Abstract
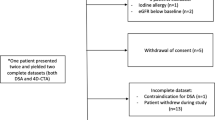
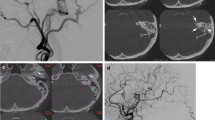
This study was to evaluate the value of four-dimensional computed tomography angiography (4D-CTA) in the diagnosis of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistula (DAVF). This study included 16 patients who were diagnosed to have intracranial DAVF by digital subtraction angiography (DSA). The 4D-CTA was performed by Aquilion ONE multi-detector CT scanner (Toshiba Medical Systems, Japan) equipped with 320 × 0.5 mm detector rows. Standard biplane fluoroscopy equipments (Infinix, Toshiba Medical Systems, Japan and ADVANTX LC/LP, GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee, WI, USA) were applied in the diagnosis of intra-arterial DSA. Examinations were performed to evaluate the findings of DSA and 4D-CTA in each patient. The examination results were read by two independent readers in a blind manner. All results were documented on standardized scoring sheets. In all 16 cases, the same diagnosis results of intracranial DAVF were obtained from DSA and 4D-CTA. The results of subtype (Borden and Cognard classification), venous reflux and fistula sites were also accurately exhibited in 4D-CTA. In addition, there was a little discrepancy in identifying smaller and specific arterial branches and in distinguishing fistula type (focal or diffuse) using 4D-CTA. Good-to-excellent agreements were made between 4D-CTA and DSA. Therefore, 4D-CTA could be a feasible tool for the characterization of intracranial DAVF, with respect to determining fistula site and venous drainage.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beijer TR, van Dijk EJ, de Vries J, Vermeer SE, Prokop M, Meijer FJ (2013) 4D-CT angiography differentiating arteriovenous fistula subtypes. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 115:1313–1316
Bendszus M, Koltzenburg M, Burger R, Warmuth-Metz M, Hofmann E, Solymosi L (1999) Silent embolism in diagnostic cerebral angiography and neurointerventional procedures: a prospective study. Lancet 354:1594–1597
Brouwer PA, Bosman T, van Walderveen MA, Krings T, Leroux AA, Willems PW (2010) Dynamic 320-section CT angiography in cranial arteriovenous shunting lesions. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:767–770
Brown RD Jr, Flemming KD, Meyer FB, Cloft HJ, Pollock BE, Link ML (2005) Natural history, evaluation, and management of intracranial vascular malformations. Mayo Clin Proc 80:269–281
Endo S, Kuwayama N, Takaku A, Nishijima M (1998) Direct packing of the isolated sinus in patients with dural arteriovenous fistulas of the transverse-sigmoid sinus. J Neurosurg 88:449–456
Evans AL, Coley SC, Wilkinson ID, Griffiths PD (2005) First-line investigation of acute intracerebral hemorrhage using dynamic magnetic resonance angiography. Acta Radiol 46:625–630
Farb RI, Agid R, Willinsky RA, Johnstone DM, Terbrugge KG (2009) Cranial dural arteriovenous fistula: diagnosis and classification with time-resolved MR angiography at 3T. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:1546–1551
Fujiwara H, Momoshima S, Akiyama T, Kuribayashi S (2013) Whole-brain CT digital subtraction angiography of cerebral dural arteriovenous fistula using 320-detector row CT. Neuroradiology 55:837–843
Hatano T, Bozinov O, Burkhardt JK, Bertalanffy H (2013) Surgical treatment of tentorial dural arteriovenous fistulae located around the tentorial incisura. Neurosurg Rev 36:429–435
Houdart E, Saint-Maurice JP, Chapot R, Ditchfield A, Blanquet A, Lot G, Merland JJ (2002) Transcranial approach for venous embolization of dural arteriovenous fistulas. J Neurosurg 97:280–286
Kwon BJ, Han MH, Kang HS, Chang KH (2005) MR imaging findings of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: relations with venous drainage patterns. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2500–2507
Lucas CP, Zabramski JM, Spetzler RF, Nishimura S, Jacobowitz R (1997) Treatment for intracranial dural arteriovenous malformations: a meta-analysis from the English language literature. Neurosurgery 40(6):1119–1130
Nishimura S, Hirai T, Sasao A, Kitajima M, Morioka M, Kai Y, Omori Y, Okuda T, Murakami R, Fukuoka H, Awai K, Kuratsu JI, Yamashita Y (2010) Evaluation of dural arteriovenous fistulas with 4D contrast-enhanced MR angiography at 3T. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:80–85
Pradilla G, Coon AL, Huang J, Tamargo RJ (2012) Surgical treatment of cranial arteriovenous malformations and dural arteriovenous fistulas. Neurosurg Clin N Am 23:105–122
Reinacher PC, Stracke P, Reinges MH, Hans FJ, Krings T (2007) Contrast-enhanced time-resolved 3-D MRA: applications in neurosurgery and interventional neuroradiology. Neuroradiology 49(Suppl 1):S3–S13
Salomon EJ, Barfett J, Willems PW, Geibprasert S, Bacigaluppi S, Krings T (2009) Dynamic CT angiography and CT perfusion employing a 320-detector row CT: protocol and current clinical applications. Klin Neuroradiol 19:187–196
Siebert E, Bohner G, Dewey M, Masuhr F, Hoffmann KT, Mews J, Engelken F, Bauknecht HC, Diekmann S, Klingebiel R (2009) 320-slice CT neuroimaging: initial clinical experience and image quality evaluation. Br J Radiol 82:561–570
Wachter D, Hans F, Psychogios MN, Knauth M, Rohde V (2011) Microsurgery can cure most intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae of the sinus and non-sinus type. Neurosurg Rev 34(3):337–345
Wang H, Ye X, Gao X, Zhou S, Lin Z (2014) The diagnosis of arteriovenous malformations by 4D-CTA: a clinical study. J Neuroradiol 41:117–123
Willems PW, Brouwer PA, Barfett JJ, terBrugge KG, Krings T (2011) Detection and classification of cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas using 4D-CT angiography: initial experience. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:49–53
Willems PW, Taeshineetanakul P, Schenk B, Brouwer PA, Terbrugge KG, Krings T (2012) The use of 4D-CTA in the diagnostic work-up of brain arteriovenous malformations. Neuroradiology 54:123–131
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Ningbo Social Developmental Research Project (No. 2012C50027).
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no financial competing interests. All authors declare no non-financial competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
X. Ye and H. Wang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, X., Wang, H., Huang, Q. et al. Four-dimensional computed tomography angiography is valuable in intracranial dural arteriovenous fistula diagnosis and fistula evaluation. Acta Neurol Belg 115, 303–309 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-014-0387-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-014-0387-7