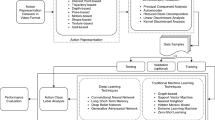
Abstract
Action recognition is a video understanding task that is carried out to recognize an action of an object in a video. In order to recognize the action, it is necessary to extract motion information through temporal modeling. However, videos typically contain high temporal redundancy, such as iterative events and adjacent frames. This high temporal redundancy weakens information related to actual action, making it difficult for the final classifier to recognize the action. In this article, we focus on preserving helpful information for action recognition by reducing the high temporal redundancy in videos. To achieve this goal, we propose a novel frame selection method called cluster-guided frame selection (CluFrame). Specifically, CluFrame compresses an input video into keyframes of clusters discovered by applying \(k\)-means clustering to frame-wise features extracted from pre-trained 2D-CNNs in the temporal compression (TC) module. In addition, CluFrame selects keyframes related to the action of the input video by optimizing the TC module based on the action recognition results. Experimental results on five benchmark datasets demonstrate that CluFrame addresses the high temporal redundancy in the video and achieves action recognition accuracy improvement over existing action recognition methods by up to 6.6% and by about 0.7% compared to state-of-the-art frame selection methods.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that all data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Segal S, Kee E, Luo W, Sadat A, Yumer E, Urtasun R (2020) Universal embeddings for spatio-temporal tagging of self-driving logs. In: proceedings of conference on robot learning (CoRL), Nov. 16–18. Cambridge, MA, USA, pp. 973–983. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2011.06165.
Li C, Chen X (2022) Video prediction for driving scenes with a memory differential motion network model. Appl Intell 53:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03813-9
Bastianelli E, Nardi D, Aiello L-C, Giacomelli F, Manes N (2016) Speaky for robots: the development of vocal interfaces for robotic applications. Appl Intell 44(1):43–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-015-0695-5
Nguyen A, Kanoulas D, Muratore L, Caldwell D-G, Tsagarakis N-G (2018) Translating videos to commands for robotic manipulation with deep recurrent neural networks. In: proceedings of the IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA), May 21–25. Brisbane, QLD, Australia, pp. 3782–3788. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2018.8460857.
Wilson A, Lin M-C (2020) AVOT: audio-visual object tracking of multiple objects for robotics. In: proceedings of the IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA), May 31-Aug. 31. Paris, France, pp. 10045–10051. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA40945.2020.9197528.
Choi S, On K-W, Heo Y-J, Seo A, Jang Y, Lee M, Zhang B-T (2021) DramaQA: character-centered video story understanding with hierarchical QA. In: proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence (AAAI), Feb. 2–9. San Francisco, CA, USA, pp. 1166–1174. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v35i2.16203.
Xiao J, Shang X, Yao A, Chua T-S (2021) Next-qa: Next phase of question-answering to explaining temporal actions. In: proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Jun. 19–25. Nashville, TN, USA, pp. 9777–9786. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00965.
Elharrouss O, Almaadeed N, Al-Maadeed S, Bouridane A, Beghdadi A (2021) A combined multiple action recognition and summarization for surveillance video sequences. Appl Intell 51(2):690–712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-01823-z
He L, Wen S, Wang L, Li F (2021) Vehicle theft recognition from surveillance video based on spatiotemporal attention. Appl Intell 51(4):2128–2143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-01933-8
Wu S, He X, Lu H, Yuille A-L (2010) A unified model of short-range and long-range motion perception. In: advances in neural information processing systems (NIPS), Dec. 6–11. Vancouver, Canada, pp. 2478–2486. https://doi.org/10.5555/2997046.2997172.
Li Y, Ji B, Shi X, Zhang J, Kang B, Wang L (2020) TEA: temporal excitation and aggregation for action recognition. In: proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Jun. 14–19. Seattle, WA, USA, pp. 909–918. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00099.
Karpathy A, Toderici G, Shetty S, Leung T, Sukthankar R, Fei-Fei L (2014) Large-scale video classification with convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Jun. 24–27. Columbus, OH, USA, pp. 1725–1732. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2014.223.
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2014) Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. In: advances in neural information processing systems (NIPS), Dec. 8–13. Montreal, Canada, pp. 568–576. https://doi.org/10.5555/2968826.2968890.
Yue-Hei Ng J, Hausknecht M, Vijayanarasimhan S, Vinyals O, Monga R, Toderici G (2015) Beyond short snippets: deep networks for video classification. In: proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Jun. 7–12. Rockville, MD, USA, pp. 4694–4702. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7299101.
Pers J, Sulic V, Kristan M, Perse M, Polanec K, Kovacic S (2010) Histograms of optical flow for efficient representation of body motion. Pattern Recognit Lett 31(11):1369–1376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2010.03.024
Sun L, Jia K, Chen K, Yeung D-Y, Shi B-E, Savarese S (2017) Lattice long short-term memory for human action recognition. In: proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), Oct. 22–29. Venice, Italy, pp. 2147–2156. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.236.
