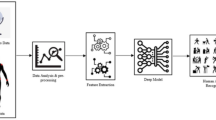
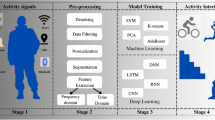
Abstract
Human Action Recognition (HAR) involves human activity monitoring task in different areas of medical, education, entertainment, visual surveillance, video retrieval, as well as abnormal activity identification, to name a few. Due to an increase in the usage of cameras, automated systems are in demand for the classification of such activities using computationally intelligent techniques such as Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL). In this survey, we have discussed various ML and DL techniques for HAR for the years 2011–2019. The paper discusses the characteristics of public datasets used for HAR. It also presents a survey of various action recognition techniques along with the HAR applications namely, content-based video summarization, human–computer interaction, education, healthcare, video surveillance, abnormal activity detection, sports, and entertainment. The advantages and disadvantages of action representation, dimensionality reduction, and action analysis methods are also provided. The paper discusses challenges and future directions for HAR.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABC:
-
Artificial Bee Colony
- ADI:
-
Average Depth Image
- ADL:
-
Activities of Daily Living
- AGC:
-
Adaptive Graph Convolution
- AGCN:
-
Adaptive Graph Convolutional Network
- ANN:
-
Artificial Neural Network
- ARA:
-
Average Recognition Accuracy
- ASAGA:
-
Adaptive Simulated Annealing Genetic Algorithm
- BN:
-
Batch Normalization
- BoVW:
-
Bag of Visual Words
- BPTT:
-
Back-Propagation-Through-Time
- CAE:
-
Convolution Autoencoder
- CHMM:
-
Coupled Hidden Markove Model
- CNN:
-
Convolution Neural Network
- CS:
-
Cross-Subject
- CV:
-
Cross-View
- DBN:
-
Deep Belief Network
- DDI:
-
Depth Difference Image
- DDS:
-
Depth Differential Silhouettes
- DE:
-
Differential Evolution
- DL:
-
Deep Learning
- DMM:
-
Depth Motion Map
- DNN:
-
Deep Neural Network
- DRNN:
-
Differential Recurrent Neural Network
- DT:
-
Decision Tree
- DTW:
-
Dynamic Time Warping
- ELM:
-
Extreme Learning Machine
- FCN:
-
Fully Convolutional Network
- FTP:
-
Fourier Temporal Pyramid
- GA:
-
Genetic Algorithm
- GAN:
-
Generative Adversarial Network
- GDI:
-
Geodesic Distance Iso
- GLCM:
-
Grey Level Co-occurrence Matrix
- GRU:
-
Gated Recurrent Unit
- HAR:
-
Human Action Recognition
- HCI:
-
Human–Computer Interface
- HMM:
-
Hidden Markov Model
- HOF:
-
Histogram of Optical Flow
- HOG:
-
Histogram of Oriented Gradient
- HoMB:
-
Histogram of Motion Boundary
- HoVW:
-
Histogram of Visual Word
- IEF:
-
Iterative Error Feedback
- JDM:
-
Joint Distance Map
- KDA:
-
Kernel Discriminant Analysis
- KELM:
-
Kernel Extreme Learning Machine
- kNN:
-
k-Nearest Neighbor
- KPCA:
-
Kernel PCA
- LBP:
-
Local Binary Pattern
- LBPH:
-
LBP Histogram
- LDA:
-
Linear Discriminant Analysis
- LHMM:
-
Layered Hidden Markove Model
- LOAO:
-
Leave One Actor Out
- LOSO:
-
Leave One Sequence Out
- LSTM:
-
Long Short-Term Memory
- MAP:
-
Mean Average Precision
- MEI:
-
Motion Energy Image
- MHI:
-
Motion History Image
- MiCT:
-
Mixed Convolution Neural Network
- ML:
-
Machine Learning
- MSE:
-
Mean Squared Error
- NBNN:
-
Naïve Bayes Nearest Neighbor
- PCA:
-
Principal Component Analysis
- PCOG:
-
Pyramid Correlogram of Oriented Gradients
- PoF2I:
-
Pose Feature to Image
- PSO:
-
Particle Swarm Optimization
- PSO-WC:
-
PSO-Weight Class
- PSO-WV:
-
PSO-Weight Views
- RBD:
-
Reduced Basis Decomposition
- RBF:
-
Radial Basis Function
- RBM:
-
Restricted Boltzman Machine
- RF:
-
Random Forest
- RNN:
-
Recurrent Neural Network
- ROI:
-
Region of Interest
- RVM:
-
Relevance Vector Machine
- RVM:
-
Relevance Vector Machine
- SDEG:
-
Spatial Edge Distribution of Gradients
- SDK:
-
Software Development Kit
- sDTD:
-
sequential Deep Trajectory Descriptor
- SIFT:
-
Scale Invariant Feature Transform
- SPD:
-
Symmetric Positive Definite
- SSM:
-
Self-Similarity Matrix
- STIP:
-
Space–Time Interest Point
- STM:
-
Spatio-Temporal Matrix
- SVM:
-
Support Vector Machine
- TDD:
-
Two-stream Deep Convolution Descriptor
- TpDD:
-
Trajectory-pooled Deep-Convolutional Descriptor
- TS-GCN:
-
Two-Stream Graph Convolutional Network
- TSN:
-
Temporal Segment Network
- WLNBNN:
-
Weighted Local NBNN
- ZSAR:
-
Zero-Shot Action Recognition
References
Abdul-Azim HA, Hemayed EE (2015) Human action recognition using trajectory-based representation. Egypt Inform J 16(2):187–198
Aggarwal JK, Ryoo MS (2011) Human activity analysis: a survey. ACM Comput Surv (CSUR) 43(3):16
Ahsan U, Sun C, Essa I (2018) Discrimnet: Semi-supervised action recognition from videos using generative adversarial networks. ArXiv preprint arXiv:1801.07230
Akilan T, Wu QJ, Safaei A, Jiang W (2017) A late fusion approach for harnessing multi-CNN model high-level features. In: 2017 IEEE international conference on systems, man, and cybernetics (SMC). IEEE, pp 566–571
