Abstract
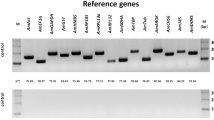
Many genes are differentially regulated by caste development in the honeybee. Identifying and understanding these differences is key to discovering the mechanisms underlying this process. To identify these gene expression differences requires robust methods to measure transcript abundance. RT-qPCR is currently the gold standard to measure gene expression, but requires stable reference genes to compare gene expression changes. Such reference genes have not been established for honeybee caste development. Here, we identify and test potential reference genes that have stable expression throughout larval development between the two female castes. In this study, 15 candidate reference genes were examined to identify the most stable reference genes. Three algorithms (GeNorm, Bestkeeper and NormFinder) were used to rank the candidate reference genes based on their stability between the castes throughout larval development. Of these genes Ndufa8 (the orthologue of a component of complex one of the mitochondrial electron transport chain) and Pros54 (orthologous to a component of the 26S proteasome) were identified as being the most stable. When these two genes were used to normalise expression of two target genes (previously found to be differentially expressed between queen and worker larvae by microarray analysis) they were able to more accurately detect differential expression than two previously used reference genes (awd and RpL12). The identification of these novel reference genes will be of benefit to future studies of caste development in the honeybee.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen, C.L., Jensen, J.L., Orntoft, T.F. (2004) Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res. 64(15), 5245–5250
Azevedo, S.V., Caranton, O.A.M., de Oliveira, T.L., Hartfelder, K. (2011) Differential expression of hypoxia pathway genes in honey bee (Apis mellifera L.) caste development. J. Insect Physiol. 57(1), 38–45
Barchuk, A.R., Cristino, A.S., Kucharski, R., Costa, L.F., Simoes, Z.L., Maleszka, R. (2007) Molecular determinants of caste differentiation in the highly eusocial honeybee Apis mellifera. BMC Dev. Biol. 7, 70
Bustin, S.A., Benes, V., Garson, J.A., Hellemans, J., Huggett, J., et al. (2009) The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin. Chem. 55(4), 611–622
Chen, X., Hu, Y., Zheng, H., Cao, L., Niu, D., Yu, D., Sun, Y., Hu, S., Hu, F. (2012) Transcriptome comparison between honey bee queen- and worker-destined larvae. Insect. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 42(9), 665–673
Corona, M., Estrada, E., Zurita, M. (1999) Differential expression of mitochondrial genes between queens and workers during caste determination in the honeybee Apis mellifera. J. Exp. Biol. 202(Pt 8), 929–938
de Azevedo, S.V., Hartfelder, K. (2008) The insulin signaling pathway in honey bee (Apis mellifera) caste development - differential expression of insulin-like peptides and insulin receptors in queen and worker larvae. J. Insect Physiol. 54(6), 1064–1071
de Boer, M., de Boer, T., Marien, J., Timmermans, M., Nota, B., van Straalen, N., Ellers, J., Roelofs, D. (2009) Reference genes for QRT-PCR tested under various stress conditions in Folsomia candida and Orchesella cincta (Insecta, Collembola). BMC Mol. Biol. 10(1), 54
Evans, J.D., Wheeler, D.E. (1999) Differential gene expression between developing queens and workers in the honey bee. Apis mellifera. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 96(10), 5575–5580
Evans, J.D., Wheeler, D.E. (2001) Expression profiles during honeybee caste determination. Genome Biol. 2(1), RESEARCH0001
Glass, G.V., Peckham, P.D., Sanders, J.R. (1972) Consequences of Failure to Meet Assumptions Underlying the Fixed Effects Analyses of Variance and Covariance. Rev. Educ. Res. 42(3), 237–288
Hellemans, J., Mortier, G., De Paepe, A., Speleman, F., Vandesompele, J. (2007) qBase relative quantification framework and software for management and automated analysis of real-time quantitative PCR data. Genome Biol. 8(2), R19
Holzl, H., Kapelari, B., Kellermann, J., Seemuller, E., Sumegi, M., et al. (2000) The regulatory complex of Drosophila melanogaster 26S proteasomes: subunit composition and localization of a deubiquitylating enzyme. J. Cell Biol. 150(1), 119–129
Humann, F.C., Hartfelder, K. (2011) Representational Difference Analysis (RDA) reveals differential expression of conserved as well as novel genes during caste-specific development of the honey bee (Apis mellifera L.) ovary. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 41(8), 602–612
Kucharski, R., Maleszka, J., Foret, S., Maleszka, R. (2008) Nutritional control of reproductive status in honeybees via DNA methylation. Science 319(5871), 1827–1830
Lix, L.M., Keselman, J.C., Keselman, H.J. (1996) Consequences of Assumption Violations Revisited: a Quantitative Review of Alternatives to the One-Way Analysis of Variance F Test. Rev. Educ. Res. 66(4), 579–619
