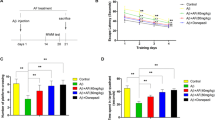
Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), a common cause of neuropsychological impairment, is characterized by the deposition of a neurotoxic and fibrillogenic form of the β-amyloid (Aβ) peptide, Aβ1–42. The present study showed the therapeutic efficacy of Sophorae Fructu (KH034) on Aβ1–42-infused memory dysfunction in mice. KH034 treatment significantly recuperated deficit in learning and memory of the Aβ1–42 –infused mice, as determined by Y-maze and Morris water maze test. Through biochemical analysis test, we suggested that KH034 treatment ameliorated Aβ accumulation and neuronal cell death in the cortex and hippocampus of the mice brain. Furthermore, KH034 treatment enhanced neuron-specific nuclear protein (NeuN) and brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels. Moreover, KH034 treatment activated the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK1/2) and cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) in the hippocampus. Thus, KH034 treatment inhibited the activity of proteins associated with neurodegeneration in AD through its anti-amyloidogenic, anti-inflammatory and pro-survival effect. These results suggest that KH034 treatment improves cognitive function and inhibits amyloidogenesis by the prevention of neuroinflammation in Aβ1–42 –infused mice. Therefore, KH034 may be useful in the prevention and treatment of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arunrungvichian K, Boonyarat C, Fokin VV, Taylor P, Vajragupta O (2015) Cognitive improvements in a mouse model with substituted 1,2,3-triazole agonists for nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. ACS Chem Neurosci 6:1331–1340. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.5b00059
Asai M, Iwata N, Yoshikawa A, Aizaki Y, Ishiura S, Saido TC, Maruyama K (2007) Berberine alters the processing of Alzheimer's amyloid precursor protein to decrease Abeta secretion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 352:498–502. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.11.043
Asuni AA, Guridi M, Pankiewicz JE, Sanchez S, Sadowski MJ (2014) Modulation of amyloid precursor protein expression reduces beta-amyloid deposition in a mouse model. Ann Neurol 75:684–699. doi:10.1002/ana.24149
Azevedo MI et al (2013) The antioxidant effects of the flavonoids rutin and quercetin inhibit oxaliplatin-induced chronic painful peripheral neuropathy. Mol Pain 9:53. doi:10.1186/1744-8069-9-53
Beauquis J, Vinuesa A, Pomilio C, Pavia P, Galvan V, Saravia F (2014) Neuronal and glial alterations, increased anxiety, and cognitive impairment before hippocampal amyloid deposition in PDAPP mice, model of Alzheimer's disease. Hippocampus 24:257–269. doi:10.1002/hipo.22219
Bhaskar K et al (2014) Microglial derived tumor necrosis factor-alpha drives Alzheimer's disease-related neuronal cell cycle events. Neurobiol Dis 62:273–285. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2013.10.007
Chang L et al (2012) Simultaneous determination and pharmacokinetic study of six flavonoids from Fructus Sophorae extract in rat plasma by LC-MS/MS. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 904:59–64. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2012.07.015
Choi DY et al (2012) Obovatol improves cognitive functions in animal models for Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem 120:1048–1059. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07642.x
De Strooper B, Vassar R, Golde T (2010) The secretases: enzymes with therapeutic potential in Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol 6:99–107
Diaz A, Limon D, Chavez R, Zenteno E, Guevara J (2012) Abeta25-35 injection into the temporal cortex induces chronic inflammation that contributes to neurodegeneration and spatial memory impairment in rats. J Alzheimer's Dis: JAD 30:505–522. doi:10.3233/jad-2012-111979
Doody RS (1999) Clinical profile of donepezil in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Gerontology 45(Suppl 1):23–32
Easton A et al (2013) Effects of sub-chronic donepezil on brain Abeta and cognition in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Psychopharmacology 230:279–289. doi:10.1007/s00213-013-3152-3
Garai K, Crick SL, Mustafi SM, Frieden C (2009) Expression and purification of amyloid-beta peptides from Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 66:107–112. doi:10.1016/j.pep.2009.02.009
Glabe CG (2008) Structural classification of toxic amyloid oligomers. J Biol Chem 283:29639–29643. doi:10.1074/jbc.R800016200
Hidaka N, Suemaru K, Takechi K, Li B, Araki H (2011) Inhibitory effects of valproate on impairment of Y-maze alternation behavior induced by repeated electroconvulsive seizures and c-Fos protein levels in rat brains. Acta Med Okayama 65:269–277
Inglis F (2002) The tolerability and safety of cholinesterase inhibitors in the treatment of dementia. Int J Clin Pract Suppl 127:45–63
Jacobsen FM, Comas-Diaz L (1999) Donepezil for psychotropic-induced memory loss. The J Clin Psychiatry 60:698–704
Joo SS, Kang HC, Lee MW, Choi YW, Lee DI (2003) Inhibition of IL-1beta and IL-6 in osteoblast-like cell by isoflavones extracted from Sophorae fructus. Arch Pharm Res 26:1029–1035
Joo SS, Kwon SH, Hwang KW, Lee DI (2005) Improvement of menopausal signs by isoflavones derived from Sophorae fructus in ovariectomized female rats and the antioxidant potentials in BV2 cells. Arch Pharm Res 28:566–572
Kamphuis W et al (2012) GFAP isoforms in adult mouse brain with a focus on neurogenic astrocytes and reactive astrogliosis in mouse models of Alzheimer disease. PLoS One 7:e42823. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0042823
Kim TI et al (2009) L-Theanine, an amino acid in green tea, attenuates beta-amyloid-induced cognitive dysfunction and neurotoxicity: reduction in oxidative damage and inactivation of ERK/p38 kinase and NF-kappaB pathways. Free Radic Biol Med 47:1601–1610. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.09.008
