Abstract
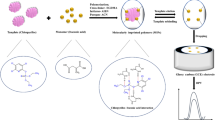
In this research, an electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) nanoparticles for selective and sensitive determination of diazinon (DZN) pesticides was developed. The nanoparticles of diazinon imprinted polymer were synthesized by suspension polymerization and then used for modification of carbon paste electrode (CPE) composition in order to prepare the sensor. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) and square wave voltammetry (SWV) methods were applied for electrochemical measurements. The obtained results showed that the carbon paste electrode modified by MIP nanoparticles (nano-MIP-CP) has much higher adsorption ability for diazinon than the CPE based non-imprinted polymer nanoparticles (nano-NIP-CP). Under optimized extraction and analysis conditions, the proposed sensor exhibited excellent sensitivity (95.08 μA L μmol−1) for diazinon with two linear ranges of 2.5 × 10−9 to 1.0 × 10−7 mol L−1 (R 2 = 0.9971) and 1.0 × 10−7 to 2.0 × 10−6 mol L−1 (R 2 = 0.9832) and also a detection limit of 7.9 × 10−10 mol.L−1. The sensor was successfully applied for determination of diaznon in well water and apple fruit samples with recovery values in the range of 92.53–100.86 %.

Procedure for preparation of electrochemical sensor based on MIP nanoparticles for determination of diazinon







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rassaei L, Marken F, Sillanpaa M, Amiri M, Cirtiu CM, Sillanpaa M. Nanoparticles in electrochemical sensors for environmental monitoring. Trends Anal Chem. 2011;30(11):1704–15.
Sohrabi MR, Jamshidi S, Esmaeilifar A. Cloud point extraction for determination of Diazinon: Optimization of the effective parameters using Taguchi method. Chemometr Intell Lab. 2012;110(1):49–54.
Davoodi D, Hassanzadeh-Khayyat M, Rezaei MA, Mohajeri SA. Preparation, evaluation and application of diazinon imprinted polymers as the sorbent in molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography analysis in cucumber and aqueous samples. Food Chem. 2014;158:421–8.
Skoulika SG, Georgiou CA, Polissiou MG. FT-Raman spectroscopy—Analytical tool for routine analysis of diazinon pesticide formulations. Talanta. 2000;51(3):599–604.
Cao H, Nam J, Harmon HJ, Branson DH. Spectrophotometric detection of organophosphate diazinon by porphyrin solution and porphyrin-dyed cotton fabric. Dyes Pigm. 2007;74(1):176–80.
Sanchez M, Mendez R, Gomez X, Martin‐Villacorta J. Determination of diazinon and fenitrothion in environmental water and soil samples by HPLC. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol. 2003;26(3):483–97.
Shayeghi M, Khoobdel M, Vatandoost H. Determination of organophosphorus insecticides (malathion and diazinon) residue in the drinking water. Pak J Biol Sci. 2007;10(17):2900–4.
Salm P, Taylor PJ, Roberts D, de Silva J. Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous quantitative determination of the organophosphorus pesticides dimethoate, fenthion, diazinon and chlorpyrifos in human blood. J Chromatogr B. 2009;877(5):568–74.
Inoue S, Saito T, Mase H, Suzuki Y, Takazawa K, Yamamoto I, et al. Rapid simultaneous determination for organophosphorus pesticides in human serum by LC–MS. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2007;44(1):258–64.
Rastrelli L, Totaro K, De Simone F. Determination of organophosphorus pesticide residues in Cilento (Campania, Italy) virgin olive oil by capillary gas chromatography. Food Chem. 2002;79(3):303–5.
Fytianos K, Raikos N, Theodoridis G, Velinova Z, Tsoukali H. Solid phase microextraction applied to the analysis of organophosphorus insecticides in fruits. Chemosphere. 2006;65(11):2090–5.
Jafari MT, Saraji M, Sherafatmand H. Polypyrrole/montmorillonite nanocomposite as a new solid phase microextraction fiber combined with gas chromatography–corona discharge ion mobility spectrometry for the simultaneous determination of diazinon and fenthion organophosphorus pesticides. Anal Chim Acta. 2014;814:69–78.
