Abstract
Context
Understanding the effects of exogenous factors on tree development is of major importance in the current context of global change. Assessing the structure development of trees is difficult given that they are large and complex organisms with lifespan of several decades.
Aims
We used a retrospective analysis to derive the ontogenetic trends in silver fir development and assess the effects of climate or light environment on tree architecture.
Methods
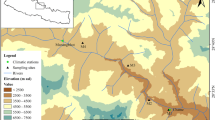
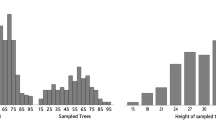
Thanks to the identification of relevant growth markers (bud cataphylls and pseudo-whorl branches), a retrospective analysis allowed to record annual shoot extension and to date them on silver firs of various sizes under different environmental conditions.
Results
The length of successive annual shoots located on different axes clearly show gradual trends related to the physiological age of meristems. Within- and between-tree variations are noted due to the plasticity of development and growth induced by light environment and climate.
Conclusion
Retrospective analysis is an efficient method for getting information on the history of trees architecture and subsequently to relate it to environmental factors.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barthélémy D, Caraglio Y (2007) Plant architecture: a dynamic, multilevel and comprehensive approach to plant form, structure and ontogeny. Ann Bot 99:375–407
Barthélémy D, Caraglio Y, Sabatier S (2010) Crown architecture of valuable broadleaved species. In: Spiecker H, Hein S, Makkonen-Spiecker K, Thies M (eds) Valuable broadleaved forests in Europe. Leyde, Brill, pp 87–101
Bonan GB (2008) Forests and climate change: forcings, feedbacks, and the climate benefits of forests. Science 320:1444–1449
Bontemps J, Herve J, Dhote J (2009) Long-term changes in forest productivity: a consistent assessment in even-aged stands. For Sci 55:549–564
Cailleret M (2011) Causes fonctionnelles du dépérissement et de la mortalité du sapin pectiné en Provence, PhD thesis. University of Aix-Marseille III, Avignon, France
Cailleret M, Davi H (2010) Effects of climate on diameter growth of co-occurring Fagus sylvatica and Abies alba along an altitudinal gradient. Trees 25:265–276
Caraglio Y, Rigolot E, Pimont F (2007) Pinus halepensis Mill. Architectural analysis for fuel modelling. Proceedings of the international workshop MEDPINE. pp 43–59
Charles-Dominique T, Mangenet T, Rey H et al (2009) Architectural analysis of root system of sexually vs. vegetatively propagated yam (Dioscorea rotundata Poir.), a tuber monocot. Plant Soil 317:61–77
Chaubert-Pereira F, Caraglio Y, Lavergne C, Guédon Y (2009) Identifying ontogenetic, environmental and individual components of forest tree growth. Ann Bot 104:883–896
Cienciala E, Cerny M, Tatarinov F et al (2006) Biomass functions applicable to Scots pine. Trees 20:483–495
De Kroon H, Visser EJW, Huber H et al (2009) A modular concept of plant foraging behaviour: the interplay between local responses and systemic control. Plant Cell Environ 32:704–712
Delagrange S, Montpied P, Dreyer E et al (2006) Does shade improve light interception efficiency? A comparison among seedlings from shade-tolerant and -intolerant temperate deciduous tree species. New Phytol 172:293–304
Drobyshev I, Overgaard R, Saygin I et al (2010) Masting behaviour and dendrochronology of European beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) in southern Sweden. For Ecol Manag 259:2160–2171
Dulamsuren C, Hauck M, Leuschner HH, Leuschner C (2011) Climate response of tree-ring width in Larix sibirica growing in the drought-stressed forest-steppe ecotone of northern Mongolia. Ann For Sci 68:275–282
Dyer M, Bailey R (1987) A test of 6 methods for estimating true heights from stem analysis data. For Sci 33:3–13
Edelin C (1977) Images de l’architecture des conifères, PhD thesis. Université de Montpellier II, Montpellier
Everett RG (2008) Dendrochronology-based fire history of mixed-conifer forests in the San Jacinto Mountains, California. For Ecol Manag 256:1805–1814
Frazer G, Canham C, Lertzman K (1999) Gap Light Analyzer (GLA): imaging software to extract canopy structure and gap light transmission indices from true-colour fisheye photographs, user’s manual and program documentation. Simon Fraser University, Burnaby
Godin C, Caraglio Y (1998) A multiscale model of plant topological structures. J Theor Biol 191:1–46
Hallé F, Martin R (1968) Etude de la croissance rythmique chez l’Hévéa (Hevea brasiliensis Müll.-Arg. Euphorbiacées-Crotonoïdées). Adansonia 8:475–503
Heuret P, Guédon Y, Guérard N, Barthélémy D (2003) Analysing branching pattern in plantations of young red oak trees (Quercus rubra L., Fagaceae). Ann Bot 91:479–492
