Abstract
Introduction
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the usefulness of CT digital subtraction angiography (CTDSA) by using 320-detector row CT in the diagnosis and classification of cerebral dural arteriovenous fistula (dAVF) and comparing it with DSA as the standard reference.
Methods
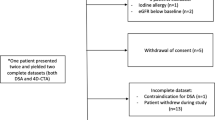
A total of 29 CTDSA/DSA from 25 patients with dAVF were retrospectively evaluated by two neuroradiologists. The presence, Cognard classification, and feeding arteries of dAVFs on CTDSA were assessed according to DSA.
Results
DSA depicted 33 dAVFs in 28 cases. By consensus reading, CTDSA correctly detected 32 dAVFs in 27 cases and properly graded 31 lesions. The intermodality agreement for the presence and classification of dAVFs was excellent (kappa = 0.955 and 0.921, respectively). CTDSA detected 77 of 109 feeding arteries (70.6 %) in 25 cases. The intermodality agreement for the feeding arteries was good (kappa = 0.713).
Conclusion
Although CTDSA is limited in temporal and spatial resolution in comparison with DSA, it is an effective non-invasive tool for the detection and classification of dAVF.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cognard C, Gobin YP, Pierot L, Bailly AL, Houdart E, Casasco A, Chiras J, Merland JJ (1995) Cerebral dural arteriovenous fistulas: clinical and angiographic correlation with a revised classification of venous drainage. Radiology 194:671–680
Borden JA, Wu JK, Shucart WA (1995) A proposed classification for spinal and cranial dural arteriovenous fistulous malformations and implications for treatment. J Neurosurg 82:166–179
van Rooij WJ, Sluzewski M, Beute GN (2007) Dural arteriovenous fistulas with cortical venous drainage: incidence, clinical presentation, and treatment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28(4):651–655
Kaufmann TJ, Huston J, Mandrekar JN, Schleck CD, Thielen KR, Kallmes DF (2007) Complications of diagnostic cerebral angiography: evaluation of 19,826 consecutive patients. Radiology 243:812–819
Willinsky RA, Taylor SM, TerBrugge K, Farb RI, Tomlinson G, Montanera W (2003) Neurologic complications of cerebral angiography: prospective analysis of 2,899 procedures and review of the literature. Radiology 227:522–528
Pekkola J, Kangasniemi M (2011) Posterior fossa dural arteriovenous fistulas: diagnosis and follow-up with time-resolved imaging of contrast kinetics (TRICKS) at 1.5 T. Acta Radiol 52:442–447
Meckel S, Maier M, Ruiz DSM, Yilmaz H, Scheffler K, Radue E-W, Wetzel SG (2007) MR angiography of dural arteriovenous fistulas: diagnosis and follow-up after treatment using a time-resolved 3D contrast-enhanced technique. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:877–884
Uchino A, Nomiyama K, Takase Y, Nakazono T, Tominaga Y, Imaizumi T, Kudo S (2007) Retrograde flow in the dural sinuses detected by three-dimensional time-of-flight MR angiography. Neuroradiology 49:211–215
Siebert E, Bohner G, Dewey M, Masuhr F, Hoffmann KT, Mews J, Engelken F, Bauknecht HC, Diekmann S, Klingebiel R (2009) 320-slice CT neuroimaging: initial clinical experience and image quality evaluation. Br J Radiol 82:561–570
Klingebiel R, Siebert E, Diekmann S, Wiener E, Masuhr F, Wagner M, Bauknecht H-C, Dewey M, Bohner G (2009) 4-D imaging in cerebrovascular disorders by using 320-slice CT: feasibility and preliminary clinical experience. Acad Radiol 16:123–129
Soga S, Ersoy H, Mitsouras D, Schultz K, Whitmore AG, Powers SL, Steigner ML, Signorelli J, Prior RF, Rybicki FJ, Pomahac B (2010) Surgical planning for composite tissue allotransplantation of the face using 320-detector row computed tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 34:766–769
Willems PWA, Taeshineetanakul P, Schenk B, Brouwer PA, Terbrugge KG, Krings T (2012) The use of 4D-CTA in the diagnostic work-up of brain arteriovenous malformations. Neuroradiology 54:123–131
Manninen A-L, Isokangas J-M, Karttunen A, Siniluoto T, Nieminen MT (2012) A comparison of radiation exposure between diagnostic CTA and DSA examinations of cerebral and cervicocerebral vessels. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:2038–2042
Willems PWA, Brouwer PA, Barfett JJ, TerBrugge KG, Krings T (2011) Detection and classification of cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas using 4D-CT angiography: initial experience. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:49–53
Brouwer PA, Bosman T, van Walderveen MAA, Krings T, Leroux AA, Willems PWA (2010) Dynamic 320-section CT angiography in cranial arteriovenous shunting lesions. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:767–770
Beijer TR, van Dijk EJ, de Vries J, Vermeer SE, Prokop M, Meijer FJA (2013) 4D-CT angiography differentiating arteriovenous fistula subtypes. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2012.12.015
Imai F, Ogura Y, Kiya N, Zhou J, Ninomiya T, Katada K, Sano H, Kanno T (1996) Synthesized surface anatomy scanning (SSAS) for surgical planning of brain metastasis at the sensorimotor region: initial experience with 5 patients. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 138:290–293
Tsuchiya K, Katase S, Yoshino A, Hachiya J, Shiokawa Y (2002) MR-angiogram-added surface anatomy scanning of superficial cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Eur Radiol 12:2330–2334
Nishimura S, Hirai T, Sasao A, Kitajima M, Morioka M, Kai Y, Omori Y, Okuda T, Murakami R, Fukuoka H, Awai K, Kuratsu J-I, Yamashita Y (2010) Evaluation of dural arteriovenous fistulas with 4D contrast-enhanced MR angiography at 3 T. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:80–85
Hori M, Aoki S, Oishi H, Nakanishi A, Shimoji K, Kamagata K, Houshito H, Kuwatsuru R, Arai H (2011) Utility of time-resolved three-dimensional magnetic resonance digital subtraction angiography without contrast material for assessment of intracranial dural arterio-venous fistula. Acta Radiol 52:808–812
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujiwara, H., Momoshima, S., Akiyama, T. et al. Whole-brain CT digital subtraction angiography of cerebral dural arteriovenous fistula using 320-detector row CT. Neuroradiology 55, 837–843 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-013-1181-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-013-1181-6