Al Machot F, Elkobaisi MR, Kyamakya K (2020) Zero-shot human activity recognition using non-visual sensors. Sensors 20(3):825
Amraee S, Vafaei A, Jamshidi K, Adibi P (2018) Abnormal event detection in crowded scenes using one-class SVM. Signal Image Video Process 12:1115–1123
Angelini F, Fu Z, Long Y, Shao L, Naqvi SM (2019) 2D pose-based real-time human action recognition with occlusion-handling. IEEE Trans Multimedia 22(6):1433–1446
Ar I, Akgul YS (2013) Action recognition using random forest prediction with combined pose-based and motion-based features. In: 2013 8th international conference on electrical and electronics engineering (ELECO). IEEE, pp 315–319
Arifoglu D, Bouchachia A (2017) Activity recognition and abnormal behaviour detection with recurrent neural networks. Procedia Comput Sci 110:86–93
Arunraj M, Srinivasan A, Juliet AV (2018) Online action recognition from RGB-D cameras based on reduced basis decomposition. J Real-Time Image Process 17:341–356
Baccouche M, Mamalet F, Wolf C, Garcia C, Baskurt A (2011) Sequential deep learning for human action recognition. In: International workshop on human behavior understanding. Springer, pp 29–39
Baldi P (2012) Autoencoders, unsupervised learning, and deep architectures. In: Proceedings of ICML workshop on unsupervised and transfer learning, pp 37–49
Berkeley (2014) Multimodal human action dataset. Last Accessed 11 Dec 2019
Bhaumik H, Bhattacharyya S, Nath MD, Chakraborty S (2015) Real-time storyboard generation in videos using a probability distribution based threshold. In: 2015 fifth international conference on communication systems and network technologies (CSNT). IEEE, pp 425–431
Bhoomika Rathod SB, Pandya D, Patel R (2017) A survey on human activity analysis techniques. Int J Future Revolut Comput Sci Commun Eng 3:462–471
Blank M, Gorelick L, Shechtman E, Irani M, Basri R (2005) Actions as space–time shapes. In: Tenth IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV’05) Volume 1, vol 2. IEEE, pp 1395–1402
Bobick AF, Davis JW (2001) The recognition of human movement using temporal templates. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 23(3):257–267
Boiman O, Shechtman E, Irani M (2008) In defense of nearest-neighbor based image classification. In: 2008 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, pp 1–8
Boulgouris NV, Chi ZX (2007) Gait recognition using radon transform and linear discriminant analysis. IEEE Trans Image Process 16(3):731–740
Boulgouris NV, Hatzinakos D, Plataniotis KN (2005) Gait recognition: a challenging signal processing technology for biometric identification. IEEE Signal Process Mag 22(6):78–90
Brand M, Oliver N, Pentland A (1997) Coupled hidden Markov models for complex action recognition. In: Proceedings of the computer vision and pattern recognition, 1997. IEEE, pp 994–999
Bulat A, Tzimiropoulos G (2016) Human pose estimation via convolutional part heatmap regression. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 717–732
Cao J, Lin Z, Huang G-B (2012) Self-adaptive evolutionary extreme learning machine. Neural Process Lett 36(3):285–305
Carreira J, Agrawal P, Fragkiadaki K, Malik J (2016) Human pose estimation with iterative error feedback. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 4733–4742
Castro D, Hickson S, Sangkloy P, Mittal B, Dai S, Hays J, Essa I (2018) Let’s dance: learning from online dance videos. ArXiv preprint arXiv:1801.07388
CGCV-Laboratory (2017) Dongguk activities and actions database. Last Accessed 11 Dec 2019
Chaaraoui AA, Flórez-Revuelta F (2014a) A low-dimensional radial silhouette-based feature for fast human action recognition fusing multiple views. International scholarly research notices, vol 2014
Chaaraoui AA, Flórez-Revuelta F (2014b) Optimizing human action recognition based on a cooperative coevolutionary algorithm. Eng Appl Artif Intell 31:116–125
Chakraborty B, Holte MB, Moeslund TB, Gonzalez J, Roca FX (2011) A selective spatio-temporal interest point detector for human action recognition in complex scenes. In: 2011 IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV). IEEE, pp 1776–1783
Chaquet JM, Carmona EJ, Fernández-Caballero A (2013) A survey of video datasets for human action and activity recognition. Comput Vis Image Underst 117(6):633–659
Chen Y (2015) Reduced basis decomposition: a certified and fast lossy data compression algorithm. Comput Math Appl 70(10):2566–2574
Chen X, Yuille AL (2014) Articulated pose estimation by a graphical model with image dependent pairwise relations. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 1736–1744
Chen C, Jafari R, Kehtarnavaz N (2015a) Improving human action recognition using fusion of depth camera and inertial sensors. IEEE Trans Hum Mach Syst 45(1):51–61