Heuret P, Meredieu C, Coudurier T et al (2006) Ontogenetic trends in the morphological features of main stem annual shoots of Pinus pinaster (Pinaceae). Am J Bot 93:1577–1587
Jourdan C, Rey H (1997) Architecture and development of the oil-palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq) root system. Plant Soil 189:33–48
Kariuki M (2002) Height estimation in complete stem analysis using annual radial growth measurements. Forestry 75:63–74
Kawamura K (2010) A conceptual framework for the study of modular responses to local environmental heterogeneity within the plant crown and a review of related concepts. Ecol Res 25:733–744
Kelty M (2006) The role of species mixtures in plantation forestry. For Ecol Manag 233:195–204
Lehtonen A, Makipaa R, Heikkinen J et al (2004) Biomass expansion factors (BEFs) for Scots pine, Norway spruce and birch according to stand age for boreal forests. For Ecol Manag 188:211–224
Linares JC, Camarero JJ, Carreira JA (2010) Competition modulates the adaptation capacity of forests to climatic stress: insights from recent growth decline and death in relict stands of the Mediterranean fir Abies pinsapo. J Ecology 98:592–603
Metsaranta J, Lieffers V (2009) Using dendrochronology to obtain annual data for modelling stand development: a supplement to permanent sample plots. Forestry 82:163–173
Pradal C, Dufour-Kowalski S, Boudon F et al (2008) OpenAlea: a visual programming and component-based software platform for plant modelling. Funct Plant Biol 35:751–760
Rey H, Godin C, Guédon Y (1997) Vers une représentation formelle des plantes. In: Bouchon J, De Reffye P, Barthélémy D (eds) Modélisation et simulation de l’architecture des végétaux, INRA éditions. INRA éditions, Paris, pp 139–174
Richardson S, Smale M, Hurst J et al (2009) Large-tree growth and mortality rates in forests of the central North Island, New Zealand. New Zealand J Ecol 33:208–215
Robakowski P, Wyka T, Samardakiewicz S, Kierzkowski D (2004) Growth, photosynthesis, and needle structure of silver fir (Abies alba Mill.) seedlings under different canopies. For Ecol Manag 201:211–227
Rutishauser E, Barthélémy D, Blanc L, Nicolini E (2011) Crown fragmentation assessment in tropical trees: method, insights and perspectives. For Ecol Manag 261:400–407
Sabatier S, Baradat Ph, Barthélémy D (2003) Intra- and interspecific variations of polycyclism in young trees of Cedrus atlantica (Endl.) Manetti ex. Carrière and Cedrus libani A. Rich (Pinaceae). Ann For Sci 60:19–29
Sato H, Itoh A, Kohyama T (2007) SEIB-DGVM: a new dynamic global vegetation model using a spatially explicit individual-based approach. Ecol Modell 200:279–307
Saulnier M, Edouard JL, Corona C, Guibal F (2011) Climate/growth relationships in a Pinus cembra high-elevation network in the Southern French Alps. Ann For Sci 68:189–200
Schenk HJ (1996) Modeling the effects of temperature on growth and persistence of tree species: a critical review of tree population models. Ecol Modell 92:1–32
Schweingruber FH (1996) Tree rings and environment: dendroecology. Paul Haupt AG Bern, Switzerland
Stoffel M, Bollschweiler M (2008) Tree-ring analysis in natural hazards research—an overview. Nat Hazard Earth Sys 8:187–202
Taugourdeau O, Chaubert-Pereira F, Sabatier S, Guédon Y (2011) Deciphering the developmental plasticity of walnut saplings in relation to climatic factors and light environment. J Exp Bot 62:5283–5296
Thabeet A, Vennetier M, Gadbin-Henry C et al (2009) Response of Pinus sylvestris L. to recent climatic events in the French Mediterranean region. Trees 23:843–853
Yagi T (2009) Ontogenetic strategy shift in sapling architecture of Fagus crenata in the dense understorey vegetation of canopy gaps created by selective cutting. Can J For Res 39:1186–1196
Zalamea P, Stevenson P, Madrinan S et al (2008) Growth pattern and age determination for Cecropia sciadophylla (Urticaceae). Am J Bot 95:263–271
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Pierre Cretin-Maitenaz, Michäel Guéroult and URFM technical team for their help in collecting field data, to MéteoFrance for providing meteorological data, to François de Coligny, the handling editor and an anonymous reviewer for their helpful comments that led to an improvement in the presentation of this paper.
Funding
OT was funded by a French Ministry of Research PhD grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Gilbert Aussenac
Contribution of the co-authors
Article writing: OT, JD, SS, YC; analysis: OT, software development: SG, supervision: JD, SS, YC, and DB
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taugourdeau, O., Dauzat, J., Griffon, S. et al. Retrospective analysis of tree architecture in silver fir (Abies alba Mill.): ontogenetic trends and responses to environmental variability. Annals of Forest Science 69, 713–721 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13595-012-0188-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13595-012-0188-1