176483788. SB Nangia, APH Publishing Corporation, New Delhi, p 98
Bhardwaj RM (2005) Water quality monitoring in India achievements and constraints, IWG-Env, International Work Session on Water Statistics, Vienna, pp 1–12
Cobbina SJ, Anvyidoho LY, Nyame F, Hodgson IO (2009) Water quality status of dugouts from five districts in Northern Ghana: implications for sustainable water resources management in a water stressed tropical savannah environment. Environ Monit Assess 167(1–4):405–416
Collins CH, Lyne PM (1980) Microbial methods. Butterworth and Co., Limited, London, pp 125–300
Fagbote EO, Olanipekun EO (2010a) Speciation of heavy metals in soil of bitumen impacted area of Western Nigeria. Eur J Sci Res 47(2):265–277
Fagbote EO, Olanipekun EO (2010b) Speciation of heavy metals in sediment of bitumen deposit area, Nigeria. J Appl Sci Environ Manage 14(4):5–11
Faniran JA, Ngceba FC, Bhat RB, Oche CY (2001) An assessment of the water quality of the Isinuka springs in the Transkei region of the Eastern Cape, Republic of South Africa. Water SA 27(2):241–250
General Fact Sheet on Water Quality Parameters (2003) Monitoring the health of the watershed. Appendix D. Delaware River Keepers. http://www.dec.ny.gov/docs/water_pdf/jan09crotontmdl.pdf. Accessed 14/Jan/2010
Gruickshank R, Duguid JP, Marmion BP, Swain RHA (1984) Medical microbiology, 13th edn. Vol 2. Churchill Living Stone, New York. pp 170–189
Mohamad RMK, Mohd KY, Wan NA, Mat YA (2007) Creation of ground water quality index for an open municipal landfill area. J Math Sci 1(2):181–192
Oboh OB, Ilori MO, Akinyemi JO, Adebusoye SA (2006) Hydrocarbon degrading potentials of bacteria isolated from a Nigerian bitumen (Tarsand) deposit. Nature Sci 4(3):51–57
Oguntimehin II, Ipinmorroti KO (2007) Solvent extraction of vanadium from Nigerian bitumen using Tri-butylphosphate. J Applied Sci 7(24):4028–4031
Olajire AA, Alade OA, Adeniyi AA, Olabemiwo MO (2007) Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface soils and water from the vicinity of Agbabu bitumen field of Southwestern Nigeria. J Environ Sci Health, Part A, 42(8):1043–1049
Olajire AA, Olojubade M, Olabemiwo O (2008) n-Alkanes distributions in soil and water samples collected near Agbabu bitumen field of southwestern Nigeria. Int J Environ Stud 65(6):769–779
Pei-yue L, Hui Q, Jian-hua W (2010a) Ground water quality assessment based on improved water quality index in Pengyang County, Ningxia, Northwest China. E-J Chem, 7(S1):S209–S216
Pei-yue L, Hui Q, Jian-hua W (2010b) Ground water quality assessment based on entropy osculating value method. Int J Environ Sci 1(4):621–630
Riyad M, Mohammed R, Mohammed IB (2006) Relationship between water, temperature, nutrients and dissolved oxygen in the northern Gulf of Aqaba, Red sea. Oceanologia 48(2):257–263
Schoenen D (1986) Microbial growth due to materials in drinking water systems. In: Rehn HJ, Reed G (eds) Biotechnology, chap 20. VCH Publishers, Weinheim, pp 627–647
Stewart JC, Lemley AT, Hogan SI, Weismiller RA, Hornsby AG (2009) Drinking water standards, University of Florida, Institute of food and agricultural sciences (IFAS) extension. http//www.edis.ifas.nfl.edu.ss297. Accessed on 08/June/2011
Tanriverdi C, Alp A, Demirkiran AR, Uckardes F (2009) Assessment of surface water quality of the Ceyhan Rivan basin, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 167(1–4):175–184
United States Environmental Protection Agency—USEPA (1996) Quality criteria for water. EPA 440/5-86-001, Washington Publication. http://www.epa.gov/waterscience/pc/wqnews/dec96.html. Accessed 02/Feb/2008
Veljkovic N, Lekic D, Jovicic M (2008) Case study of water management processes: Serbian water quality index. u: conference of the Danubian countries on the hydrological forecasting and hydrological bases of water management (XXIVth), Slovenia
Whitman RL, Nevers BM, Byappanahali MN (2006) Examination of the watershed-wide distribution of the Escherichia coli along Southern Lake Michigan: an integrated approach. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(11):7301–7310
World Energy Council (2007) Survey of energy resources. WEC London. Publication accessed online at http://web.mit.edu/mission/www/m2013/ser_interim_update_2009_final.pdf on 17/Feb/2010
World Health Organization—WHO (1982) World health organization. Guideline for drinking water quality. WHO Geneva. http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/9241545356.pdf. Accessed 18/Oct/2007
World Health Organization—WHO (1993) Guidelines for drinking water quality. World health organisation, Geneva. http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/fulltext.pdf. Accessed 12/Aug/2009
World Health Organization—WHO (1996) Guidelines for drinking water quality. Vol 3. Geneva. http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/GDWQ2004web.pdf. Accessed 12/Aug/2009
Yisa J, Jimoh T (2010) Analytical studies on water quality index of River Ladzu. Am J Appl Sci 7(4):453–458
Acknowledgments
The authors which to express their gratitude to the Department of Chemistry, University of Ado-Ekiti, Ado-Ekiti, Nigeria and the management of the University of Ado-Ekiti, Nigeria, for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fagbote, E.O., Olanipekun, E.O. & Uyi, H.S. Water quality index of the ground water of bitumen deposit impacted farm settlements using entropy weighted method. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 11, 127–138 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-012-0149-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-012-0149-0