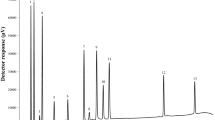
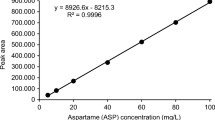
Abstract
A sensitive and inexpensive method involving ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (UA-DLLME) and pre-column derivatization followed by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection (HPLC-FLD) was developed for the analysis of glycyrrhetinic acid. In this work, glycyrrhetinic acid could be obtained by hydrolyzing glycyrrhizic acid to remove glucuronic acid and subsequently extracted by UA-DLLME using chloroform and acetone as the extraction and disperser solvents, respectively. The sample extraction was firstly concentrated to dry under nitrogen and then rapidly derivatized with 2-(12-oxobenzo[b]acridin-5(12H)-yl)-ethyl-4-toluenesulfonate (BAETS) after the UA-DLLME. The prime parameters influencing the UA-DLLME and derivatization procedure were optimized using response surface methodology. Under the optimum conditions, the proposed method has a better linearity in a wider range of 6–300 ng mL−1 and a high square of correlation coefficient (R 2) at 0.9994. Limit of detection and limit of quantification were found to be 1.7 ng mL−1 and 5.8 ng mL−1, respectively. The proposed method was applied to the analysis of glycyrrhetinic acid in liquorice, liquorice apricot and sugar plum samples. For the analysis of the spiked samples, the spiked recoveries were in the range of 90.4–103.0 % with RSD less than 5.18 %. All results demonstrated that the UA-DLLME-HPLC-FLD (ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction-high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection) was a sensitive, accurate, efficient analytical method for the determination of glycyrrhetinic acid.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Kim, S. Lee, B. Kim, E. Lee, J. Ryu, G. Lim, Food Sci. Biotechnol. 9, 447 (2004)
G.R. Fenwick, J. Lutomski, C. Nieman, Food Chem. 38, 119 (1990)
E. İbanoğlu, Ş. İbanoğlu, Food Chem. 70, 333 (2000)
J.R. Hennell, S. Lee, C.S. Khoo, M.J. Gray, A. Bensoussan, J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. Anal. 47, 494 (2008)
P. Montoro, M. Maldini, M. Russo, S. Postorino, S. Piacente, C. Pizza, J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. Anal. 54, 535 (2011)
C.S. Lee, Y.J. Kim, M.S. Lee, E.S. Han, S.J. Lee, Life Sci. 83, 481 (2008)
M.N. Asl, H. Hosseinzadeh, Phytother. Res. 22, 709 (2008)
T.C. Kao, M.H. Shyu, G.C. Yen, J. Agr. Food Chem. 58, 8623 (2010)
W.T. Chung, S.H. Lee, J.D. Kim, N.S. Sung, B. Hwang, S.Y. Lee, C.Y. Yu, H.Y. Lee, Cytotechnology 37, 55 (2001)
J. Li, H. Yu, S. Li, G.J. Wang, J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. Anal. 51, 1147 (2010)
A. Serra, D.E. Uehlinger, P. Ferrari, B. Dick, B.M. Frey, F.J. Frey, B. Vogt, J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 13, 191 (2002)
O. A. Adegoke, L. L. Xiang, O. S. Idowu, D.Y. Chen, Acta. Chromatogr. 24, 445 (2012)
J. You, Y. Fu, Z. Sun, Y. Suo, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 396, 2657 (2010)
G. Li, X. Zhang, J. You, C. Song, Z. Sun, L. Xia, Y. Suo, Anal. Chim. Acta 688, 208 (2011)
N. Jing, G. Li, Z. Sun, J. You, J. Liq. Chromatogr. R. T. 35, 1882 (2012)
C.B. Ojeda, F.S. Rojas, Chromatographia 69, 1149 (2009)
P. Viñas, N. Campillo, I. López-García, M. Hernández-Córdoba, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 406, 2067 (2014)
P. Shakeri, Z.M. Kiasari, M.R. Hadjmohammadi, M.H. Fatemi, J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 11, 1337 (2014)
B. Daneshvand, F. Raofie, J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 12, 1287 (2015)
X. Zang, Q. Wu, M. Zhang, G. Xi, Z. Wang, Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 37, 161 (2009)
P. Hashemi, S. Beyranvand, R.S. Mansur, A.R. Ghiasvand, Anal. Chim. Acta 655, 60 (2009)
P. Rathee, S. Rathee, D. Ahuja, Eurasian. J. Anal. Chem. 5, 95 (2010)
US Department of Health and Human Services, Guidance for industry, bioanalytical method validation 4 (2001)
P. Wang, S.F.Y. Li, H.K. Lee, J. Chromatogr. A 811, 219 (1998)
N.K. Glavač, R. Injac, S. Kreft, Chromatographia 71, 917 (2010)
C. Sabbioni, A. Ferranti, F. Bugamelli, G.C. Forti, M.A. Raggi, Phytochem. Anal. 17, 25 (2006)
Q. Zou, P. Wei, J. Li, Z.X. Ge, P. Ouyang, Biomed. Chromatogr. 23, 5 (2009)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by The National Natural Science Foundation of China (NO. 31301595, NO.21475074 and NO. 21275089), The Scientific Research Fund of Qufu Normal University (xkj201302) and PhD research start-up funds of Qufu Normal University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Jinmao You and Hongliang Wu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
You, J., Wu, H., Li, G. et al. Ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction method combined with HPLC-fluorescence detection for the determination of glycyrrhetinic acid in liquorice and liquorice-derived food products. J IRAN CHEM SOC 13, 359–367 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-015-0744-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-015-0744-3