Lourenco, A., Mackert, A., Cristino, A., Simões, Z. (2008) Validation of reference genes for gene expression studies in the honey bee, Apis mellifera, by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Apidologie 39(3), 372–385
Mutti, N.S., Wang, Y., Kaftanoglu, O., Amdam, G.V. (2011) Honey Bee PTEN Description, Developmental Knockdown, and Tissue-Specific Expression of Splice-Variants Correlated with Alternative Social Phenotypes. PLoS One 6(7), e22195
Okoniewski, M., Miller, C. (2006) Hybridization interactions between probesets in short oligo microarrays lead to spurious correlations. BMC Bioinforma. 7(1), 276
Patel, A., Fondrk, M.K., Kaftanoglu, O., Emore, C., Hunt, G., Frederick, K., Amdam, G.V. (2007) The Making of a Queen: TOR Pathway Is a Key Player in Diphenic Caste Development. PLoS One 2(6), e509
Pfaffl, M.W. (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 29(9)
Pfaffl, M.W., Tichopad, A., Prgomet, C., Neuvians, T.P. (2004) Determination of stable housekeeping genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: BestKeeper—Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations. Biotechnol. Lett. 26(6), 509–515
Rozen, S., Skaletsky, H., Misener, S., Krawetz, S.A. (1999) Primer3 on the WWW for General Users and for Biologist Programmers. In: Walker, J.M. (ed.) Bioinformatics Methods and Protocols, pp. 365–386. Humana Press, New York
Sardiello, M., Licciulli, F., Catalano, D., Attimonelli, M., Caggese, C. (2003) MitoDrome: a database of Drosophila melanogaster nuclear genes encoding proteins targeted to the mitochondrion. Nucleic Acids Res. 31(1), 322–324
Scharlaken, B., de Graaf, D.C., Goossens, K., Brunain, M., Peelman, L.J., Jacobs, F.J. (2008) Reference gene selection for insect expression studies using quantitative real-time PCR: the head of the honeybee, Apis mellifera, after a bacterial challange. J. Insect Sci. 8, 33
Severson, D.W., Williamson, J.L., Aiken, J.M. (1989) Caste-Specific Transcription in the Female Honey Bee. Insect Biochem. 19(2), 215–220
Stabe, H. (1930) The rate of growth of worker, drone and queen larvae of the honeybee Apis mellifera Linn. J. Econ. Entomol. 23(2), 447–453
Taylor, S., Wakem, M., Dijkman, G., Alsarraj, M., Nguyen, M. (2010) A practical approach to RT-qPCR—publishing data that conform to the MIQE guidelines. Methods. 50(4), S1–S5
Valasek, M.A., Repa, J.J. (2005) The power of real-time PCR. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 29(3), 151–159
Vandesompele, J., De Preter, K., Pattyn, F., Poppe, B., Van Roy, N., De Paepe, A., Speleman, F. (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 3(7), RESEARCH0034
Wang, G.-H., Xia, Q.-Y., Cheng, D.-J., Duan, J., Zhao, P., Chen, J., Zhu, L. (2008) Reference genes identified in the silkworm Bombyx mori during metamorphism based on oligonucleotide microarray and confirmed by qRT-PCR. Insect Sci. 15(5), 405–413
Wheeler, D.E., Buck, N., Evans, J.D. (2006) Expression of insulin pathway genes during the period of caste determination in the honey bee. Apis mellifera. Insect Mol. Biol. 15(5), 597–602
Wolschin, F., Mutti, N.S., Amdam, G.V. (2011) Insulin receptor substrate influences female caste development in honeybees. Biol. Lett. 7(1), 112–115
Acknowledgments
RCC would like to thank Caroline Walker for advice and discussion that led to the development of this study. All authors would like to thank Frans Laas and Bettabees for help obtaining larval samples. This work was funded by the Royal Society of New Zealand Marsden Fund Grant (UOO0707) to P.K.D.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Gènes de référence stables pour mesurer l’abondance de transcrits chez les larves d’abeilles durant le développement des castes
Développement/ caste/ développement larvaire/ expression génique/ PCR quantitative
Stabile Referenzgene für quantitative Transkriptbestimmungen in der Kastenentwicklung von Honigbienenlarven
quantitative RT-PCR/ Referenzgene/ Kastenentwicklung
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Figure 1
Expression of the 15 candidate genes in queens and workers throughout larval development. Raw Cq values are represented in box and whisker plots for queens and workers. The y-axis indicates the Cq values and the x-axis indicates the caste and time point sampled (Q = queens, W = workers). A two-way ANOVA and LSD post-hoc test were used to determine time points where queens and workers showed a significant difference in gene expression. P values < 0.05 are indicated by a single asterisk and P values < 0.01 by two asterisks. (DOC 19 kb)
Supplementary Figure 1b
(PDF 35.3 KB)
ESM 1
(DOCX 77 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cameron, R.C., Duncan, E.J. & Dearden, P.K. Stable reference genes for the measurement of transcript abundance during larval caste development in the honeybee. Apidologie 44, 357–366 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13592-012-0187-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13592-012-0187-0