Shi Y, Tian Y, Wang Y, Huang T (2017) Sequential deep trajectory descriptor for action recognition with three-stream CNN. IEEE Trans Multimedia 19(7):1510–1520
Tran D, Bourdev L, Fergus R, Torresani L, Paluri M, (2015) Learning spatiotemporal features with 3d convolutional networks. In: proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), Dec. 11–18. Santiago, Chile, pp. 4489–4497. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.510.
Wang L, Xiong Y, Wang Z, Qiao Y, Lin D, Tang X, Gool L-V (2016) Temporal segment networks: Towards good practices for deep action recognition. In: proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), Oct. 8–16. Amsterdam, Netherlands, pp. 20–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46484-8_2.
Girdhar R, Ramanan D, Gupta A, Sivic J, Russell B (2017) ActionVLAD: learning spatio-temporal aggregation for action recognition. In: proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Jul. 21–26. Honolulu, HI, USA, pp. 971–980. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.337.
Gao R, Oh T-H, Grauman K, Torresani L (2020) Listen to look: action recognition by previewing audio. In: proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Jun. 14–19. Seattle, WA, USA, pp. 10457–10467. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01047.
Zhu C, Tan X, Zhou F, Liu X, Yue K, Ding E, and Ma Y, (2018) Fine-grained video categorization with redundancy reduction attention. In: proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), Sep. 8–14, Munich, Germany, pp 136–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01228-1_9.
Wu C-Y, Zaheer M, Hu H, Manmatha R, Smola A-J, Krähenbühl P (2018) Compressed video action recognition. In: proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Jun. 18–22, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, pp. 6026–6035. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00631.
Goyal R, Ebrahimi Kahou S, Michalski V, Materzynska J., Westphal S, Kim H, Haenel V, Fruend I, Yianilos P, Mueller-Freitag M, Hoppe F, Thurau C, Bax I, Memisevic R (2017) The “something something” video database for learning and evaluating visual common sense. In: proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Oct. 22–29. Venice, Italy, pp. 5842–5850. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.622.
Mahdisoltani F, Berger G, Gharbieh W, Fleet D, Memisevic R (2018) Fine-grained video classification and captioning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.09235.
Soomro K, Zamir A-R, Shah M (2012) UCF101: a dataset of 101 human actions classes from videos in the wild. arXiv preprint arXiv:1212.0402.
Kay W, Carreira J, Simonyan K, Zhang B, Hillier C, Vijayanarasimhan S, Viola F, Green T, Back T, Natsev P, Suleyman M, Zisserman A (2017) The kinetics human action video dataset. arXiv preprint arXiv:1705.06950.
Caba Heilbron F, Escorcia V, Ghanem B, Carlos Neibles J (2015) ActivityNet: a large-scale video benchmark for human activity understanding. In: proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Jun. 7–12. Rockville, MD, USA, pp. 961–970. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298698.
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G-E (2012) ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: advances in neural information processing systems (NIPS), Dec. 3–8. Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, pp. 84–90. https://doi.org/10.1145/3065386.
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2015) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In: proceedings of the international conference on learning representations (ICLR), May 7–9. San Diego, CA, USA, pp. 1–14. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1409.1556.
Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Vanhoucke V, Rabinovich A (2015) Going deeper with convolutions. In: proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Jun. 7–12. Boston, MA, USA, pp. 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298594.
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Jun. 27–30. Las Vegas, NV, USA, pp. 770–778. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90.
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Identity mappings in deep residual networks. In: proceedings of the european conference on computer vision (ECCV), Oct. 8–16. Amsterdam, Netherlands, pp. 630–645. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46493-0_38.
Tan, M., Le, Q., 2019. EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Jun. 9–15. Long Beach, CA, USA, pp. 6105–6114. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1905.11946.
Liu C, Huang L, Wei Z, Zhang W (2021) Subtler mixed attention network on fine-grained image classification. Appl Intell 51(11):7903–7916. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02280-y
Ji S, Xu W, Yang M, Yu K (2012) 3D convolutional neural networks for human action recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(1):221–231. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2012.59
Donahue J, Anne Hendricks L, Guadarrama S, Rohrbach M, Venugopalan S, Saenko K, Darrell T (2015) Long-term recurrent convolutional networks for visual recognition and description. In: proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Jun. 7–12. Boston, MA, USA, pp. 2625–2634. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298878.
Yao L, Torabi A, Cho K, Ballas N, Pal C, Larochelle H, Courville A (2015) Describing videos by exploiting temporal structure. In: proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), Dec. 11–18. Santiago, Chile, pp. 4507–4515. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.512.
Feichtenhofer C, Pinz A, Zisserman A (2016) Convolutional two-stream network fusion for video action recognition. In: proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Jun. 27–30. Las Vegas, NV, USA, pp. 1933–1941. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.213.
Zhang, J., Zheng, Y., Qi, D., 2017. Deep spatio-temporal residual networks for citywide crowd flows prediction. In: proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence (AAAI), Feb. 2–9. San Francisco, CA, USA, pp. 1166–1174. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v31i1.10735.
Carreira J, Zisserman A (2017) Quo vadis, action recognition? A new model and the kinetics dataset. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Jul. 21–26. Honolulu, HI, USA, pp. 6299–6308. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.502.
