Abstract
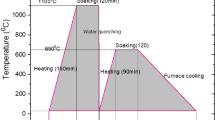
The objective of this work is to evaluate the mechanical properties and immersion corrosion performance of 0.35%C–10.5%Mn steel processed by austenite reverted transformation (ART) annealing process. Microstructure analysis revealed the formation of the well-refined microstructure having martensite (α′) and retained austenite (γ) phases after 4 h of ART-annealing compared to non-heat-treated steel. This phase transformation caused a 50% improvement in total elongation and 42.85% in impact toughness. ART-annealing for 16 h offered an optimum combination of mechanical properties. Immersion corrosion test of 168 h was also performed to evaluate the corrosion performance in a 5% NaCl solution. ART-annealed samples exhibited crack-free, thick and uniform oxide layer with Cl precipitates. ART-annealing for 4 and 16 h produced a porous-structured corrosion product, while 8 and 12 h of ART-annealing produced rod-shaped corrosion product. The performance of the porous-structured corrosion product in inhibiting corrosion mechanism was much better than the rod-shaped corrosion product. The ART-annealing process performed for 16 h exhibited maximum corrosion resistance as evidenced by the lowest value of weight loss (0.64 mg/cm2).









Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Han, Y.K. Lee, The effects of the heating rate on the reverse transformation mechanism and the phase stability of reverted austenite in medium Mn steels. Acta Mater 67, 354–361 (2014)
M. Pourmajidian, J.R. McDermid, On the reactive wetting of a medium-Mn advanced high-strength steel during continuous galvanizing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 357, 418–426 (2019)
Z. Dai, R. Ding, Z. Yang, C. Zhang, H. Chen, Thermo-kinetic design of retained austenite in advanced high strength steels. Acta Mater 152, 288–299 (2018)
Q.S. Allen, T.W. Nelson, Microstructural evaluation of hydrogen embrittlement and successive recovery in advanced high strength steel. J. Mater Process. Technol. 265, 12–19 (2018)
M.A. Paykani, H.R. Shahverdi, R. Miresmaeili, First and third generations of advanced high-strength steels in a FeCrNiBSi system. J. Mater Process. Technol. 238, 383–439 (2016)
W.Q. Cao, C. Wang, J. Shi, M.Q. Wang, W.J. Hui, H. Dong, Microstructure and mechanical properties of Fe–0.2C–5Mn steel processed by ART-annealing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528, 6661–6666 (2011)
M. Bhargava, A. Tewari, S.K. Mishra, Forming limit diagram of advanced high strength steels (AHSS) based on strain-path diagram. Mater. Des. 85, 149–155 (2015)
I. Mejía, G. Altamirano, A.B. Jacuinde, J.M. Cabrera, Modeling of the hot flow behavior of advanced ultra-high strength steels (AUHSS) microalloyed with boron. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 610, 116–125 (2014)
T. Park, L.G. Hector, J.X. Hu, F.A. Farha, M.R. Fellinger, H. Kim, R. Esmaeilpour, F. Pourboghrat, Crystal plasticity modeling of 3rd generation multi-phase AHSS with martensitic transformation. Int. J. Plasticity 120, 1–46 (2019)
A. Srivastava, H.G. Armaki, H. Sung, P. Chen, S. Kumar, A.F. Bower, Micromechanics of plastic deformation and phase transformation in a three-phase TRIP-assisted advanced high strength steel: Experiments and modeling. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 78, 46–69 (2015)
Z.C. Li, H. Ding, R.D.K. Misra, Z.H. Cai, Microstructure mechanical property relationship and austenite stability in medium-Mn TRIP steels: the effect of austenite-reverted transformation and quenching-tempering treatments. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 682, 211–219 (2017)
