Abstract
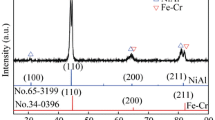
This study aims to investigate the dry sliding wear behavior of Al0.4FeCrNiCox(x = 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0 mol) high-entropy alloys (HEAs) at room temperature by varying sliding speed and normal load. X-ray diffraction studies indicate that the BCC phase decreases and completely disappears as cobalt content increases from x = 0–1.0 mol. Correspondingly, the hardness of the proposed alloys decreases from 377.7 to 199.5 HV with the addition of cobalt content from x = 0–1.0 mol. The wear analysis indicates that the highest specific wear rate occurs in the case of Al0.4FeCrNiCox=1 HEA with varying sliding velocity and normal load, respectively. The worn surface was analyzed by using scanning electron microscopy with attached energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, 3D profiling, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) in order to understand the wear mechanism and oxides formed during the wear process. Results indicated that the wear occurred due to adhesion along with delamination, plastic flow, and oxidative wear. XPS results indicate that the presence of Al2O3, Fe2O3, Cr2O3, and Co3O4 oxides formed on the worn surface.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, S.J. Lin, J.Y. Gan, T.S. Chin, T.T. Shun, C.H. Tsau, S.Y. Chang, Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 6, 299–303 (2004)
J.W. Yeh, Physical metallurgy of high-entropy alloys. JOM 67, 2254–2261 (2015)
B.S. Murty, J.W. Yeh, S. Ranganathan, High-Entropy Alloys, 1st edn. (Elsevier, London, 2014)
D. Kumar, O. Maulik, S. Kumar, Y.V.S.S. Prasad, V. Kumar, Phase and thermal study of equiatomic AlCuCrFeMnW high entropy alloy processed via spark plasma sintering. Mater. Chem. Phys. 210, 71–77 (2017)
A. Munitz, S. Salhov, S. Hayun, N. Frage, Heat treatment impacts the micro-structure and mechanical properties of AlCoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 683, 221–230 (2016)
T.T. Shun, Y.C. Du, Microstructure and tensile behaviors of FCC Al0.3CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 479, 157–160 (2009)
R. Wang, K. Zhang, C. Davies, X. Wu, Evolution of microstructure, mechanical and corrosion properties of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy prepared by direct laser fabrication. J. Alloys Compd. 694, 971–981 (2017)
T.M. Butler, M.L. Weaver, Oxidation behavior of arc melted AlCoCrFeNi multi-component high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 674, 229–244 (2016)
Y. Wang, Y. Yang, H. Yang, M. Zhang, J. Qiao, Effect of nitriding on the tribological properties of Al1.3CoCuFeNi2 high-entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 725, 365–372 (2017)
T.M. Butler, M.L. Weaver, Investigation of the phase stabilities in AlNiCoCrFe high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 691, 119–129 (2016)
W. Chen, Z. Fu, S. Fang, H. Xiao, D. Zhu, Alloying behavior, microstructure and mechanical properties in a FeNiCrCo0.3Al0.7 high entropy alloy. Mater. Des. 51, 854–860 (2013)
S. Fang, W. Chen, Z. Fu, Microstructure and mechanical properties of twinned Al0.5CrFeNiCo0.3C0.2 high entropy alloy processed by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Mater. Des. 54, 973–979 (2014)
G. Qin, W. Xue, C. Fan, R. Chen, L. Wang, Y. Su, H. Ding, J. Guo, Effect of Co content on phase formation and mechanical properties of (AlCoCrFeNi)100–x Cox high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 710, 200–205 (2018)
C.J. Tong, M.R. Chen, S.K. Chen, J.W. Yeh, T.T. Shun, S.J. Lin, S.Y. Chang, Mechanical performance of the AlxCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy system with multiprincipal elements. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 36, 1263–1271 (2005)
C.Y. Hsu, J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, T.T. Shun, Wear resistance and high-temperature compression strength of Fcc CuCoNiCrAl0.5Fe alloy with boron addition. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 35, 1465–1469 (2004)
M.R. Chen, S.J. Lin, J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, Y.S. Huang, M.H. Chuang, Effect of vanadium addition on the microstructure, hardness, and wear resistance of Al0.5CoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 37, 1363–1369 (2006)
M.R. Chen, S.J. Lin, J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, Y.S. Huang, C.P. Tu, Microstructure and properties of Al0.5CoCrCuFeNiTix (x = 0–2.0) high-entropy alloys. Mater. Trans. 47, 1395–1401 (2006)
X. Liu, W. Lei, L. Ma, J. Liu, J. Liu, J. Cui, On the microstructures, phase assemblages and properties of Al0.5CoCrCuFeNiSix high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 630, 151–157 (2015)
