Abstract
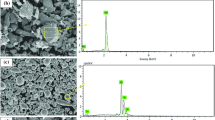
To examine the impact of tin (Sn) element on the microstructure and properties of biomedical β-type Ti-Ni shape memory-based alloys, porous Ti-51 at.%Ni-xSn (x = 0, 0.225, 0.453, and 1.375) alloys were investigated. The microstructure of the Sn-modified and unmodified alloys showed two main regions, viz. Ti- and Ni-rich regions, corresponding to Ti2Ni and TiNi3 phases, plus some intermetallic compounds (Ti3Sn and Sn5Ti6) as Sn was added. The transformation temperature curves of the Ti-Ni and Ti-Ni-xSn samples displayed a multistep phase transformation (β19´ → R → β2) during the heating process. Addition of 0.225 at.% Sn to the Ti-51 at.%Ni sample improved its fracture strength, strain and shape memory behavior, polarization resistance, and antibacterial properties. On the other hand, the antibacterial properties further increased when the Sn content was increased to 0.453 and 1.375 at.%, although the mechanical and shape memory properties were degraded.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Liu, The superelastic anisotropy in a NiTi shape memory alloy thin sheet. Acta Mater. 95, 411–427 (2015)
R. Artiaga et al., DMTA study of a nickel-titanium wire. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 70(1), 199–207 (2002)
L.J. Gibson, The mechanical behaviour of cancellous bone. J. Biomech. 18(5), 317–328 (1985)
A. Nouri, P. Hodgson, C. Wen, Effect of process control agent on the porous structure and mechanical properties of a biomedical Ti–Sn–Nb alloy produced by powder metallurgy. Acta Biomater. 6(4), 1630–1639 (2010)
A. Bansiddhi, T. Sargeant, S. Stupp, D. Dunand, Porous NiTi for bone implants: a review. Acta Biomater. 4(4), 773–782 (2008)
I.P. Lipscomb and L.D. Nokes, in The Application of Shape Memory Alloys in Medicine, ed. I.P. Lipscomb, L.D.M Nokes (Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 1996), p. 154
H. Hosoda, S. Hanada, K. Inoue, T. Fukui, Y. Mishima, T. Suzuki, Martensite transformation temperatures and mechanical properties of ternary NiTi alloys with offstoichiometric compositions. Intermetallics. 6(4), 291–301 (1998)
S. Zlá et al., Determination of thermophysical properties of high temperature alloy IN713LC by thermal analysis. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 110(1), 211–219 (2012)
A. Kapanen, J. Ryhänen, A. Danilov, J. Tuukkanen, Effect of nickel–titanium shape memory metal alloy on bone formation. Biomaterials. 22(18), 2475–2480 (2001)
M. Geetha, A. Singh, R. Asokamani, A. Gogia, Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants–a review. Prog. Mater Sci. 54(3), 397–425 (2009)
K. Otsuka, X. Ren, Physical metallurgy of Ti–Ni-based shape memory alloys. Prog. Mater Sci. 50(5), 511–678 (2005)
A. McKelvey, R. Ritchie, Fatigue-crack propagation in Nitinol, a shape-memory and superelastic endovascular stent material. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 47(3), 301–308 (1999)
J. Li, H. Yang, H. Wang, J. Ruan, Low elastic modulus titanium–nickel scaffolds for bone implants. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 34, 110–114 (2014)
D. Wever, A. Veldhuizen, J. De Vries, H. Busscher, D. Uges, J. Van Horn, Electrochemical and surface characterization of a nickel–titanium alloy. Biomaterials. 19(7), 761–769 (1998)
S.D. Plant, D.M. Grant, L. Leach, Behaviour of human endothelial cells on surface modified NiTi alloy. Biomaterials. 26(26), 5359–5367 (2005)
O. Mockers, D. Deroze, J. Camps, Cytotoxicity of orthodontic bands, brackets and archwires in vitro. Dent. Mater. 18(4), 311–317 (2002)
J. Ryhänen et al., In vivo biocompatibility evaluation of nickel-titanium shape memory metal alloy: Muscle and perineural tissue responses and encapsule membrane thickness. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 41(3), 481–488 (1998)
T. Duerig, A. Pelton, D. Stöckel, An overview of nitinol medical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 273, 149–160 (1999)
P.J.S. Buenconsejo, H.Y. Kim, S. Miyazaki, Effect of ternary alloying elements on the shape memory behavior of Ti–Ta alloys. Acta Mater. 57(8), 2509–2515 (2009)
P.J.S. Buenconsejo, H.Y. Kim, S. Miyazaki, Novel β-TiTaAl alloys with excellent cold workability and a stable high-temperature shape memory effect. Scr. Mater. 64(12), 1114–1117 (2011)
H.Y. Kim, T. Fukushima, P.J.S. Buenconsejo, T.-H. Nam, S. Miyazaki, Martensitic transformation and shape memory properties of Ti–Ta–Sn high temperature shape memory alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 528(24), 7238–7246 (2011)
