Abstract
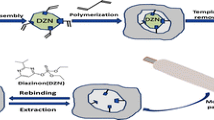
Dicloran pesticide is used to inhibit the fungal spore germination for different crops. Because of the increasing application of pesticides, reliable and accurate analytical methods are necessary. The aim of this work is designing the highly selective sensor to determine the dicloran in biological and environmental samples. Multi-walls carbon nanotubes and a molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) were used as modifiers in the sensor composition. A dicloran MIP and a nonimprinted polymer (NIP) were synthesized and applied in the carbon paste electrode. After the optimization of electrode composition, it was used to determine the concentration of analyte. Parameters affecting the sensor response were optimized, such as sample pH, electrolyte concentration and its pH, and the instrumental parameters of square wave voltammetry. The MIP-CP electrode showed very high recognition ability in comparison with NIP-CP. The obtained linear range was 1 × 10−6 to 1 × 10−9 mol L−1. The detection limit was 4.8 × 10−10 mol L−1. This sensor was used to determine the dicloran in real samples (human urine, tap and river water samples) without special sample preparation before analysis. All important parameters were optimized, improving the sensor response considerably.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Bolognesi, G. Morasso, Trends Food Sci. Technol. (2000). doi:10.1016/S0924-2244(00)00060-1
M. Stoytcheva, Pesticides—Strategies for Pesticides Analysis, 1st edn. (InTech, Rijeka, 2011). doi:10.5772/565
United States Environmental Protection Agency (US-EPA), Reregistration Eligibility Decision for DCNA (Dicloran). EPA-738-F-05-003 (2006)
R. Rouabhi, in Fungicides, ed. by O. Carisse (InTech, Rijeka, 2010), p. 363. doi:10.5772/12967
M. Ahmed Azmi, S.N.H. Naqvi, in Pesticides—The Impacts of Pesticides Exposure, ed. by M. Stoytcheva (InTech, Rijeka, 2011), pp. 1–24. doi:10.5772/1003
M.R.C. Massaroppi, S.A.S. Machado, L.A. Avaca, J. Braz. Chem. Soc. (2003). doi:10.1590/S0103-50532003000100018
M.S. Lin, B.I. Jan, H.J. Leu, J.S. Lin, Anal. Chim. Acta (1999). doi:10.1016/S0003-2670(99)00026-4
M.A. El-Mhammedi, M. Bakasse, A. Chtaini, J. Hazard. Mater. (2007). doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.02.054
Z. Meng, Y. Ma, Microchem. J. (1996). doi:10.1006/mchj.1996.0053
A.M. Carro, R.A. Lorenzo, Analyst (2001). doi:10.1039/B009910O
E.N. Efremenko, V.S. Sergeeva, Russ. Chem. Bull. (2001). doi:10.1023/A:1014377912147
R. Bhadekar, S. Pote, V. Tale, B. Nirichan, Am. J. Anal. Chem. (2011). doi:10.4236/ajac.2011.228118
A.N. Ivanov, G.A. Evtyugin, K.Z. Brainina, G.K. Budnikov, L.E. Stenina, J. Anal. Chem. (2002). doi:10.1023/A:1020985609601
T. Alizadeh, Electroanalysis (2009). doi:10.1002/elan.200804541
A.H. Kamel, F.T.C. Moreira, S.A.A. Almeida, M.G.F. Sales, Electroanalysis (2007). doi:10.1002/elan.200704039
T.P. Rao, K. Prasad, R. Kala, J.M. Gladis, Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. (2007). doi:10.1080/10408340701244664
S. Wu, X. Lan, L. Cui, L. Zhang, S. Tao, H. Wang et al., Anal. Chim. Acta (2011). doi:10.1016/j.aca.2011.05.032
M. Rahiminezhad, S.J. Shahtaheri, M.R. Ganjali, A.R. Koohpaei, A.R. Forushani, F. Golbabaei, J. Anal. Chem. (2010). doi:10.1134/S1061934810070063
F. Omidi, M. Behbahani, H.S. Abandansari, A.R. Sedighi, S.J. Shahtaheri, J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. (2014). doi:10.1186/s40201-014-0137-z
A.R. Koohpaei, S.J. Shahtaheri, M.R. Ganjali, A.R. Forushani, F. Golbabaei, Talanta (2008). doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2007.12.046
T. Alizadeh, M.R. Ganjali, P. Norouzi, M. Zare, A. Zeraatkar, Talanta (2009). doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2009.02.051
L. Wu, B. Sun, Y. Li, W. Chang, Analyst (2003). doi:10.1039/B212731H
Y. Dineiro, M.I. Menendez, M.C. Blanco-Lopez, M.J. Lobo-Castanon, A.J. Miranda-Ordieres, P. Tunon-Blanco, Anal. Chem. (2005). doi:10.1021/ac0513461
S.A. Piletsky, K. Karim, E.V. Piletska, C.J. Day, K.W. Freebairn, C. Legge, A.P.F. Turner, Analyst (2001). doi:10.1039/B102426B
R. Schirhagl, U. Latif, F.L. Dickert, J. Mater. Chem. (2011). doi:10.1039/c1jm11576f
M. Javanbakht, S. EynollahiFard, M. Abdouss, A. Mohammadi, M.R. Ganjali, P. Norouzi, L. Safaraliee, Electroanalysis (2008). doi:10.1002/elan.200804284
P. Norouzi, V.K. Gupta, B. Larijani, M.R. Ganjali, F. Faridbod, Talanta (2014). doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2014.03.061
Y. Ni, P. Qui, S. Kokot, Anal. Chim. Acta (2004). doi:10.1016/j.aca.2004.04.007
A. Nezamzadeh, M.K. Amini, H. Faghihian, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2, 583–594 (2007)
Acknowledgments
This research has been supported by Tehran University of Medical Sciences grant (Project No. 21892). The authors acknowledge the University for all valuable supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khadem, M., Faridbod, F., Norouzi, P. et al. Biomimetic electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer for dicloran pesticide determination in biological and environmental samples. J IRAN CHEM SOC 13, 2077–2084 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-016-0925-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-016-0925-8