Y. Wang, Y. Yang, H. Yang, M. Zhang, S. Ma, J. Qiao, Microstructure and wear properties of nitrided AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 210, 233–239 (2018)
L.M. Du, L.W. Lan, S. Zhu, H.J. Yang, X.H. Shi, P.K. Liaw, J.W. Qiao, Effects of temperature on the tribological behavior of Al0.25CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 35, 917–925 (2019)
L. Ma, L. Wang, Z. Nie, F. Wang, Y. Xue, J. Zhou, T. Cao, Y. Wang, Y. Ren, Reversible deformation-induced martensitic transformation in Al0.6CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy investigated by in situ synchrotron- based high-energy X-ray diffraction. Acta Mater. 128, 12–21 (2017)
Y.F. Kao, T.J. Chen, S.K. Chen, J.W. Yeh, Microstructure and mechanical property of as-cast, -homogenized, and -deformed AlxCoCrFeNi (0 ≤ x≤2) high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 488, 57–64 (2009)
S. Kumar, A. Patnaik, A.K. Pradhan, V. Kumar, Room temperature wear study of Al0.4FeCrNiCox(x = 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0 mol) high-entropy alloys under oil lubricating conditions. J. Mater. Res. 34, 841–853 (2019)
F. He, Z. Wang, Q. Wu, S. Niu, J. Li, J. Wang, C.T. Liu, Solid solution island of the Co–Cr–Fe–Ni high entropy alloy system. Scr. Mater. 131, 42–46 (2017)
M.M. Khruschov, Principles of abrasive wear. Wear 28, 69–88 (1974)
I. Hutching, Tribology; Friction And Wear of Engineering Materials (Elsevier, London, 2017)
G. Rasool, M.M. Stack, Mapping the role of Cr content in dry sliding of steels: comparison between maps for material and counterface. Tribiol. Int. 80, 49–57 (2014)
A. Gaard, N. Hallback, P. Krakhmalev, J. Bergstrom, Temperature effects on adhesive wear in dry sliding contacts. Wear 268, 968–975 (2010)
P.C. Okonkwo, G. Kelly, B.F. Rolfe, M.P. Pereira, The effect of sliding speed on the wear of steel—tool steel pairs. Tribiol. Int. 97, 218–227 (2016)
M.K. Mondal, K. Biswas, J. Maity, Dry sliding wear behaviour of a novel 6351 Al–Al4 SiC4 composite at high loads. Can. Metall. Q. 55, 75–93 (2016)
P. Heilmann, J. Don, T.C. Sun, D.A. Rigney, Sliding wear and transfer. Wear 91, 171–190 (1983)
A.F. Smith, The influenc of surface oxidation and sliding speed on the unlubricated wear of 316 stainless steel at low load. Wear 105, 91–107 (1985)
X. Ji, S.H. Alavi, S.P. Harimkar, Y. Zhang, Sliding wear of spark plasma sintered CrFeCoNiCu high-entropy alloy coatings: effect of aluminum addition. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 27, 5815–5822 (2018)
J.M. Wu, S.J. Lin, J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, Y.S. Huang, H.C. Chen, Adhesive wear behavior of AlxCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloys as a function of aluminum content. Wear 261, 513–519 (2006)
L.D. Conceicao, A.S.C.M. D’Oliveira, The effect of oxidation on the tribolayer and sliding wear of a Co-based coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 288, 69–78 (2016)
E.S. Zanoria, S. Danyluk, M.J. Mcnallan, Formation of cylindrical sliding-wear debris on silicon in humid conditions and elevated temperatures. Tribol. Trans. 38, 721–727 (1995)
A. Zmitrowicz, Wear debris: a review of properties and constitutive models. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 43, 3–35 (2005)
D. Mandal, B.K. Dutta, S.C. Panigrahi, Wear and friction behavior of stir cast aluminium-base short steel fiber reinforced composites. Wear 257, 654–664 (2004)
V. Singh, K. Marchev, C.V. Cooper, E.I. Meletis, Intensified plasma-assisted nitriding of AISI 316L stainless steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 160, 249–258 (2002)
M.R. Andres, A. Conde, J.D. Damborenea, I. Garcia, Friction and wear behaviour of dual phase steels in discontinuous sliding contact conditions as a function of sliding speed and contact frequency. Tribol. Int. 90, 32–42 (2015)
H. So, C.T. Chen, Y.A. Chen, Wear behaviours of laser-clad stellite alloy 6. Wear 192, 78–84 (1996)
I. Velkavrh, F. Ausserer, S. Klien, J. Brenner, P. Foret, A. Diem, The effect of gaseous atmospheres on friction and wear of steel–steel contacts. Tribol. Int. 79, 99–110 (2014)
Acknowledgements
The author is thankful to the Advanced Research Laboratory for Tribology, Department of Mechanical Engineering MNIT Jaipur, Material Research Centre, MNIT Jaipur for carrying out the experimental work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Patnaik, A., Pradhan, A.K. et al. Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of Al0.4FeCrNiCox(x = 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0 mol) High-Entropy Alloys. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 8, 545–557 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-019-00551-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-019-00551-2