Abstract
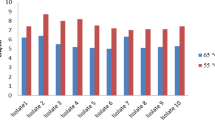
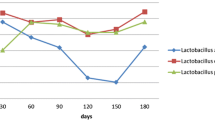
The market of cheeses from ewe’s milk has been growing steadily in Argentina. The nutritional benefits of these products can be enhanced by adding probiotic cultures. In the present study, the survival of a mix of probiotic microorganisms (Lactobacillus acidophilus La-5 and Bifidobacterium animalis ssp. lactis Bb12) in a semi-hard ovine cheese, manufactured with a technology previously developed in our institute was evaluated. Besides, the effect of its incorporation on the chemical composition and ripening parameters of cheeses, including the fatty acid composition and CLA production, was investigated. Experimental cheeses made with Bb12 and La-5 retained counts of the probiotic strains at the required therapeutic level (107 CFU g−1). No significant differences were detected between experimental and control cheeses with respect to the different parameters evaluated: gross composition, nitrogen fractions, lipolysis, fatty acids profiles of cheese fat including CLA, and volatile fraction. Results demonstrated that the ovine cheese matrix seems to be suitable for delivery of probiotic microorganisms.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-Salam M, El-Shibiny S (2012) Conjugated linoleic acid and vaccenic acid contents in cheeses: an overview from the literature. J Food Compos Anal. doi:10.1016/j.jfca.2012.08.004
Abd El-Salam M, Hippen A, Assem F, El-Shafei K, Tawfik N, El-Aassar M (2011) Preparation and properties of probiotic cheese high in conjugated linoleic acid content. Int J Dairy Technol 64:64–74
Albenzio M, Santillo A, Caroprese M, Marino R, Trani A, Faccia M (2010) Biochemical patterns in ovine cheese: influence of probiotic strains. J Dairy Sci 93:3487–3496
Albenzio M, Santillo A, Caroprese M, Ruggieri D, Napolitano F, Sevi A (2013) Physicochemical properties of Scamorza ewe milk cheese manufactured with different probiotic cultures. J Dairy Sci 96:2781–2791
Bergamini C, Hynes E, Meinardi C, Suarez V, Quiberoni A, Zalazar C (2010a) Pategrás cheese as a suitable carrier for six probiotic cultures. J Dairy Res 77:265–272
Bergamini C, Wolf I, Perotti M, Zalazar C (2010b) Characterization of biochemical changes during ripening in Argentinean sheep cheeses. Small Rumin Res 94:79–89
Brearty S, Ross R, Fitzgerald G, Collins J, Wallace J, Stanton C (2001) Influence of two commercially available bifidobacteria cultures on Cheddar cheese quality. Int Dairy J 11:599–610
Buriti F, da Rocha J, Saad S (2005) Incorporation of Lactobacillus acidophilus in Minas fresh cheese and its implications for textural and sensorial properties during storage. Int Dairy Sci 15:1279–1288
Candioti M, Bergamini C, Palma S, Busetti M, Meinardi C, Zalazar C (2010) Characterisation of proteolysis profile of Argentinean sheep cheeses made by two different production methods. J Sci Food Agric 90:36–42
Coakley M, Ross R, Nordgren M, Fitzgerald G, Devery R, Stanton C (2003) Conjugated linoleic acid biosynthesis by human-derived Bifidobacterium species. J Appl Microbiol 94:138–145
Collins Y, McSweeney P, Wilkinson M (2003) Lipolysis and free fatty acid catabolism in cheese: a review of current knowledge. Int Dairy J 13:841–866
Comunian R, Paba A, Daga E, Dupré I, Scintu M (2010) Traditional and innovative production methods of Fiore Sardo cheese: a comparison of microflora with a PCR-Culture Technique. Int J Dairy Technol 63:224–233
Corbo M, Albenzio M, De Angelis M, Sevi A, Gobbetti M (2001) Microbiological and biochemical properties of Canestrato Pugliese hard cheese supplemented with Bifidobacteria. J Dairy Sci 84:551–561
De Jong C, Badings H (1990) Determination of free fatty acids in milk and cheese. Procedures for extraction, clean up, and capillary gas chromatographic analysis. J High Resol Chromatogr 13:94–98
Di Cagno R, Banks E, Sheehan L, Fox P, Brechany E, Corsetti A, Gobbetti M (2003) Comparison of the microbiological, compositional, biochemical, volatile profile and sensory characteristics of three Italian PDO ewe’s milk cheeses. Int Dairy J 13:961–972
dos Santos K, Bomfima M, Vieira A, Benevides S, Saad S, Buriti F, Egito A (2012) Probiotic caprine Coalho cheese naturally enriched in conjugated linoleic acid as a vehicle for Lactobacillus acidophilus and beneficial fatty acids. Int Dairy J 24:107–112
Gomes A, Braga S, Cruz A, Cadena R, Lollo P, Carvalho C, Amaya-Farfán J, Faria J, Bolini H (2011) Effect of the inoculation level of Lactobacillus acidophilus in probiotic cheese on the physicochemical features and sensory performance compared with commercial cheeses. J Dairy Sci 94:4777–4786
Gripon JC, Desmazeaud M, Le Bars D, Bergère J (1975) Etude du rôle des micro-organismes et des enzymes au cours de la maturation des fromages. II Influence de la présure commerciale. Lait 55:502–516
Hernandez I, Barron L, Virto M, Perez-Elortondo F, Flanagan C, Rozas U, Najera A, Albisu M, Vicente M, de Renobales M (2009) Lipolysis, proteolysis and sensory properties of ewe’s raw milk cheese (Idiazabal) made with lipase addition. Food Chem 116:158–166