Wang X, Girshick R, Gupta A, He K (2018) Non-local neural networks. In: proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Jun. 18–22. Salt Lake City, UT, USA, pp. 7794–7803. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00813.
Yang C, Xu Y, Shi J, Dai B, Zhou B (2020) Temporal pyramid network for action recognition. In: proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Jun. 14–19. Seattle, WA, USA, pp. 591–600. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00067.
Feichtenhofer C, Fan H, Malik J, He K (2019) SlowFast networks for video recognition. In: proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), Oct. 27-Nov. 2. Seoul, South Korea, pp. 6202–6211. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00630.
Tran D, Wang H, Torresani L, Ray J, LeCun Y, Paluri M (2018) A closer look at spatiotemporal convolutions for action recognition. In: proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Jun. 18–22. Salt Lake City, UT, USA, pp. 6450–6459. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00675.
Xie S, Sun C, Huang J, Tu Z, Murphy K (2018) Rethinking spatiotemporal feature learning: speed-accuracy trade-offs in video classification. In: proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), Sep. 8–14. Munich, Germany, pp. 305–321. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01267-0_19.
Tran D, Wang H, Torresani L, Feiszli M (2019) Video classification with channel-separated convolutional networks. In: proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision (ICCV), Oct. 27-Nov. 2. Seoul, South Korea, pp. 5552–5561. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00565.
Lin J, Gan C, Han S (2019) TSM: temporal shift module for efficient video understanding. In: proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision (ICCV), Oct. 27-Nov. 2. Seoul, South Korea, pp. 7083–7093. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00718.
Wang L, Tong Z, Ji B, Wu G (2021) Tdn: temporal difference networks for efficient action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Jun. 19–25. Nashville, TN, USA, pp. 1895–1904. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00193.
Wang P, Liu L, Shen C, Shen H-T (2019) Order-aware convolutional pooling for video based action recognition. Pattern Recognit 91:357–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2019.03.002
Yeung S, Russakovsky O, Mori G, Fei-Fei L (2016) End-to-end learning of action detection from frame glimpses in videos. In: proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Jun. 27–30. Las Vegas, NV, USA, pp. 2678–2687. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.293.
Fan H, Xu Z, Zhu L, Yan C, Ge J, Yang Y (2018) Watching a small portion could be as good as watching all: towards efficient video classification. In: international joint conference on artificial intelligence (IJCAI), Jul. 13–19. Stockholm, Sweden, pp. 705–711
Wu Z, Xiong C, Ma C-Y, Socher R, Davis L-S (2019) AdaFrame: adaptive frame selection for fast video recognition. In: proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Jun. 16–20. Long Beach, CA, USA, pp. 1278–1287. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00137.
Dong W, Zhang Z, Song C, Tan T (2022) Identifying the key frames: an attention-aware sampling method for action recognition. Patt Recognit. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2022.108797
Korbar B, Tran D, Torresani L (2019) SCSampler: sampling salient clips from video for efficient action recognition. In: proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), Oct. 27-Nov. 2. Seoul, South Korea, pp. 6232–6242. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00633
Gowda S-N, Rohrbach M, Sevilla-Lara L (2021) Smart frame selection for action recognition. In: proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence (AAAI), Feb. 2–9. San Francisco, CA, USA, pp. 1451–1459. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v35i2.16235
Lin J (1991) Divergence measures based on the Shannon entropy. IEEE Trans on Inform Theory 37(1):145–151. https://doi.org/10.1109/18.61115
Caron M, Bojanowski P, Joulin A, Douze M (2018) Deep clustering for unsupervised learning of visual features. In: proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), Sep. 8–14, Munich, Germany, pp 132–149. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01264-9_9
Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, Li L-J, Li K, Fei-Fei L (2009) ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Jun. 20–25. Miami, FL, USA, pp. 248–255. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2009.5206848
Teed Z, Deng J, (2020) Raft: recurrent all-pairs field transforms for optical flow. In: proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), Aug. 23–28. Glasgow, UK, pp 402–419. doi https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58536-5_24
Zhou B, Khosla A, Lapedriza A, Oliva A, Torralba A, (2016) Learning deep features for discriminative localization. In: proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Jun. 27–30. Las Vegas, NV, USA, pp 2921–2929. doi https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.319
Acknowledgements
This article is funded by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (Grant No: 2021R1I1A3042145). This research was supported by the MSIT (Ministry of Science and ICT), Korea, under the Grand Information Technology Research Center support program (IITP-2023-2020-0-01462) supervised by the IITP (Institute for Information & communications Technology Planning & Evaluation).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jeong-Hun Kim and Prof. Aziz Nasridinov designed the study. Jeong-Hun Kim performed the bibliographic review, wrote the draft manuscript, and developed the proposed algorithm. Prof. Fei Hao shared his expertise with regard to the overall review of this article. Prof. Aziz Nasridinov and Prof. Carson Leung supervised the entire process.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, JH., Hao, F., Leung, C.KS. et al. Cluster-guided temporal modeling for action recognition. Int J Multimed Info Retr 12, 15 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13735-023-00280-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13735-023-00280-x