Ahmadi F, Assadi Y, Hosseini SM, Rezaee M. Determination of organophosphorus pesticides in water samples by single drop microextraction and gas chromatography-flame photometric detector. J Chromatogr A. 2006;1101(1):307–12.
Menezes Filho A, dos Santos FN, Pereira PAP. Development, validation and application of a method based on DI-SPME and GC–MS for determination of pesticides of different chemical groups in surface and groundwater samples. Microchem J. 2010;96(1):139–45.
Chen P-S, Huang S-D. Determination of ethoprop, diazinon, disulfoton and fenthion using dynamic hollow fiber-protected liquid-phase microextraction coupled with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Talanta. 2006;69(3):669–75.
Brun EM, Garces-Garcia M, Escuin E, Morais S, Puchades R, Maquieira A. Assessment of novel diazinon immunoassays for water analysis. Environ Sci Technol. 2004;38(4):1115–23.
Zaruk D, Comba M, Struger J, Young S. Comparison of immunoassay with a conventional method for the determination of Diazinon® in surface waters. Anal Chim Acta. 2001;444(1):163–8.
Garces-Garcia M, Brun EM, Puchades R, Maquieira A. Immunochemical determination of four organophosphorus insecticide residues in olive oil using a rapid extraction process. Anal Chim Acta. 2006;556(2):347–54.
Pogacnik L, Franko M. Determination of organophosphate and carbamate pesticides in spiked samples of tap water and fruit juices by a biosensor with photothermal detection. Biosens Bioelectron. 1999;14(6):569–78.
Mulchandani P, Chen W, Mulchandani A. Flow injection amperometric enzyme biosensor for direct determination of organophosphate nerve agents. Environ Sci Technol. 2001;35(12):2562–5.
Everett WR, Rechnitz GA. Mediated bioelectrocatalytic determination of organophosphorus pesticides with a tyrosinase-based oxygen biosensor. Anal Chem. 1998;70(4):807–10.
Martínez RC, Domínguez FB, Méndez JH, Martín PG. Electroanalytical determination of diazinon: direct current and differential pulse polarography and adsorptive stripping voltammetry. Electroanalysis. 1990;2(7):567–71.
Erdogdu G. A sensitive voltammetric method for the determination of diazinon insecticide. J Anal Chem. 2003;58(6):569–72.
de Albuquerque YDT, Ferreira LF. Amperometric biosensing of carbamate and organophosphate pesticides utilizing screen-printed tyrosinase-modified electrodes. Anal Chim Acta. 2007;596(2):210–21.
Ly SY. Assay of diazinon pesticides in cucumber juice and in the deep brain cells of a live carp. Microchim Acta. 2008;163(3-4):283–8.
Guziejewski D, Skrzypek S, Ciesielski W. Square wave adsorptive stripping voltammetric determination of diazinon in its insecticidal formulations. Environ Monit Assess. 2012;184(11):6575–82.
Arvand M, Vaziri M, Zanjanchi M. Voltammetric characteristics of diazinon on carbon paste electrode modified with tris (ethylenediamine) cobalt (II) iodide. J Anal Chem. 2013;68(5):429–35.
Taillefert M, Rozan TF. Electrochemical Methods for the Environmental Analysis of Trace Elements Biogeochemistry. In: Environmental Electrochemistry. ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, 2002. pp. 2–14. doi:10.1021/bk-2002-0811.ch001.
Milani Hosseini MR, Motaharian A. Electroanalytical determination of diazepam in tablet and human serum samples using a multiwalled carbon nanotube embedded molecularly imprinted polymer-modified carbon paste electrode. RSC Adv. 2015;5(99):81650–9.
Alizadeh T, Zare M, Ganjali MR, Norouzi P, Tavana B. A new molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP)-based electrochemical sensor for monitoring 2, 4, 6-trinitrotoluene (TNT) in natural waters and soil samples. Biosens Bioelectron. 2010;25(5):1166–72.
Alizadeh T, Ganjali MR, Akhoundian M. Fabrication of an Extra Sensitive Voltammetric Sensor Using Nanoparticles of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Determination of Ultra-Trace Promethazine in Plasma Sample. Int J Electrochem Sci. 2012;7:10427–41.
