Abstract
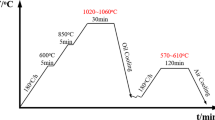
In the present study, the effect of the double quenching–tempering heat treatment on the mechanical properties of the HSLA-100 steel has been investigated. In this regard, the steel studied was first subjected to two consecutive austenitization treatments at 940°C and 870°C for 45 and 30 minutes, respectively, and quenching, followed by tempering in the temperature range of 510°C to 700°C for 60 min, and finally all the samples were cooled in air. Also, to compare the results with the conventional heat treatment cycle of this steel, some samples were subjected to single quenching–tempering. Furthermore, the variations of mechanical properties of HSLA-100 steel and the resultant microstructures were investigated in terms of different tempering conditions. Accordingly, it was found that the double quenching–tempering treatment could create a substantial difference in the total elongation percentage (+24%) of the samples by making minor changes in the strength parameters.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Spanos, R.W. Fonda, R.A. Vandermeer, A. Matuszeski, Microstructural changes in HSLA-100 steel thermally cycled to simulate the heat-affected zone during welding. Metal. Mater. Trans. 26, 3277–3293 (1995)
M. Alkhader, B. Laurence, Large strain mechanical behavior of HSLA-100 Steel over a wide range of strain rates. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 134, 011005 (2012)
High-Strength structural and high strength low alloy steels, properties and selection: Iron, Steels and High Performance alloys, ASM Handbook, ASM International, 1990, pp. 389–423
S.K. Dhua, D. Mukerjee, D.S. Sarma, Influence of thermomechanical treatments on the microstructure and mechanical properties of HSLA-100 steel plates. Metal. Mater. Trans. 34, 241–253 (2003)
S.K. Dhua, D. Mukerjee, D.S. Sarma, Influence of tempering on the microstructure and mechanical properties of HSLA-100 steel plates. Metal. Mater. Trans. 32, 2259–2270 (2001)
M. Mujahid, A.K. Lis, C.I. Garcia, A.J. DeArdo, HSLA-100 steels: influence of aging heat treatment on microstructure and properties. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 7, 247–257 (1998)
S.K. Dhua, D. Mukerjee, D.S. Sarma, Effect of cooling rate on the as-quenched microstructure and mechanical properties of HSLA-100 steel plates. Metal. Mater. Trans. 34, 2493–2504 (2003)
S.K. Dhua, R. Amitava, D.S. Sarma, Effect of tempering temperatures on the mechanical properties and microstructures of HSLA-100 type copper-bearing steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. 318, 197–210 (2001)
P.K. Ray, R.I. Ganguly, A.K. Panda, Optimization of mechanical properties of an HSLA-100 steel through control of heat treatment variables. Mater. Sci. Eng. 346, 122–131 (2003)
S. Sivaprasad, S. Tarafder, V.R. Ranganath, K.K. Ray, Effect of prestrain on fracture toughness of HSLA steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. 284, 195–201 (2000)
S.W. Thompson, D. VinCol, G. Krauss, Continuous cooling transformations and microstructures in a low-carbon, high-strength low-alloy plate steel. Metal. Trans. 21, 1493–1507 (1990)
S.K. Das, S. Sivaprasad, S. Das, S. Chatterjee, S. Tarafder, The effect of variation of microstructure on fracture mechanics parameters of HSLA-100 steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. 431, 68–79 (2006)
Y. Chen, D. Zhang, Y. Liu, H. Li, D. Xu, Effect of dissolution and precipitation of Nb on the formation of acicular ferrite/bainite ferrite in low-carbon HSLA steels. Mater. Charact. 84, 232–239 (2013)
S.K. Dhua, S.K. Sen, Effect of direct quenching on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the lean-chemistry HSLA-100 steel plates. Mater. Sci. Eng. 528, 6356–6365 (2011)
X. Xiong, F. Yang, X. Zou, J. Suo, Effect of twice quenching and tempering on the mechanical properties and microstructures of SCRAM steel for fusion application. J. Nucl. Mater. 430, 114–118 (2012)
Ch. Pandey, M.M. Mahapatra, P. Kumar, P. Kumar, N. Saini, J.G. Thakare, S. Kumar, Study on effect of double austenitization treatment on fracture morphology tensile tested nuclear grade P92 steel. Eng. Fail. Anal. 96, 158–167 (2019)
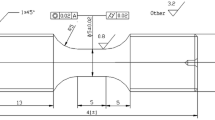
ASTM E8/E8M, Standard test methods for tension testing of metallic materials (2009). https://doi.org/10.1520/E0008_E0008M-09
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shafiei, E., Heydarian, M., Ostovan, F. et al. Effect of Double Quenching–Tempering on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of HSLA-100. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 10, 768–775 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-021-00796-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-021-00796-w