Abstract
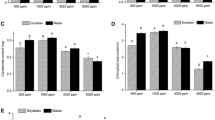
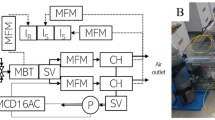
CO2 is usually supplied to the bottom of crops in greenhouses. However, optimal CO2 enrichment positions may differ depending on plant architecture and cultivation conditions. The objective of this study was to estimate the photosynthesis of greenhouse-grown mangoes (Mangifera indica L. “Irwin”) depending on the vertical position of CO2 enrichment using a three-dimensional plant model and ray-tracing simulation. Twenty-seven CO2 sensors were installed at each vertex of a grid around a 4-year-old mango tree. The distributions of CO2 concentration were measured under four different CO2 treatments: without CO2 enrichment (control) and with CO2 enrichment at 0.5 m (E0.5), 1.0 m (E1.0), and 1.5 m (E1.5). The intercepted light intensity of the plants was estimated using ray-tracing simulations. The leaf photosynthetic rates were calculated using the Faquhar, von Caemmerer, and Berry models. The accumulated CO2 consumptions from 08:00 to 10:30 were obtained under the four CO2 treatments. The CO2 concentrations in E0.5, E1.0, and E1.5 were 45.6%, 48.4%, and 153.6% higher than that of the control (544.6, 455.8, and 406.3 µmol CO2·mol–1, respectively). Using the leaf photosynthesis model at each position, the CO2 consumptions per plant in E0.5, E1.0, and E1.5 were estimated to be 50.0%, 63.6%, and 49.8% higher, respectively, than that of the control (1.76 g CO2·h–1). The highest CO2 consumption per plant was estimated to be 8.82 g CO2, obtained by enriching CO2 at 1.2 m. The results confirm that CO2 enrichment at adequate positions can enhance crop photosynthesis and CO2 utilization efficiency in greenhouses.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Ainsworth EA, Leakey ADB, Ort DR, Long SP (2008) FACE-ing the facts: inconsistencies and interdependence among field, chamber, and modeling studies of elevated [CO2] impacts on crop yield and food supply. New Phytol 179:5–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02500.x
An MR, Keum YS, Lee SK (2015) Comparative analysis of volatile flavor compounds in Taiwan apple mango and Philippines Carabao mango. Kor J Food Sci Technol 47:191–197. https://doi.org/10.9721/kjfst.2015.47.2.191
Buck-Sorlin G, de Visser PHB, Henke M, Sarlikioti V, van der Heijden GWAM, Marcelis LFM, Vos J (2011) Towards a functional-structural plant model of cut-rose: simulation of light environment, light absorption, photosynthesis, and interference with the plant structure. Ann Bot 108:1121–1134. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcr190
Bugbee B (1992) Steady-state canopy gas exchange: system design and operation. HortScience 27:770–776. https://doi.org/10.21273/hortsci.27.7.770
Chamchaiyaporn T, Jutamanee K, Kasemsap P, Vaithanomsat P (2013) Selection of the most appropriate coating particle film for improving photosynthesis in mango. Kasetsart J (Nat Sci) 47:323–332
Chen TW, Nguyen TM, Kahlen K, Stützel H (2015) High temperature and vapor pressure deficit aggravate architectural effects but ameliorate non-architectural effects of salinity on drymass production of tomato. Front Plant Sci 6:887. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00887
Cohen S, Raveh E, Li Y, Grava A, Goldschmidt EE (2005) Physiological responses of leaves, tree growth, and fruit yield of grapefruit trees under reflective shade screens. Sci Hortic 107:25–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2005.06.004
De Visser PHB, Buck-Sorlin GH, van der Heijden GWAM (2014) Optimizing illumination in the greenhouse using a 3D model of tomato and a ray tracer. Front Plant Sci 5:48. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00048
Der Zande DV, Struckens J, Verstraeten WW, Mereu S, Muys B, Coppin P (2011) 3D modeling of light interception in heterogeneous forest canopies using ground-based LiDAR data. Intl J Appl Earth Obs Geol Inf 13:792–800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2011.05.005
Farquhar GD, von Caemmerer S, Berry JA (1980) A biochemical model of photosynthetic CO2 assimilation in leaves of C3 species. Planta 149:78–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00386231
Fernandez JE, Bailey BJ (1994) The influence of fans on environmental conditions in greenhouses. J Agric Eng Res 58:201–210. https://doi.org/10.1006/jaer.1994.1049
Hartz-Rubin JS, de Lucia EH (2001) Canopy development of a model herbaceous community exposed to elevated atmospheric CO2 and soil nutrients. Physiol Plant 113:258–266. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1399-3054.2001.1130214.x
Hihara Y, Kamei A, Kanehisa M, Kaplan A, Ikeuchi M (2001) DNA microarray analysis of cyanobacterial gene expression during acclimation to high light. Plant Cell 13:793–806. https://doi.org/10.2307/3871341
Hu E, Tong L, Hu D, Liu H (2011) Mixed effects of CO2 concentration on photosynthesis of lettuce in a closed artificial ecosystem. Ecol Eng 37:2082–2086. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2011.08.012