Chen C, Jafari R, Kehtarnavaz N (2015b) Action recognition from depth sequences using depth motion maps-based local binary patterns. In: 2015 IEEE winter conference on applications of computer vision (WACV). IEEE, pp 1092–1099
Chen C, Liu M, Zhang B, Han J, Jiang J, Liu H (2016) 3D action recognition using multi-temporal depth motion maps and fisher vector. In: IJCAI, pp 3331–3337
Chen C, Liu M, Liu H, Zhang B, Han J, Kehtarnavaz N (2017) Multi-temporal depth motion maps-based local binary patterns for 3-D human action recognition. IEEE Access 5:22590–22604
Chintalapati S, Raghunadh M (2013) Automated attendance management system based on face recognition algorithms. In: 2013 IEEE international conference on computational intelligence and computing research (ICCIC). IEEE, pp 1–5
Computer-Vision-Lab (2012) SBU Kinect interaction dataset. Last Accessed 11 Dec 2019
Cortes C, Vapnik V (1995) Support-vector networks. Mach Learn 20(3):273–297
Craley J, Murray TS, Mendat DR, Andreou AG (2017) Action recognition using micro-Doppler signatures and a recurrent neural network. In: 2017 51st annual conference on information sciences and systems (CISS). IEEE, pp 1–5
CRCV (2010) UCF Sports Action dataset. Last Accessed 11 Dec 2019
CRCV (2012) UCF50 dataset. Last Accessed 11 Dec 2019
CRCV (2013) UCF101 dataset. Last Accessed 1 Feb 2020
CRCV (2020) UMN video dataset. Last Accessed 1 Feb 2020
Cutler R, Davis LS (2000) Robust real-time periodic motion detection, analysis, and applications. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 22(8):781–796
Czuszynski K, Ruminski J, Wtorek J (2017) Pose classification in the gesture recognition using the linear optical sensor. In: 2017 10th international conference on human system interactions (HSI). IEEE, pp 18–24
Dai C, Liu X, Lai J, Li P, Chao H-C (2019) Human behavior deep recognition architecture for smart city applications in the 5G environment. IEEE Netw 33(5):206–211
Dalal N, Triggs B, Schmid C (2006) Human detection using oriented histograms of flow and appearance. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 428–441
Das S, Koperski M, Bremond F, Francesca G (2018) Deep-temporal lstm for daily living action recognition. In: 2018 15th IEEE international conference on advanced video and signal based surveillance (AVSS). IEEE, pp 1–6
Das S, Chaudhary A, Bremond F, Thonnat M (2019a) Where to focus on for human action recognition? In: 2019 IEEE winter conference on applications of computer vision (WACV). IEEE, pp 71–80
Das S, Dai R, Koperski M, Minciullo L, Garattoni L, Bremond F, Francesca G (2019b) Toyota smarthome: real-world activities of daily living. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 833–842
De-La-Hoz-Franco E, Ariza-Colpas P, Quero JM, Espinilla M (2018) Sensor-based datasets for human activity recognition: a systematic review of literature. IEEE Access 6:59192–59210
D’Orazio T, Marani R, Renó V, Cicirelli G (2016) Recent trends in gesture recognition: how depth data has improved classical approaches. Image Vis Comput 52:56–72
Duque D, Santos H, Cortez P (2007) Prediction of abnormal behaviors for intelligent video surveillance systems. In: IEEE symposium on computational intelligence and data mining, 2007. CIDM 2007. IEEE, pp 362–367
Everts I, Van Gemert JC, Gevers T (2014) Evaluation of color spatio-temporal interest points for human action recognition. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(4):1569–1580
Feichtenhofer C, Pinz A, Zisserman A (2016) Convolutional two-stream network fusion for video action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1933–1941
Feng Y, Yuan Y, Lu X (2017) Learning deep event models for crowd anomaly detection. Neurocomputing 219:548–556
Fisher PR (2012) CAVIAR dataset. Last Accessed 1 Feb 2020
Foggia P, Percannella G, Saggese A, Vento M (2013) Recognizing human actions by a bag of visual words. In: 2013 IEEE international conference on systems, man, and cybernetics (SMC). IEEE, pp 2910–2915
Foggia P, Saggese A, Strisciuglio N, Vento M (2014) Exploiting the deep learning paradigm for recognizing human actions. In: 2014 11th IEEE international conference on advanced video and signal based surveillance (AVSS). IEEE, pp 93–98
Gan L, Chen F (2013) Human action recognition using APJ3D and random forests. JSW 8(9):2238–2245
Gao J, Zhang T, Xu C (2019) I know the relationships: zero-shot action recognition via two-stream graph convolutional networks and knowledge graphs. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, vol 33, pp 8303–8311
Gavrila DM (1999) The visual analysis of human movement: a survey. Comput Vis Image Underst 73(1):82–98
Gkalelis N, Kim H, Hilton A, Nikolaidis N, Pitas I (2009) The i3DPost multi-view and 3D human action/interaction database. In: 2009 conference for visual media production. IEEE, pp 159–168