X. Wu, Q. Peng, J. Zhao, J. Lin, Effect of Sn Content on the Corrosion Behavior of Ti-based Biomedical Amorphous Alloys. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 10, 2045–2054 (2015)
H. Bakhsheshi-Rad et al., Mechanical and bio-corrosion properties of quaternary Mg–Ca–Mn–Zn alloys compared with binary Mg–Ca alloys. Mater. Des. 53, 283–292 (2014)
G. Argade, K. Kandasamy, S. Panigrahi, R. Mishra, Corrosion behavior of a friction stir processed rare-earth added magnesium alloy. Corros. Sci. 58, 321–326 (2012)
N. Iqbal et al., Characterization and biological evaluation of silver containing fluoroapatite nanoparticles prepared through microwave synthesis. Ceram. Int. 41(5), 6470–6477 (2015)
J. Mentz et al., Powder metallurgical processing of NiTi shape memory alloys with elevated transformation temperatures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 491(1), 270–278 (2008)
B. Yuan, X. Zhang, C. Chung, M. Zhu, The effect of porosity on phase transformation behavior of porous Ti–50.8 at.% Ni shape memory alloys prepared by capsule-free hot isostatic pressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 438, 585–588 (2006)
P. Su, S. Wu, The four-step multiple stage transformation in deformed and annealed Ti 49 Ni 51 shape memory alloy. Acta Mater. 52(5), 1117–1122 (2004)
J. Gutiérrez-Moreno, Y. Guo, K. Georgarakis, A. Yavari, G. Evangelakis, C.E. Lekka, The role of Sn doping in the β-type Ti–25at% Nb alloys: Experiment and ab initio calculations. J. Alloys Compd. 615, S676–S679 (2014)
N. Vellios, P. Tsakiropoulos, The role of Sn and Ti additions in the microstructure of Nb–18Si base alloys. Intermetallics. 15(12), 1518–1528 (2007)
I. Gorna et al., Alloys of the Ti-Si-Sn system (titanium corner): phase equilibria, structure, and mechanical properties. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 50(7–8), 452–461 (2011)
M.K. Ibrahim, E. Hamzah, S.N. Saud, E. Nazim, N. Iqbal, A. Bahador, Effect of Sn additions on the microstructure, mechanical properties, corrosion and bioactivity behaviour of biomedical Ti–Ta shape memory alloys. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 131(2), 1165–1175 (2018)
A. Locci, R. Orru, G. Cao, Z.A. Munir, Field-activated pressure-assisted synthesis of NiTi. Intermetallics. 11(6), 555–571 (2003)
B.-Y. Li, L.-J. Rong, Y.-Y. Li, V. Gjunter, A recent development in producing porous Ni–Ti shape memory alloys. Intermetallics. 8(8), 881–884 (2000)
A. Terayama, N. Fuyama, Y. Yamashita, I. Ishizaki, H. Kyogoku, Fabrication of Ti–Nb alloys by powder metallurgy process and their shape memory characteristics. J. Alloys Compd. 577, S408–S412 (2013)
Z. Gao, Q. Li, F. He, Y. Huang, Y. Wan, Mechanical modulation and bioactive surface modification of porous Ti–10Mo alloy for bone implants. Mater. Des. 42, 13–20 (2012)
J. Xu et al., Microstructure, mechanical properties and superelasticity of biomedical porous NiTi alloy prepared by microwave sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 46, 387–393 (2015)
J. Xu et al., Effect of pore sizes on the microstructure and properties of the biomedical porous NiTi alloys prepared by microwave sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 645, 137–142 (2015)
J. Nagels, M. Stokdijk, P.M. Rozing, Stress shielding and bone resorption in shoulder arthroplasty. J. Shoulder Elbow Surg. 12(1), 35–39 (2003)
M. Niinomi, Metallic biomaterials. J. Artif. Organs. 11(3), 105–110 (2008)
T. Ozaki, H. Matsumoto, S. Watanabe, S. Hanada, Beta Ti alloys with low Young’s modulus. Mater. Trans. 45(8), 2776–2779 (2004)
Q.-M. Hu, S.-J. Li, Y.-L. Hao, R. Yang, B. Johansson, L. Vitos, Phase stability and elastic modulus of Ti alloys containing Nb, Zr, and/or Sn from first-principles calculations. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93(12), 121902 (2008)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Ministry of Higher Education of Malaysia and Universiti Teknologi Malaysia for providing financial support under the University Research Grant No. Q.J130000.2524.12H60 and research facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ibrahim, M.K., Saud, S.N., Hamzah, E. et al. In Vitro Microstructure, Shape Memory, Corrosion, and Biocompatibility Characteristics of Porous Ti-51 at.%Ni-xSn Shape Memory Alloys. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 11, 150–157 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-022-00832-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-022-00832-3