Kim BK, Shin MS, Kim CJ, Baek SB, Ko YC, Kim YP (2014) Treadmill exercise improves short-term memory by enhancing neurogenesis in amyloid beta-induced Alzheimer disease rats. Journal of exercise rehabilitation 10:2-8. doi:10.12965/jer.140086
Kimura Y, Fujita Y, Shibata K, Mori M, Yamashita T (2013) Sigma-1 receptor enhances neurite elongation of cerebellar granule neurons via TrkB signaling. PLoS One 8:e75760. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0075760
Kite GC, Veitch NC, Boalch ME, Lewis GP, Leon CJ, Simmonds MS (2009) Flavonol tetraglycosides from fruits of Styphnolobium japonicum (Leguminosae) and the authentication of Fructus Sophorae and Flos Sophorae. Phytochemistry 70:785–794. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2009.04.003
Kulijewicz-Nawrot M, Verkhratsky A, Chvatal A, Sykova E, Rodriguez JJ (2012) Astrocytic cytoskeletal atrophy in the medial prefrontal cortex of a triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J Anat 221:252–262. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2012.01536.x
Kuperstein F, Yavin E (2002) ERK activation and nuclear translocation in amyloid-beta peptide- and iron-stressed neuronal cell cultures. Eur J Neurosci 16:44–54
Lanz TA, Carter DB, Merchant KM (2003) Dendritic spine loss in the hippocampus of young PDAPP and Tg2576 mice and its prevention by the ApoE2 genotype. Neurobiol Dis 13:246–253. doi:10.1016/s0969-9961(03)00079-2
Lesne S et al (2006) A specific amyloid-beta protein assembly in the brain impairs memory. Nature 440:352–357. doi:10.1038/nature04533
Lim YY et al (2013) BDNF Val66Met, Abeta amyloid, and cognitive decline in preclinical Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 34:2457–2464. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.05.006
Lima Cavendish R et al (2015) Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects of Brazilian red propolis extract and formononetin in rodents. J Ethnopharmacol 173:127–133. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2015.07.022
Liu R et al (2014b) Pinocembrin improves cognition and protects the neurovascular unit in Alzheimer related deficits. Neurobiol Aging 35:1275–1285. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.12.031
Morris R (1984) Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 11:47–60
Mullen RJ, Buck CR, Smith AM (1992) NeuN, a neuronal specific nuclear protein in vertebrates. Development (Cambridge, England) 116:201-211
Pei JJ, Braak H, An WL, Winblad B, Cowburn RF, Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I (2002) Up-regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinases ERK1/2 and MEK1/2 is associated with the progression of neurofibrillary degeneration in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 109:45–55
Prvulovic D, Schneider B (2014) Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic evaluation of donepezil for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 10:1039–1050. doi:10.1517/17425255.2014.915028
Rao AA (2013) Views and opinion on BDNF as a target for diabetic cognitive dysfunction. Bioinformation 9:551–554. doi:10.6026/97320630009551
Rohn TT, Catlin LW, Poon WW (2013) Caspase-cleaved glial fibrillary acidic protein within cerebellar white matter of the Alzheimer's disease brain. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 6:41–48
Salminen A, Kauppinen A, Suuronen T, Kaarniranta K, Ojala J (2009) ER stress in Alzheimer's disease: a novel neuronal trigger for inflammation and Alzheimer's pathology. J Neuroinflammation 6:41. doi:10.1186/1742-2094-6-41
Selkoe DJ (2002) Alzheimer's disease is a synaptic failure. Science (New York, NY) 298:789-791. doi:10.1126/science.1074069
Shim JG et al (2005) Bone loss preventing effect of Sophorae Fructus on ovariectomized rats. Arch Pharm Res 28:106–110
Takeda S, Hashimoto T, Roe AD, Hori Y, Spires-Jones TL, Hyman BT (2013) Brain interstitial oligomeric amyloid beta increases with age and is resistant to clearance from brain in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. FASEB J Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 27:3239–3248. doi:10.1096/fj.13-229666
Vorhees CV, Williams MT (2006) Morris water maze: procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of learning and memory. Nat Protoc 1:848–858. doi:10.1038/nprot.2006.116
Walker Z et al (2002) Differentiation of dementia with Lewy bodies from Alzheimer's disease using a dopaminergic presynaptic ligand. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 73:134–140
Weyer A, Schilling K (2003) Developmental and cell type-specific expression of the neuronal marker NeuN in the murine cerebellum. J Neurosci Res 73:400–409. doi:10.1002/jnr.10655
Zhang Z et al (2014) 7,8-dihydroxyflavone prevents synaptic loss and memory deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Neuropsychopharmacology: Off Publ Am Coll Neuropsychopharmacology 39:638–650. doi:10.1038/npp.2013.243
Zhu QW, Tang H, Hou WJ (2002) [effects of wide band frequency noise on ERK, GDNF and ABR threshold in the different area of brain of AD rats poisoned by glutamatic acid]. Zhongguo ying yong sheng li xue za zhi = Zhongguo yingyong shenglixue zazhi = Chinese journal of applied physiology 18:324-328
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea(NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning(NRF-2013R1A1A1063477).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Statement
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the the Kyung Hee University Medical Center Institutional Animal Care (approver number; KHMC-IACUC 2015–31).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, HY., Kwon, Y. & Cho, SH. Protective effects of the Sophorae Fructus on cognitive impairment and neuroinflammatory alteration in an Aβ1-42-infused Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Orient Pharm Exp Med 17, 255–268 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-017-0267-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-017-0267-9