Gowda SN (2017) Human activity recognition using combinatorial deep belief networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops, pp 1–6
Guo G, Lai A (2014) A survey on still image based human action recognition. Pattern Recogn 47(10):3343–3361
Gupta JP, Singh N, Dixit P, Semwal VB, Dubey SR (2013) Human activity recognition using gait pattern. Int J Comput Vis Image Process (IJCVIP) 3(3):31–53
Haria A, Subramanian A, Asokkumar N, Poddar S, Nayak JS (2017) Hand gesture recognition for human computer interaction. Procedia Comput Sci 115:367–374
Hassan MM, Uddin MZ, Mohamed A, Almogren A (2018) A robust human activity recognition system using smartphone sensors and deep learning. Future Gener Comput Syst 81:307–313
Herath S, Harandi M, Porikli F (2017) Going deeper into action recognition: a survey. Image Vis Comput 60:4–21
Huang G-B, Zhu Q-Y, Siew C-K (2004) Extreme learning machine: a new learning scheme of feedforward neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE international joint conference on neural networks, 2004, vol 2. IEEE, pp 985–990
Huang Z, Wan C, Probst T, Van Gool L (2017) Deep learning on lie groups for skeleton-based action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 6099–6108
Huang Y, Lai S-H, Tai S-H (2018) Human action recognition based on temporal pose CNN and multi-dimensional fusion. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV)
Huynh-The T, Hua-Cam H, Kim D-S (2019) Encoding pose features to images with data augmentation for 3D action recognition. IEEE Trans Industr Inform 16:3100–3111
Ijjina EP, Chalavadi KM (2016) Human action recoxgnition using genetic algorithms and convolutional neural networks. Pattern Recogn 59:199–212
INRIA (2016) IXMAS dataset. Last Accessed 1 Feb 2020
Iosifidis A, Tefas A, Pitas I (2014) Regularized extreme learning machine for multi-view semi-supervised action recognition. Neurocomputing 145:250–262
Jalal A (2017) IM-daily depth activity dataset. Last Accessed 1 Feb 2020
Jalal A, Kim Y (2014) Dense depth maps-based human pose tracking and recognition in dynamic scenes using ridge data. In: 2014 11th IEEE international conference on advanced video and signal based surveillance (AVSS). IEEE, pp 119–124
Jalal A, Uddin MZ, Kim T-S (2012) Depth video-based human activity recognition system using translation and scaling invariant features for life logging at smart home. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 58:3
Jalal A, Kim Y-H, Kim Y-J, Kamal S, Kim D (2017) Robust human activity recognition from depth video using spatiotemporal multi-fused features. Pattern Recogn 61:295–308
Jhuang H (2013) HMDB dataset. Last Accesed 11 Dec 2019
Ji S, Xu W, Yang M, Yu K (2013) 3D convolutional neural networks for human action recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(1):221–231
Jian M, Zhang S, Wu L, Zhang S, Wang X, He Y (2019) Deep key frame extraction for sport training. Neurocomputing 328:147–156
Jiang Z, Lin Z, Davis L (2012) Recognizing human actions by learning and matching shape-motion prototype trees. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 34(3):533–547
Kalaivani P, Vimala D (2015) Human action recognition using background subtraction method. Int Res J Eng Technol (IRJET) 2(3):1032–1035
Kang SB, Szeliski R (2004) Extracting view-dependent depth maps from a collection of images. Int J Comput Vis 58(2):139–163
Karpathy A (2014) Sports-1M dataset. Last Accessed 11 Dec 2019
Kastaniotis D, Theodorakopoulos I, Theoharatos C, Economou G, Fotopoulos S (2015) A framework for gait-based recognition using Kinect. Pattern Recogn Lett 68:327–335
Kay W, Carreira J, Simonyan K, Zhang B, Hillier C, Vijayanarasimhan S, Viola F, Green T, Back T, Natsev P, et al (2017) The kinetics human action video dataset. ArXiv preprint arXiv:1705.06950
Ke Y, Sukthankar R, Hebert M (2007) Event detection in crowded videos. In: 2007 IEEE 11th international conference on computer vision. IEEE, pp 1–8
Khan ZA, Sohn W (2011) Abnormal human activity recognition system based on R-transform and kernel discriminant technique for elderly home care. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 57:4
Kim SH, Park R-H (2002) An efficient algorithm for video sequence matching using the modified hausdorff distance and the directed divergence. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 12(7):592–596
Kim TS, Reiter A (2017) Interpretable 3D human action analysis with temporal convolutional networks. In: 2017 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops (CVPRW). IEEE, pp 1623–1631
Kim H, Lee S, Kim Y, Lee S, Lee D, Ju J, Myung H (2016) Weighted joint-based human behavior recognition algorithm using only depth information for low-cost intelligent video-surveillance system. Expert Syst Appl 45:131–141
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 1097–1105
