Abstract
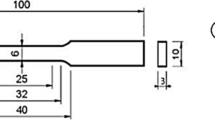
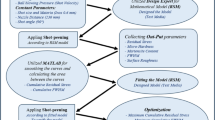
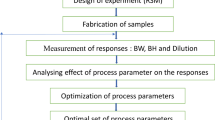
Controlling grain size in stainless steel 304 (SS304) is vital for tailoring its properties for specific applications. In this study, we have employed response surface methodology (RSM) to optimize the processing routes to achieve the desired grain size in SS304 through a combination of cold rolling and annealing. By utilizing the face-centered central composite design of RSM, experimental runs were generated, considering % cold rolling and annealing time as the input factors. Subsequently, based on the experimental runs of RSM, SS304 was subjected to cold rolling to a different extent, followed by annealing at a constant temperature for varying durations. As a result of variation in thermomechanical treatment, steels with various grain sizes were developed which is treated as the output of the experimental runs. An analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted on the experimental data. Findings show a strong correlation between SS304 grain size, cold rolling reduction, and annealing duration. The proposed model precisely predicts grain size evolution, aiding effective thermomechanical processing optimization which could be useful for various thermomechanical processing industries.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.W. Zhang, Z.K. Hei, G. Liu, J. Lu, K. Lu, Formation of nanostructured surface layer on AISI 304 stainless steel by means of surface mechanical attrition treatment. Acta Mater. 51, 1871–1881 (2003)
R.Z. Valiev, T.G. Langdon, Principles of equal-channel angular pressing as a processing tool for grain refinement. Prog. Mater. Sci. 51, 881–981 (2006)
M. Toofaninejad, M.N. Ahmadabadi, Effect of equal channel angular pressing on the microstructure and mechanical properties of AISI type 304 austenitic stainless steel. Adv. Mater. Res. 829, 86–90 (2014)
A.P. Zhilyaev, G.V. Nurislamova, B.-K. Kim, M.D. Baró, J.A. Szpunar, T.G. Langdon, Experimental parameters influencing grain refinement and microstructural evolution during high-pressure torsion. Acta Mater. 51, 753–765 (2003)
Y. Saito, N. Tsuji, H. Utsunomiya, T. Sakai, R.G. Hong, Ultra-fine grained bulk aluminum produced by accumulative roll-bonding (ARB) process. Scr. Mater. 39, 1221–1227 (1998)
M. Tikhonova, Y. Kuzminova, A. Belyakov, R. Kaibyshev, Nanocrystalline S304H austenitic stainless steel processed by multiple forging. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 31, 68–73 (2012)
K.E. Huang, R.E. Logé, A review of dynamic recrystallization phenomena in metallic materials. Mater. Des. 111, 548–574 (2016)
H. Mirzadeh, J.M. Cabrera, A. Najafizadeh, P.R. Calvillo, EBSD study of a hot deformed austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 538, 236–245 (2012)
S. Saadatkia, H. Mirzadeh, J.-M. Cabrera, Hot deformation behavior, dynamic recrystallization, and physically-based constitutive modeling of plain carbon steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 636, 196–202 (2015)
G. Sun, M. Zhao, L. Du, H. Wu, Significant effects of grain size on mechanical response characteristics and deformation mechanisms of metastable austenitic stainless steel. Mater Charact. 184, 111674 (2022)
M.J. Sohrabi, H. Mirzadeh, S. Sadeghpour, R. Mahmudi, Grain size dependent mechanical behavior and TRIP effect in a metastable austenitic stainless steel. Int. J. Plast. 160, 103502 (2023)
D. Maréchal, Linkage between mechanical properties and phase transformations in a 301LN austenitic stainless steel (2011)
M. Naghizadeh, H. Mirzadeh, Effects of grain size on mechanical properties and work-hardening behavior of AISI 304 austenitic stainless steel. Steel Res. Int. 90, 1900153 (2019)
Y. Matsuoka, T. Iwasaki, N. Nakada, T. Tsuchiyama, S. Takaki, Effect of grain size on thermal and mechanical stability of austenite in metastable austenitic stainless steel. ISIJ Int. 53, 1224–1230 (2013)
A. Järvenpää, M. Jaskari, J. Man, L.P. Karjalainen, Austenite stability in reversion-treated structures of a 301LN steel under tensile loading. Mater Charact. 127, 12–26 (2017)
A. Rezaee, A. Kermanpur, A. Najafizadeh, M. Moallemi, H.S. Baghbadorani, Investigation of cold rolling variables on the formation of strain-induced martensite in 201L stainless steel. Mater. Des. 46, 49–53 (2013)