H. Liu, L.X. Du, J. Hu, H.Y. Wu, X.H. Gao, R.D.K. Misra, Interplay between reversed austenite and plastic deformation in a directly quenched and intercritically annealed 0.04C–5Mn low-Al steel. J. Alloy Compd. 695, 2072–2082 (2017)
D.P. Yang, D. Wu, H.L. Yi, Reverse transformation from martensite into austenite in a medium-Mn steel. Scr. Mater. 161, 1–5 (2019)
Z. Wang, K. Wang, Y. Liu, B. Zhu, Y. Zhang, S. Li, Multi-scale simulation for hot stamping quenching and partitioning process of high-strength steel. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 269, 150–162 (2019)
J. Shi, J. Hu, C. Wang, C.Y. Wang, H. Dong, W. Cao, Ultrafine grained duplex structure developed by ART-annealing in cold rolled medium Mn steels. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 21, 208–214 (2014)
C. Wang, J. Shi, C.Y. Wang, W.J. Hui, M.Q. Wang, H. Dong, W.Q. Cao, Development of ultrafine lamellar ferrite and austenite duplex structure in 0.2C5Mn steel during ART annealing. ISIJ Int. 51, 651–656 (2011)
P. Mahana, N. Prasad, Microstructure evolution of high Mn steel through ART annealing. IJMET 9, 1115–1128 (2018)
L. Zhang, X. Huang, Y. Guo, Y. Wang, J. Gao, G. Dai, Effect of ART-annealing conditions on microstructural regulation and deformation behavior of 0.17C–9Mn–3.5Al TRIP-aided steel. Steel Res. Int. 87, 1–11 (2017)
C. Liu, Z. Zhao, D.O. Northwood, Y. Liu, A new empirical formula for the calculation of MS in pure iron super low alloy steels. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 113, 556–562 (2001)
M.A. Hafeez, A. Farooq, Microstructural, mechanical and tribological investigation of 30CrMnSiNi2A ultra-high strength steel under various tempering temperatures. Mater. Res. Express 5, 016505 (2018)
M.A. Hafeez, A. Farooq, Effect of quenching baths on microstructure and hardness of AISI1035 steel. NJTR 13, 82–88 (2018)
M.A. Hafeez, Effect of microstructural transformation during tempering on mechanical properties of quenched and tempered 38CrSi steel. Mater. Res. Express 6, 086552 (2019)
M.A. Hafeez, A. Farooq, Effect of heat treatments on the mechanical and electrochemical behavior of 38CrSi and AISI 4140 steels. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 8, 479–487 (2019)
M.A. Hafeez, A. Inam, M.A. Arshad, Investigation on microstructural, mechanical, and electrochemical properties of water, brine quenched and tempered low carbon steel. Mater. Res. Express 6, 096524 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab2c7f
G.E. Dieter, Mechanical Metallurgy, 3rd edn. (McGraw–Hill, New York, 2017)
W.D. Callister, J. David, G. Rethwisch, Material Science and Engineering an Introduction, 8th edn. (Wiley, New Jersey, 2009)
X.G. Li, D.W. Zhang, Z.Y. Liu, Z. Li, C.W. Du, C.F. Dong, Materials Science: Share corrosion data. Nature 527, 441–442 (2015)
W. Zhao, Y. Zou, K. Matsuda, Z.D. Zou, Corrosion behaviour of reheated CGHAZ of X80 pipeline steel in H2S-containing environments. Mater. Des. 99, 44–56 (2016)
S. Zhang, H. Zhao, F. Shu, W. He, G. Wang, Microstructure and corrosion behavior of simulated welding HAZ of Q315NS steel in sulfuric acid solution. Metal (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/met7060194
M.A. Hafeez, A. Inam, A. Farooq, Mechanical and corrosion properties of medium carbon low alloy steel after cyclic quenching and tempering heat–treatments. Mater. Res. Express 7, 016553 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hafeez, M.A. Investigation on Mechanical Properties and Immersion Corrosion Performance of 0.35%C–10.5%Mn Steel Processed by Austenite Reverted Transformation (ART) Annealing Process. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 9, 159–168 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-020-00629-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-020-00629-2