Kumar K, Kishore P, Kumar DA, Kumar EK (2018) Indian classical dance action identification using adaboost multiclass classifier on multifeature fusion. In: 2018 conference on signal processing and communication engineering systems (SPACES). IEEE, pp 167–170
Laptev I (2005) On space–time interest points. Int J Comput Vis 64(2–3):107–123
Laptev I (2012) Hollywood2 dataset. Last Accessed 11 Dec 2019
Laptev I, Marszalek M, Schmid C, Rozenfeld B (2008) Learning realistic human actions from movies. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2008. CVPR 2008. IEEE, pp 1–8
Lee LH, Wan CH, Yong TF, Kok HM (2010) A review of nearest neighbor-support vector machines hybrid classification models. J Appl Sci 10:1841–1858
Lee H-Y, Huang J-B, Singh M, Yang M-H (2017) Unsupervised representation learning by sorting sequences. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 667–676
Li W (2017a) MSR daily activity 3D dataset. Last Accessed 11 Dec 2019
Li W (2017b) MSR-action3D dataset. Last Accessed 1 Feb 2020
Li W, Zhang Z, Liu Z (2010) Action recognition based on a bag of 3D points. In: 2010 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition-workshops. IEEE, pp 9–14
Li C, Hou Y, Wang P, Li W (2017a) Joint distance maps based action recognition with convolutional neural networks. IEEE Signal Process Lett 24(5):624–628
Li C, Wang P, Wang S, Hou Y, Li W (2017b) Skeleton-based action recognition using LSTM and CNN. In: 2017 IEEE international conference on multimedia and expo workshops (ICMEW). IEEE, pp 585–590
Li M, Chen S, Chen X, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Tian Q (2019) Actional-structural graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3595–3603
Lim JH, Teh EY, Geh MH, Lim CH (2017) Automated classroom monitoring with connected visioning system. In: Asia-Pacific signal and information processing association annual summit and conference (APSIPA ASC), 2017. IEEE, pp 386–393
Liu DZ (2016) MSR action dataset. Last Accessed 1 Feb 2020
Liu J, Luo J, Shah M (2009) Recognizing realistic actions from videos in the wild. In: 2009 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, pp 1996–2003
Liu L, Shao L, Zhen X, Li X (2013) Learning discriminative key poses for action recognition. IEEE Trans Cybern 43(6):1860–1870
Liu L, Shao L, Li X, Lu K (2016) Learning spatio-temporal representations for action recognition: a genetic programming approach. IEEE Trans Cybern 46(1):158–170
Liu W, Wang Z, Liu X, Zeng N, Liu Y, Alsaadi FE (2017a) A survey of deep neural network architectures and their applications. Neurocomputing 234:11–26
Liu M, Liu H, Chen C (2017b) Enhanced skeleton visualization for view invariant human action recognition. Pattern Recogn 68:346–362
Lu K, Chen J, Little JJ, He H (2018) Lightweight convolutional neural networks for player detection and classification. Comput Vis Image Underst 172:77–87
Mabrouk AB, Zagrouba E (2018) Abnormal behavior recognition for intelligent video surveillance systems: a review. Expert Syst Appl 91:480–491
M. C. Laboratory (2012) DHA video dataset. Last Accessed 1 Feb 2020
Miao Y, Song J (2014) Abnormal event detection based on SVM in video surveillance. In: 2014 IEEE workshop on advanced research and technology in industry applications (WARTIA). IEEE, pp 1379–1383
MICC (2012) Florence 3D actions dataset. Last Accessed 11 Dec 2019
Mika S, Schölkopf B, Smola AJ, Müller K-R, Scholz M, Rätsch G (1999) Kernel PCA and de-noising in feature spaces. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 536–542
Mishra A, Verma VK, Reddy MSK, Arulkumar S, Rai P, Mittal A (2018) A generative approach to zero-shot and few-shot action recognition. In: 2018 IEEE winter conference on applications of computer vision (WACV). IEEE, pp 372–380
MIVIA-Lab (2017) MIVIA Dataset. Last Accessed 11 Dec 2019
Moya Rueda F, Grzeszick R, Fink G, Feldhorst S, ten Hompel M (2018) Convolutional neural networks for human activity recognition using body-worn sensors. In: Informatics, vol 5. Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute, p 26
Murray TS, Mendat DR, Pouliquen PO, Andreou AG (2015) The Johns Hopkins University multimodal dataset for human action recognition. In: Radar sensor technology XIX; and active and passive signatures VI, vol 9461. International Society for Optics and Photonics, p 94611U
NADA (2004) KTH dataset. Last Accessed 1 Feb 2020
Nazir S, Yousaf MH, Velastin SA (2018) Evaluating a bag-of-visual features approach using spatio-temporal features for action recognition. Comput Electr Eng 72:660–669
Neha TK (2020) A review on PSO-SVM based performance measurement on different datasets. Int J Res Appl Sci Eng Technol 8:444–448
Nizam Y, Mohd MNH, Jamil MMA (2017) Human fall detection from depth images using position and velocity of subject. Procedia Comput Sci 105:131–137