Tokonami S, Shiigi H, Nagaoka T. Review: micro-and nanosized molecularly imprinted polymers for high-throughput analytical applications. Anal Chim Acta. 2009;641(1):7–13.
Wackerlig J, Lieberzeit PA. Molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles in chemical sensing–Synthesis, characterisation and application. Sens Actuator B-Chem. 2015;207:144–57.
Alizadeh T, Ganjali MR, Akhoundian M. Synthesis and application of different nano-sized imprinted polymers for the preparation of promethazine membrane electrodes and comparison of their efficiencies. Int J Electrochem Sci. 2012;7:7655.
Alizadeh T, Akbari A. A capacitive biosensor for ultra-trace level urea determination based on nano-sized urea-imprinted polymer receptors coated on graphite electrode surface. Biosens Bioelectron. 2013;43:321–7.
Li Y, Zhang L, Liu J, Zhou S-F, Al-Ghanim KA, Mahboob S, et al. A novel sensitive and selective electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer on a nanoporous gold leaf modified electrode for warfarin sodium determination. RSC Adv. 2016;6(49):43724–31.
Zamora-Gálvez A, Ait-Lahcen A, Mercante LA, Morales-Narváez E, Amine A, Merkoçi A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Decorated Magnetite Nanoparticles for Selective Sulfonamide Detection. Anal Chem. 2016;88(7):3578–84.
Madrakian T, Haryani R, Ahmadi M, Afkhami A. A sensitive electrochemical sensor for rapid and selective determination of venlafaxine in biological fluids using carbon paste electrode modified with molecularly imprinted polymer-coated magnetite nanoparticles. J Iranian Chem Soc. 2016;13(2):243–51.
Bayat M, Hassanzadeh-Khayyat M, Mohajeri SA. Determination of Diazinon Pesticide Residue in Tomato Fruit and Tomato Paste by Molecularly Imprinted Solid-Phase Extraction Coupled with Liquid Chromatography Analysis. Food Anal Methods. 2015;8(4):1034–41.
Rahiminejad M, Shahtaheri S, Ganjali M, Forushani AR, Golbabaei F. Molecularly imprinted solid phase extraction for trace analysis of diazinon in drinking water. J Environ Health Sci. 2009;6(2):97–106.
Rahiminezhad M, Shahtaheri S, Ganjali M, Koohpaei A, Forushani AR, Golbabaei F. An experimental investigation of the molecularly imprinted polymers as tailor-made sorbents of diazinon. J Anal Chem. 2010;65(7):694–8.
Sanagi MM, Salleh S, Ibrahim WAW, Naim AA. Determination of organophosphorus pesticides using molecularly imprinted polymer solid phase extraction. Malaysian J Anal Sci. 2011;15(2):175–83.
Sanagi MM, Salleh S, Ibrahim WAW, Naim AA, Hermawan D, Miskam M, et al. Molecularly imprinted polymer solid-phase extraction for the analysis of organophosphorus pesticides in fruit samples. J Food Compost Anal. 2013;32(2):155–61.
Wang Y-L, Gao Y-L, Wang P-P, Shang H, Pan S-Y, Li X-J. Sol–gel molecularly imprinted polymer for selective solid phase microextraction of organophosphorous pesticides. Talanta. 2013;115:920–7.
Zhao Y, Ma Y, Li H, Wang L. Composite QDs@ MIP nanospheres for specific recognition and direct fluorescent quantification of pesticides in aqueous media. Anal Chem. 2011;84(1):386–95.
Pieda DC. Acid and base catalysed aqueous hydrolysis of the organophosphorus pesticide, diazinon. Ontario: Queen’s University Kingston; 2001. M.Sc. thesis.
Rezaei B, Foroughi-Dehnavi S, Ensafi AA. Fabrication of electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer and nanoparticles for determination trace amounts of morphine. Ionics. 2015;21(10):2969–80.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of this work by the Electroanalytical Chemistry Research Centre of Iran University of Science and Technology and the Pharmaceutical Research Center of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 323 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Motaharian, A., Motaharian, F., Abnous, K. et al. Molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles-based electrochemical sensor for determination of diazinon pesticide in well water and apple fruit samples. Anal Bioanal Chem 408, 6769–6779 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9802-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9802-7