Jeong ST, Goto-Yamamoto N, Kobayashi S, Esaka M (2004) Effects of plant hormones and shading on the accumulation of anthocyanins and the expression of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes in grape berry skins. Plant Sci 167:247–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2004.03.021
Jung DH, Shin JH, Cho YY, Son JE (2015) Development of a two-variable spatial leaf photosynthetic model of Irwin mango grown in greenhouse. Protec Hortic Plant Fact 24:161–166. https://doi.org/10.12791/ksbec.2015.24.3.161
Jung DH, Cho YY, Lee JG, Son JE (2016) Estimation of leaf area, leaf fresh weight, and leaf dry weight of Irwin mango grown in greenhouse using leaf length, leaf width, petiole length, and SPAD value. Protec Hortic Plant Fact 25:146–152. https://doi.org/10.12791/ksbec.2016.25.3.146
Jung DH, Lee JW, Kang WH, Hwang IH, Son JE (2018) Estimation of whole plant photosynthetic rate of Irwin mango under artificial and natural lights using a three-dimensional plant model and ray-tracing. Intl J Mol Sci 19:152. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010152
Jung DH, Hwang I, Shin J, Son JE (2021) Analysis of leaf photosynthetic rates of hydroponically-grown paprika (Capsicum annuum L.) plants according to vertical position with multivariable photosynthesis models. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 62:41–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-020-00295-x
Kim HS, Palmroth S, Thérezién M, Stenberg P, Oren R (2010) Analysis of the sensitivity of absorbed light and incident light profile to various canopy architecture and stand conditions. Tree Physiol 31:30–47. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpq098
Kim JH, Lee JW, Ahn TI, Shin JH, Park KS, Son JE (2016) Sweet pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) canopy photosynthesis modeling using 3D plant architecture and light ray-tracing. Front Plant Sci 7:1321. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01321
Kuroyanagi T, Yasuba K, Higashide T, Iwasaki Y, Takaichi M (2014) Efficiency of carbon dioxide enrichment in an unventilated greenhouse. Biosyst Eng 119:58–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2014.01.007
Larbi A, Vázquez S, El-Jendoubi H, Msallem M, Abadía J, Abadía A, Morales F (2015) Canopy light heterogeneity drives leaf anatomical, eco-physiological, and photosynthetic changes in olive trees grown in a high-density plantation. Photosyn Res 123:141–155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-014-0052-2
Lawlor DW (2002) Limitation to photosynthesis in water-stressed leaves: stomata vs. metabolism and the role of ATP. Ann Bot 89:871–885. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcf110
Le Roux X, Grand S, Dreyer E, Daudet FA (1999) Parameterization and testing of a biochemically based photosynthesis model for walnut (Juglans regia) trees and seedlings. Tree Physiol 19:481–492. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/19.8.481
Leakey ADB, Uribelarrea M, Ainsworth EA, Naidu SL, Rogers A, Ort DR, Long SP (2006) Photosynthesis, productivity, and yield of maize are not affected by open-air elevation of CO2 concentration in the absence of drought. Plant Physiol 140:779–790. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.105.073957
Léchaudel M, Lopez-Lauri F, Vidal V, Sallanon H, Joas J (2013) Response of the physiological parameters of mango fruit (transpiration, water relations, and antioxidant system) to its light and temperature environment. J Plant Physiol 170:567–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2012.11.009
Maheshwari N, Kumar M, Thakur IS, Srivastava S (2017) Recycling of carbon dioxide by free air CO2 enriched (FACE) Bacillus sp. SS105 for enhanced production and optimization of biosurfactant. Bioresour Technol 242:2–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.03.124
Marcelis LFM, Heuvelink E, Goudriaan J (1998) Modeling biomass production and yield of horticultural crops: a review. Sci Hortic 74:83–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-4238(98)00083-1
Moon T, Choi HY, Jung DH, Chang SH, Son JE (2020) Prediction of CO2 concentration via long short-term memory using environmental factors in greenhouses. Hortic Sci Technol 38:201–209. https://doi.org/10.7235/HORT.20200019
Mortensen LM (1987) CO2 enrichment in greenhouses. crop responses. Sci Hortic 33:1–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4238(87)90028-8
Ohyama K, Kozai T, Ishigami Y, Ohno Y, Toida H, Ochi Y (2005) A CO2 control system for a greenhouse with a high ventilation rate. Acta Hortic 691:649–654. https://doi.org/10.17660/actahortic.2005.691.79
Park IG, Yoon HJ, Kim MA, Lee KY, Park HC, Kim SH (2014) Effect on pollinating activities on mango flower by bumblebee (Bombus terrestris), honeybee (Apis mellifera), and oriental latrine fly (Chrysomyia megacephala) in greenhouse. J Apic 29:235–243. https://doi.org/10.17519/apiculture.2014.11.29.4.235