Norouzi M, Mikolov T, Bengio S, Singer Y, Shlens J, Frome A, Corrado GS, Dean J (2013) Zero-shot learning by convex combination of semantic embeddings. ArXiv preprint arXiv:1312.5650
Nunes UM, Faria DR, Peixoto P (2017) A human activity recognition framework using max-min features and key poses with differential evolution random forests classifier. Pattern Recogn Lett 99:21–31
Nweke HF, Teh YW, Mujtaba G, Al-Garadi MA (2019) Data fusion and multiple classifier systems for human activity detection and health monitoring: review and open research directions. Inf Fusion 46:147–170
Ohlberger M, Rave S (2015) Reduced basis methods: success, limitations and future challenges. ArXiv preprint arXiv:1511.02021
Oikonomopoulos A, Patras I, Pantic M (2005) Spatiotemporal salient points for visual recognition of human actions. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B Cybern 36(3):710–719
Oliver N, Horvitz E, Garg A (2002) Layered representations for human activity recognition. In: Proceedings of the 4th IEEE international conference on multimodal interfaces. IEEE Computer Society, p 3
Oreifej O, Liu Z (2013) HON4D: Histogram of oriented 4D normals for activity recognition from depth sequences. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 716–723
Pagliari D, Pinto L (2015) Calibration of Kinect for xbox one and comparison between the two generations of microsoft sensors. Sensors 15(11):27569–27589
Panahi L, Ghods V (2018) Human fall detection using machine vision techniques on RGB-D images. Biomed Signal Process Control 44:146–153
Patel CI, Garg S, Zaveri T, Banerjee A, Patel R (2018) Human action recognition using fusion of features for unconstrained video sequences. Comput Electr Eng 70:284–301
Paul M, Haque SM, Chakraborty S (2013) Human detection in surveillance videos and its applications: a review. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process 2013(1):176
Peng X, Zou C, Qiao Y, Peng Q (2014) Action recognition with stacked fisher vectors. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 581–595
Pham HH, Salmane H, Khoudour L, Crouzil A, Velastin SA, Zegers P (2020) A unified deep framework for joint 3D pose estimation and action recognition from a single RGB camera. Sensors 20(7):1825
Popoola OP, Wang K (2012) Video-based abnormal human behavior recognition: a review. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part C Appl Rev 42(6):865–878
Poppe R (2010) A survey on vision-based human action recognition. Image Vis Comput 28(6):976–990
Prasnthi Mandha SVR, Lavanya Devi G (2017) A random forest based classification model for human activity recognition. Int J Adv Sci Technol Eng Manag Sci 3:294–300
Presti LL, La Cascia M (2016) 3D skeleton-based human action classification: a survey. Pattern Recogn 53:130–147
Qi M, Wang Y, Qin J, Li A, Luo J, Van Gool L (2019) stagNet: an attentive semantic RNN for group activity and individual action recognition. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 30:549–565
Qian H, Mao Y, Xiang W, Wang Z (2010) Recognition of human activities using svm multi-class classifier. Pattern Recogn Lett 31(2):100–111
Qin Y, Mo L, Xie B (2017) Feature fusion for human action recognition based on classical descriptors and 3D convolutional networks. In: 2017 eleventh international conference on sensing technology (ICST). IEEE, pp 1–5
Rapid-Rich-Object-Search Lab (2016) NTU RGB+D action recognition dataset. Last Accessed 11 Dec 2019
Razzak MI, Naz S, Zaib A (2018) Deep learning for medical image processing: overview, challenges and the future. In: Classification in BioApps. Springer, pp 323–350
Rensink RA (2000) The dynamic representation of scenes. Vis Cognit 7(1–3):17–42
Robot-Learning-Lab (2017) Cornell activity dataset (CAD-60). Last Accessed 11 Dec 2019
Rodriguez-Galiano VF, Ghimire B, Rogan J, Chica-Olmo M, Rigol-Sanchez JP (2012) An assessment of the effectiveness of a random forest classifier for land-cover classification. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 67:93–104
Ronao CA, Cho S-B (2016) Human activity recognition with smartphone sensors using deep learning neural networks. Expert Syst Appl 59:235–244
Roy Y, Banville H, Albuquerque I, Gramfort A, Falk TH, Faubert J (2019) Deep learning-based electroencephalography analysis: a systematic review. J Neural Eng 16(5):051001
Saini O, Sharma S (2018) A review on dimension reduction techniques in data mining. Comput Eng Intell Syst 9:7–14
Shao L, Ji L, Liu Y, Zhang J (2012) Human action segmentation and recognition via motion and shape analysis. Pattern Recogn Lett 33(4):438–445
Sharma RP, Verma GK (2015) Human computer interaction using hand gesture. Procedia Comput Sci 54:721–727
Sharma S, Kiros R, Salakhutdinov R (2015) Action recognition using visual attention. ArXiv preprint arXiv:1511.04119
