Abstract
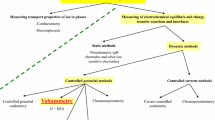
This study aims to develop an electrochemical method for determining cefprozil (CFP) and a stability-indicating chromatographic analysis method for determining CFP’s isomers. CFP was determined for the first time via voltammetric methods in this study. The electrochemical behavior of CFP was examined over a pH ranging between 0.3 and 10.0 using cyclic voltammetry and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV). CFP oxidized irreversibly and by diffusion-controlled at a glassy carbon electrode. Quantification studies with DPV were carried out. The repeatability, reproducibility, sensitivity, precision, and accuracy of the method were statistically evaluated. To determine CFP's diastereoisomers, a high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method was devised and validated using paracetamol as the internal standard. The moving phase, buffer solutions at various concentrations, pH, temperature, and flow rate impacts were all tuned in the experiments. The optimum separation via chromatography was sustained through the ACE 5 C8 (150 × 4.6 mm × 5 µm) column and acetonitrile: buffer solution (5 mM, ammonium acetate), 90:10 (v/v) mobile phase composition. The CFP diastereomers were separated at a flow rate of 1 mL min−1, 45 °C, and a wavelength of detection at 280 nm. The proposed method was validated in line with the International Conference on Harmonization guidelines, and HPLC degradation studies (oxidation, UV light, acid, base and temperature) were also performed. The proposed voltammetric and stability-indicating chromatographic methods have been successfully applied in pharmaceutical dosage forms. Thus, it has been shown that the analysis results were not affected by the excipients and their applicability to drug samples. Both methods were validated, and their applicability for analysis from synthetic biological samples will be demonstrated. The developed methods were fast, selective, sensitive, reliable, and environmentally friendly.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Bhargava, R. Lodha, S.K. Kabra, Indian. J. Pediatr. 70, 395 (2003)
A. Marzo, L. Dal Bo, J. Chromatogr. A 812, 17 (1998)
L.R. Wiseman, P. Benfield, Drug Eval. 45, 295 (1993)
L. Xu, J. Su, H. Muhetaer, C. Zhang, C. Huang, Y. Tang, X. Fu, Z. Liang, Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/cpdd.1304
H. Shikshaky, M.S. Rashed, A.A. Mohamed, Egypt. J. Chem. 63, 3129 (2020)
K. Tomatsu, S. Ando, S. Masuyoshi, S. Kondo, M. Hirano, T. Miyaki, H. Kawaguchi, J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 40, 1175 (1987)
N.X. Chin, H.C. Neu, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 31, 480 (1987)
R.H. Barbhaiya, U.A. Shukla, C.R. Gleason, W.C. Shyu, R.B. Wilber, R.R. Martin, K.A. Pittman, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 34, 1198 (1990)
E.A. Gadkariem, M.M. Mutasim, K.E.E. Ibrahim, H.A. El-Obeid, Int. J. Biomed. Sci. 5, 267 (2009)
K. Jadhav, D. Dhamecha, G. Asnani, V. Bhalekar, S. Lahoti, Chronicles Young Sci. 4, 158 (2013)
V. Jagapathi Raju, J.V.L.N. Seshagiri Rao, J. Chem. 5, 427 (2008)
T.H. Park, J.K. Kim, J.P. Jee, J.S. Park, C.K. Kim, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 36, 243 (2004)
N.O. Can, J. Sep. Sci. 34, 2223 (2011)
M. Liu, J.Y. Ma, Y. Zhang, X. Wang, H. Zhao, A. Du, M. Yang, L. Meng, M. Deng, H. Liu, Biomed. Chromatogr. 30, 288 (2016)
G. He, L. Mai, X. Wang, Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2018, (2018)
N.A. Alarfaj, S.A. Abd El-Razeq, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 41, 1423 (2006)
K. Nagy, K. Vékey, Med. Appl. Mass Spectrom. 61 (2007)
B. Bozal, B. Doğan-Topal, B. Uslu, S.A. Özkan, H.Y. Aboul-Enein, Anal. Lett. 42, 2322 (2009)
Ç. Kanbeş Dindar, B. Bozal-Palabiyik, B. Uslu, Electroanalysis 34, 1174 (2022)
S.E. Elugoke, O.E. Fayemi, A.S. Adekunle, P.S. Ganesh, S.Y. Kim, E.E. Ebenso, J. Electroanal. Chem. 929, 117120 (2023)
Validation of Analytical Procedures: ICH Guidelines Q2(R2) (2022)
B. Tunç, K. Amudi, P. Talay Pinar, J. Res. Pharm. 26, 1484 (2022)
A.M. AboulMagd, N.S. Abdelwahab, M.M. Abdelrahman, H.M. Abdel-Rahman, N.F. Farid, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 206, 114358 (2021)
D. Boczar, K. Bus, K. Michalska, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 15252 (2022)
S.W. Baertschi, K.M. Alsante, D. Santafianos, Pharmaceutical stress testing, in Predicting drug degradation, 2nd edn., ed. by S.W. Baertschi, K.M. Alsante, R.A. Reed (Informa Healthcare, London, 2011), pp.49–141
V.T. Gawande, K.G. Bothara, A.M. Marathe, Chromatographia 80, 1545 (2017)
A. von Ahn, A. Dallegrave, J.H.Z. dos Santos, Chromatographia 85, 263 (2022)
A. Karlesa, G.A.D. De Vera, M.C. Dodd, J. Park, M.P.B. Espino, Y. Lee, Environ. Sci. Technol. 48, 10380 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This study was produced from Ayşenur Ortak's (Ankara University Health Sciences Institute) master's thesis. Cem Erkmen acknowledges TUBİTAK for funding in the form of the Research Fellowship [2218-TUBİTAK project number: 122C252] through the 2218 - National Postdoctoral Research Fellowship Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors also declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ortak, A., Erkmen, C., Bozal-Palabiyik, B. et al. Development of electrochemical and stability-indicating chromatographic methods for the determination of cefprozil. J IRAN CHEM SOC 21, 263–273 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-023-02923-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-023-02923-6