A. Kisko, R.D.K. Misra, J. Talonen, L.P. Karjalainen, The influence of grain size on the strain-induced martensite formation in tensile straining of an austenitic 15Cr-9Mn-Ni-Cu stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 578, 408–416 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2013.04.107
M.C. Somani, P. Juntunen, L.P. Karjalainen, R.D.K. Misra, A. Kyröläinen, Enhanced mechanical properties through reversion in metastable austenitic stainless steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 40, 729–744 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-008-9723-y
V. Shrinivas, S.K. Varma, L.E. Murr, Deformation-induced martensitic characteristics in 304 and 316 stainless steels during room-temperature rolling. Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 26, 661–671 (1995)
K. Tomimura, S. Takaki, Y. Tokunaga, Reversion mechanism from deformation induced martensite to austenite in metastable austenitic stainless steels. ISIJ Int. 31, 1431–1437 (1991)
S. Kheiri, H. Mirzadeh, M. Naghizadeh, Tailoring the microstructure and mechanical properties of AISI 316L austenitic stainless steel via cold rolling and reversion annealing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 759, 90–96 (2019)
M. Zhao, H. Wu, J. Lu, G. Sun, L. Du, Effect of grain size on mechanical property and corrosion behavior of a metastable austenitic stainless steel. Mater Charact. 194, 112360 (2022)
Y. Ma, J.-E. Jin, Y.-K. Lee, A repetitive thermomechanical process to produce nano-crystalline in a metastable austenitic steel. Scr. Mater. 52, 1311–1315 (2005)
M. Eskandari, A. Kermanpur, A. Najafizadeh, Formation of nanocrystalline structure in 301 stainless steel produced by martensite treatment. Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 40, 2241–2249 (2009)
R.D.K. Misra, S. Nayak, S.A. Mali, J.S. Shah, M.C. Somani, L.P. Karjalainen, On the significance of nature of strain-induced martensite on phase-reversion-induced nanograined/ultrafine-grained austenitic stainless steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 41, 3–12 (2010)
G.S. Sun, L.X. Du, J. Hu, H. Xie, H.Y. Wu, R.D.K. Misra, Ultrahigh strength nano/ultrafine-grained 304 stainless steel through three-stage cold rolling and annealing treatment. Mater Charact. 110, 228–235 (2015)
A. Jain, A. Varshney, Effect of grain size and dislocation density on the work hardening behavior of SS 304. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 12, 1–18 (2024)
A. Di Schino, M. Barteri, J.M. Kenny, Effects of grain size on the properties of a low nickel austenitic stainless steel. J. Mater. Sci. 38, 4725–4733 (2003)
A. Di Schino, J.M. Kenny, Grain size dependence of the fatigue behaviour of a ultrafine-grained AISI 304 stainless steel. Mater. Lett. 57, 3182–3185 (2003)
A. Jain, A. Varshney, A critical review on deformation-induced transformation kinetics of austenitic stainless steels. Mater. Sci. Technol. 40, 75–106 (2024)
A. El Hami, P. Pougnet, Embedded Mechatronic Systems 2: Analysis of Failures, Modeling, Simulation and Optimization (Elsevier, New York, 2020)
R.U. Owolabi, M.A. Usman, A.J. Kehinde, Modelling and optimization of process variables for the solution polymerization of styrene using response surface methodology. J. King Saud Univ. Eng. Sci. 30, 22–30 (2018)
M.F. McGuire, Stainless Steels for Design Engineers (ASM International, London, 2008)
C. Nickel, ASM Specialty Handbook (ASM International Materials Park, OH, 2000), pp.44072–44073
G.E. Dieter, D. Bacon, Mechanical Metallurgy (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1976)
H. Abrams, Grain size measurement by the intercept method. Metallography. 4, 59–78 (1971)
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate MANIT Bhopal for arranging the facilities to conduct my research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ashish Jain contributed to writing—original draft, methodology, and data curation; Abhinav Varshney was involved in writing—review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This invited article is part of a special topical focus in the journal Metallography, Microstructure, and Analysis on Quantitative Metallography and Microstructure Modeling.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jain, A., Varshney, A. Optimizing Thermomechanical Processing Routes to Achieve Desired Grain Size in SS 304 Using Response Surface Methodology. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-024-01077-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-024-01077-y