International Dairy Federation (IDF) (1982) Cheese and processed cheese. Determination of total solid content. IDF Standard 4A
International Dairy Federation (IDF) (1993) Determination de la teneur en azote total nitrogen (NT) (Kjeldhal method). IDF Standard 20B
International Dairy Federation (IDF) (1996) Milk and milk products preparation of samples and dilutions for microbiological examination. IDF Standard 122 C
International Dairy Federation (IDF) (1999) Milk fat preparation of fatty acid methyl esters. IDF Standard 182
International Dairy Federation (IDF) (2001) Milk and Milk products—extraction methods for lipids and liposoluble compounds. IDF Standard 172
Irigoyen A, Ortigosa M, Juansaras I, Oneca M, Torre P (2007) Influence of an adjunct culture of Lactobacillus on the free amino acids and volatile compounds in a Roncal-type ewe’s-milk cheese. Food Chem 100:71–80
Isolini D, Grand M, Glattli H (1990) Selective media for the enumeration of obligately and facultatively heterofermentative lactobacilli. Schweiz Milchwirtschaft Forschung 19:57–59
Jiang J, Bjoerck L, Fonden R, Emanuelson M (1996) Occurrence of conjugated cis-9, trans-11-Octadecadienoic acid in bovine milk: effects of feed and dietary regimen. J Dairy Sci 79:438–445
Kılıç G, Kuleaşan H, Eralp I, Karahan A (2009) Manufacture of Turkish Beyaz cheese added with probiotic strains. LWT Food Sci Technol 42:1003–1008
Mannu L, Comunian R, Scintu MF (2000) Mesophilic lactobacilli in Fiore Sardo cheese: PCR-identification and evolution during cheese ripening. Int Dairy J 10:383–389
McSweeney P, Sousa M (2000) Biochemical pathways for the production of flavour compounds in cheeses during ripening: a review. Lait 80:293–324
Ong L, Henriksson A, Shah N (2006) Development of probiotic Cheddar cheese containing Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lb. casei, Lb. paracasei and Bifidobacterium spp. and the influence of these bacteria on proteolytic patterns and production of organic acid. Int Dairy J 16:446–456
Ong L, Henriksson A, Shah N (2007) Proteolytic pattern and organic acid profiles of probiotic Cheddar cheese as influenced by probiotic strains of Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lb. paracasei, Lb. casei or Bifidobacterium sp. Int Dairy J 17:67–78
Özer B, Kirmaci H, Senel E, Atamer M, Hayaloğlu A (2009) Improving the viability of Bifidobacterium bifidum BB-12 and Lactobacillus acidophilus LA-5 in white-brined cheese by microencapsulation. Int Dairy J 19:22–29
Reid G (2008) Probiotics and prebiotics—progress and challenges. Review. Int Dairy J 18:969–975
Santillo A, Albenzio M (2008) Influence of lamb rennet paste containing probiotic on proteolysis and rheological properties of Pecorino cheese. J Dairy Sci 91:1733–1742
Santillo A, Albenzio M, Quinto M, Caroprese M, Marino R, Sevi A (2009) Probiotic in lamb rennet paste enhances rennet lipolytic activity, and conjugated linoleic acid and linoleic acid content in Pecorino cheese. J Dairy Sci 92:1330–1337
Santillo A, Albenzio M, Bevilacqua A, Corbo M, Sevi A (2012) Encapsulation of probiotic bacteria in lamb rennet paste: effects on the quality of Pecorino cheese. J Dairy Sci 95:3489–3500
Saxelin M, Korpela R, Mäyrä-Mäkinen A (2003) In: Smith G (ed) Dairy processing. Improving quality. CRC Press, Washington
Shahab Lavasani S, Ehsani M, Mirdamadi S, Mousavi S (2012) Study of the proteolysis and lipolysis of probiotic Lighvan cheese. Int J Agric Sci 2:341–352
Song YL, Kato N, Liu CX, Matsumiya Y, Kato H, Watanabe K (2000) Rapid identification of 11 human intestinal Lactobacillus species by multiplex PCR assays using group- and species-specific primers derived from the 16S–23S rRNA intergenic spacer region and its flanking 23S rRNA. FEMS Microbiol 187:167–173
Souza C, Saad S (2009) Viability of Lactobacillus acidophilus La-5 added solely or in co-culture with a yoghurt starter culture and implications on physico-chemical and related properties of Minas fresh cheese during storage. LWT Food Sci Technol 42:633–640
Ventura M, Reniero R, Zink R (2001) Specific identification and targeted characterization of Bifidobacterium lactis from different environmental isolates by a combined multiplex-PCR approach. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:2760–2765
Acknowledgments
This work has been carried out within the framework of bilateral agreement CNR/CONICET (2009–2010). The authors thank the Italian and Argentinean coordinators, Dr. Mauro Marchetti and Ing. Carlos Zalazar for their scientific supports in the accomplishment of the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Perotti, M.C., Wolf, I.V., Addis, M. et al. Incorporation of probiotic bacteria (Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium ssp.) in Argentinean ovine cheese. Dairy Sci. & Technol. 94, 255–267 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13594-013-0158-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13594-013-0158-x