Shereena V, David JM (2014) Content based image retrieval: classification using neural networks. Int J Multimedia Appl 6(5):31
Shi Y, Tian Y, Wang Y, Huang T (2017) Sequential deep trajectory descriptor for action recognition with three-stream cnn. IEEE Trans Multimedia 19(7):1510–1520
Shi L, Zhang Y, Cheng J, Lu H (2019) Two-stream adaptive graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 12026–12035
Shotton J, Fitzgibbon A, Cook M, Sharp T, Finocchio M, Moore R, Kipman A, Blake A (2011) Real-time human pose recognition in parts from single depth images. In: CVPR 2011. IEEE, pp 1297–1304
Si C, Chen W, Wang W, Wang L, Tan T (2019) An attention enhanced graph convolutional LSTM network for skeleton-based action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1227–1236
Singh D, Mohan CK (2017) Graph formulation of video activities for abnormal activity recognition. Pattern Recogn 65:265–272
Singh S, Velastin SA, Ragheb H (2010) Muhavi: a multicamera human action video dataset for the evaluation of action recognition methods. In: Seventh IEEE international conference on advanced video and signal based surveillance (AVSS). IEEE, pp 48–55
Song Y, Demirdjian D, Davis R (2011) NATOPS aircraft handling signals database. Last Accessed 11 Dec 2019
Statistical Visual Computing Lab (2014) UCSD anomaly detection dataset. Last Accessed 11 Dec 2019
Sze V, Chen Y-H, Yang T-J, Emer JS (2017) Efficient processing of deep neural networks: a tutorial and survey. Proc IEEE 105(12):2295–2329
Taha A, Zayed HH, Khalifa M, El-Horbaty E-S (2014) Human action recognition based on msvm and depth images. Int J Comput Sci Issues (IJCSI) 11(4):42
Thakkar A, Lohiya R (2020) Attack classification using feature selection techniques: a comparative study. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02167-9
Thi TH, Zhang J, Cheng L, Wang L, Satoh S (2010) Human action recognition and localization in video using structured learning of local space–time features. In: 2010 seventh IEEE international conference on advanced video and signal based surveillance (AVSS). IEEE, pp 204–211
Thomas G, Gade R, Moeslund TB, Carr P, Hilton A (2017) Computer vision for sports: current applications and research topics. Comput Vis Image Underst 159:3–18
Toshev A, Szegedy C (2014) Deeppose: human pose estimation via deep neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1653–1660
Turaga P, Chellappa R, Subrahmanian VS, Udrea O (2008) Machine recognition of human activities: a survey. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 18(11):1473–1488
Ullah A, Muhammad K, Haq IU, Baik SW (2019) Action recognition using optimized deep autoencoder and CNN for surveillance data streams of non-stationary environments. Future Gener Comput Syst 96:386–397
University of Minnesota (2010) Unusual crowd activity dataset. Last Accessed 11 Dec 2019
Varadarajan J, Odobez J-M (2009) Topic models for scene analysis and abnormality detection. In: 2009 IEEE 12th international conference on computer vision workshops (ICCV workshops). IEEE, pp 1338–1345
Veeriah V, Zhuang N, Qi G-J (2015) Differential recurrent neural networks for action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 4041–4049
Vezzani R, Baltieri D, Cucchiara R (2010) Hmm based action recognition with projection histogram features. In: International conference on pattern recognition. Springer, pp 286–293
Vishwakarma DK, Kapoor R (2015) Hybrid classifier based human activity recognition using the silhouette and cells. Expert Syst Appl 42(20):6957–6965
Vishwakarma DK, Kapoor R, Dhiman A (2016) A proposed unified framework for the recognition of human activity by exploiting the characteristics of action dynamics. Robot Auton Syst 77:25–38
Vrigkas M, Nikou C, Kakadiaris IA (2015) A review of human activity recognition methods. Front Robot AI 2:28
Wang Y, Mori G (2009) Human action recognition by semilatent topic models. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 31(10):1762–1774
Wang H, Schmid C (2013) Action recognition with improved trajectories. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 3551–3558
Wang H, Kläser A, Schmid C, Liu C-L (2011) Action recognition by dense trajectories. In: CVPR 2011. IEEE, pp 3169–3176
Wang L, Qiao Y, Tang X (2015) Action recognition with trajectory-pooled deep-convolutional descriptors. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 4305–4314
Wang L, Xiong Y, Wang Z, Qiao Y, Lin D, Tang X, Van Gool L (2016) Temporal segment networks: towards good practices for deep action recognition. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 20–36
Wang P, Cao Y, Shen C, Liu L, Shen HT (2017) Temporal pyramid pooling-based convolutional neural network for action recognition. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 27(12):2613–2622
Wang J, Chen Y, Hao S, Peng X, Hu L (2018) Deep learning for sensor-based activity recognition: a survey. Pattern Recogn Lett 119:3–11