Parry ML, Rosenzweig C, Iglesias A, Livermore M, Fischer G (2004) Effects of climate change on global food production under SRES emissions and socio-economic scenarios. Glob Environ Change 14:53–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2003.10.008
Phillips DL, Lee JJ, Dodson RF (1996) Sensitivity of the US corn belt to climate change and elevated CO2: I. corn and soybean yields. Agric Syst 52:481–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0308-521x(96)00014-5
Qian T, Elings A, Dieleman JA, Gort G, Marcelis LFM (2012) Estimation of photosynthesis parameters for a modified Farquhar-von Caemmerer-Berry model using simultaneous estimation method and nonlinear mixed effects model. Environ Exp Bot 82:66–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2012.03.014
Raines CA (2011) Increasing photosynthetic carbon assimilation in C3 plants to improve crop yield: current and future strategies. Plant Physiol 155:36–42. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.168559
Schaffer B, Whiley AW, Searle C, Nissen RJ (1997) Leaf gas exchange, dry matter partitioning, and mineral element concentrations in mangos as influenced by elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide and root restriction. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 122:849–855. https://doi.org/10.21273/jashs.122.6.849
Schaffer B, Whiley AW, Searle C (1999) Atmospheric CO2 enrichment, root restriction, photosynthesis, and dry-matter partitioning in subtropical and tropical fruit crops. HortScience 34:1033–1037. https://doi.org/10.21273/hortsci.34.6.1033
Singh VK, Rajan S (2009) Changes in photosynthetic rate, specific leaf weight and sugar contents in mango (Mangifera indica L.). Open Hortic J 2:40–43
Sinoquet H, le Roux X, Adam B, Ameglio T, Daudet FA (2001) RATP: a model for simulating the spatial distribution of radiation absorption, transpiration and photosynthesis within canopies: application to an isolated tree crown. Plant Cell Environ 24:395–406. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3040.2001.00694.x
Son JE, Park JS, Park HY (1999) Analysis of carbon dioxide changes in urban-type plant factory system. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 40:205–208
Takahashi N, Ling PP, Frantz JM (2008) Considerations for accurate whole plant photosynthesis measurement. Environ Contr Biol 46:91–101. https://doi.org/10.2525/ecb.46.91
Takeya S, Muromachi S, Maekawa T, Yamamoto Y, Mimachi H, Kinoshita T, Murayama T, Umeda H, Ahn DH, Iwasaki Y, Hashmoto H, Yamaguchi T, Okaya K, Matsuo S (2017) Design of ecological CO2 enrichment system for greenhouse production using TBAB + CO2 semi-clathrate hydrate. Energies 10:927. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10070927
Tang L, Hou C, Huang H, Chen C, Zou J, Lin D (2015) Light interception efficiency analysis based on three-dimensional peach canopy models. Ecol Inf 30:60–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoinf.2015.09.012
Xu W, Yin Y, Zhou S (2007) Social and economic impacts of carbon sequestration and land use change on peasant households in rural China: a case study of Liping, Guizhou Province. J Environ Manag 85:736–745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2006.09.013
Yin X, Struik PC, Romero P, Harbinson J, Evers JB, van der Putten PEL, Vos J (2009) Using combined measurements of gas exchange and chlorophyll fluorescence to estimate parameters of a biochemical C3 photosynthesis model: a critical appraisal and a new integrated approach applied to leaves in a wheat (Triticum aestivum) canopy. Plant Cell Environ 32:448–464. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.01934.x
Yonemoto Y (2006) Tropical fruit. (Ed.), Horticulture in Japan 2006. Shoukadoh Publication, Kyoto, Japan, pp 100–106. J Jpn Soc Hortic Sci
Zhu XG, Song Q, Ort DR (2012) Elements of a dynamic systems model of canopy photosynthesis. Curr Opin Plant Biol 15:237–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2012.01.010
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the MSIT (Ministry of Science and ICT), Korea, under the Grand Information Technology Research Center support program (IITP-2022-2020-0-01489) supervised by the IITP (Institute for Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, investigation, and writing—review and editing, DHJ and JES; formal analysis and data curation, DHJ and IH; supervision, project administration, and funding acquisition, JES. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Ali Sarkhosh.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, D.H., Hwang, I. & Son, J.E. Three-dimensional estimation of greenhouse-grown mango photosynthesis with different CO2 enrichment heights. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 63, 823–834 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-022-00453-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-022-00453-3