Wang W, Zheng VW, Yu H, Miao C (2019) A survey of zero-shot learning: settings, methods, and applications. ACM Trans Intell Syst Technol (TIST) 10(2):1–37
Wanqing Li XN (2014) Northwestern-UCLA multiview action 3D dataset. Last Accessed 11 Dec 2019
Weimer D, Scholz-Reiter B, Shpitalni M (2016) Design of deep convolutional neural network architectures for automated feature extraction in industrial inspection. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 65(1):417–420
Xia L (2016) UT Kinect-action 3D dataset. Last Accessed 11 Dec 2019
Xia L, Chen C-C, Aggarwal J (2012) View invariant human action recognition using histograms of 3D joints. In: 2012 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops (CVPRW). IEEE, pp 20–27
Xu D, Xiao X, Wang X, Wang J (2016) Human action recognition based on Kinect and PSO-SVM by representing 3D skeletons as points in lie group. In: 2016 international conference on audio, language and image processing (ICALIP). IEEE, pp 568–573
Xu L, Yang W, Cao Y, Li Q (2017) Human activity recognition based on random forests. In: 2017 13th international conference on natural computation, fuzzy systems and knowledge discovery (ICNC-FSKD). IEEE, pp 548–553
YACVID (2014) MuHAVi dataset. Last Accessed 11 Dec 2019
Yamato J, Ohya J, Ishii K (1992) Recognizing human action in time-sequential images using hidden Markov model. In: Proceedings CVPR’92 of the 1992 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 1992. IEEE, pp 379–385
Yang Y, Ramanan D (2012) Articulated human detection with flexible mixtures of parts. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(12):2878–2890
Yang X, Tian Y (2014) Effective 3D action recognition using EigenJoints. J Vis Commun Image Represent 25(1):2–11
Yang X, Zhang C, Tian Y (2012) Recognizing actions using depth motion maps-based histograms of oriented gradients. In: Proceedings of the 20th ACM international conference on Multimedia. ACM, pp 1057–1060
Yan S, Xiong Y, Lin D (2018) Spatial temporal graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In: Thirty-second AAAI conference on artificial intelligence
Yang Y, Hou C, Lang Y, Guan D, Huang D, Xu J (2019) Open-set human activity recognition based on micro-Doppler signatures. Pattern Recogn 85:60–69
Yao A, Gall J, Fanelli G, Van Gool L (2011) Does human action recognition benefit from pose estimation? In: BMVC 2011-proceedings of the British machine vision conference 2011
You D, Hamsici OC, Martinez AM (2010) Kernel optimization in discriminant analysis. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 33(3):631–638
You I, Choo K-KR, Ho C-L et al (2018) A smartphone-based wearable sensors for monitoring real-time physiological data. Comput Electr Eng 65:376–392
Yu M, Yu Y, Rhuma A, Naqvi SM, Wang L, Chambers JA et al (2013) An online one class support vector machine-based person-specific fall detection system for monitoring an elderly individual in a room environment. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 17(6):1002–1014
Zellers R, Choi Y (2017) Zero-shot activity recognition with verb attribute induction. ArXiv preprint arXiv:1707.09468
Zhang Z (2012) Microsoft Kinect sensor and its effect. IEEE Multimedia 19(2):4–10
Zhang X, Yao L, Wang X, Monaghan J, Mcalpine D, Zhang Y (2019a) A survey on deep learning based brain computer interface: recent advances and new frontiers. ArXiv preprint arXiv:1905.04149
Zhang X, Yao L, Wang X, Zhang W, Zhang S, Liu Y (2019b) Know your mind: adaptive cognitive activity recognition with reinforced CNN. In: 2019 IEEE international conference on data mining (ICDM). IEEE, pp 896–905
Zhou X, Zhu M, Pavlakos G, Leonardos S, Derpanis KG, Daniilidis K (2018a) Monocap: monocular human motion capture using a CNN coupled with a geometric prior. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 41(4):901–914
Zhou Y, Sun X, Zha Z-J, Zeng W (2018b) Mict: Mixed 3D/2D convolutional tube for human action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 449–458
Zhu Y, Chen W, Guo G (2014) Evaluating spatiotemporal interest point features for depth-based action recognition. Image Vis Comput 32(8):453–464
Zhu F, Shao L, Xie J, Fang Y (2016a) From handcrafted to learned representations for human action recognition: a survey. Image Vis Comput 55:42–52
Zhu W, Lan C, Xing J, Zeng W, Li Y, Shen L, Xie X et al (2016b) Co-occurrence feature learning for skeleton based action recognition using regularized deep LSTM networks. In: AAAI, vol 2, p 8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pareek, P., Thakkar, A. A survey on video-based Human Action Recognition: recent updates, datasets, challenges, and applications. Artif Intell Rev 54, 2259–2322 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-020-09904-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-020-09904-8