Abstract
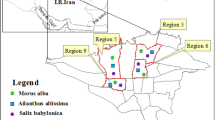
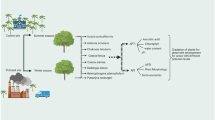
The aim of this study was to compare the ability to absorb various air pollutants of common roadside ornamental plants growing in an industrial center of Faisalabad, Pakistan, with that of ornamental plants growing at University of Agriculture, Main Campus, Faisalabad, Pakistan. Leaf samples of 17 plant species were collected from both locations and four physiological and biochemical parameters, i.e., relative water content, leaf extract pH, total chlorophyll content, and ascorbic acid content, were assessed. The air pollution tolerance index (APTI) was calculated from the obtained values. The results demonstrated the substantial impact of pollutants on the APTI; most of the tested plants grown at the industrial site had a higher APTI than those grown on the campus. Among the tested ornamental plant species, Hibiscus rosa-sinensis (9.8) had the highest APTI value, which was similar to Alstonia scholaris (9.4), Bougainvillea spectabilis (9.6), Morus nigra (9.5), Murraya exotica (9.0), and Nerium oleander (9.0) at the industrial location, while at the campus, B. spectabilis (7.2) had the highest APTI value, which was similar to Ficus benjamina (6.5), H. rosa-sinensis (6.6), Lagerstroemia indica (6.6), and Nerium oleander (6.5). However, Duranta repens, Melia azedarach, and Tecoma stans had the lowest APTI values at both locations, with values of 6.6, 7.5, and 7.7 at the industrial location and 5.5, 5.5, and 5.6 at the campus, respectively. Moreover, Alstonia scholaris, H. rosa-sinensis, and M. nigra had the highest relative difference in APTI between the two sites, with differences of 3.7, 3.2, and 3.2, respectively. In summary, among 17 ornamental species, A. scholaris, B. spectabilis, H. rosa-sinensis, L. indica, M. nigra, and N. oleander are the most desirable for planting around industrial zones on the basis of APTI and can be used as bio-monitors of environmental pollutants in industrial zones.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achakzai K, Khalid S, Adress M, Bibi A, Ali S, Nawaz R, Rizwan M (2017) Air pollution tolerance index of plants around brick kilns in Rawalpindi, Pakistan. J Environ Manag 190:252–258
Agbaire PO, Esiefarienrhe E (2009) Air pollution tolerance indices (APTI) of some plants around otorogun gas plant in Delta State, Nigeria. J Appl Sci Environ Manag 13:11–14
Akilan M, Nandhakumar S (2016) Air pollution tolerance index of selected plants in industrial and urban areas of vellore District. Agric Sci Digest A Res J 35:66–68
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzyme in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24:1–15
Bajaj KL, Kaur G (1981) Spectrophotometric determination of L. Ascorbic acid in vegetables and fruits. Analyst 106:117–120
Bora M, Joshi N (2014) A study on variation in biochemical aspects of different tree species with tolerance and performance index. The Bioscan Intl Quart J Life Sci 9:59–63
Campos FM, Ribeiro SMR, Pinheiro-Sant’Ana CMDLHM (2009) Optimization of methodology to analyze ascorbic and dehydroascorbic acid in vegetables. Quim Nova 32:87–91
Chauhan A (2010) Photosynthetic pigment changes in some selected trees induced by automobile exhaust in Dehradun, Uttarakhand. N Y Sci J 3:45–51
Cornelissen JHC, Sibma F, van Logtestijn RSP, Broekman RA, Thompson K (2011) Leaf pH as a plant trait: species-driven rather than soil-driven variation. Func Ecol (online) 25:449–455
Das S, Prasad P (2010) Seasonal variation in air pollution tolerance indices and selection of plant species for industrial areas of Roukela. Ind J Environ Protec 30:978–988
Deepalakshmi AP, Ramakrishnaiah H, Ramachandra YL, Radhika RN (2013) Roadside plants as bio-indicators of urban air pollution. IOSR J Environ Sci Toxicol Food Technol 3:10–14
Deepika, Gour P, Haritash AK (2016) Air pollution tolerance of trees in an educational institute in Dehli. Intl J Environ Sci 6:979–986
Enete IC, Chukwudeluzu VU, Okolie AO (2013) Evaluation of air pollution tolerance index of plants and ornamental shrubs in Enugu city: implications for urban heat island effect. World Environ 3:108–115
Garsed SG (1984) Uptake and distribution of pollutants in the plant and residence time at active species. In: Kozioł MJ, Whatley FR (eds) Gaseous air pollutants and plant metabolism. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford
GOP (2016) Faisalabad industry. https://www.punjab.gov.pk/faisalabad_industry. Accessed 1 Aug 2017
Joshi N, Chauhan A, Joshi PC (2009) Impact of industrial air pollutants on some biochemical parameters and yield in wheat and mustard plants. Environmentalist 29:398–404
Khan FI, Abbasi SA (2001) Effective design of greenbelts using mathematical models. J Hazard Mater 81:33–65
Krishnaveni M (2013) Biochemical changes in plants indicating air pollution. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 5:585–586
Krishnaveni M, Lavanya K (2014) Air pollution tolerance index of plants a comparative study. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 6:320–324
Kuddus M, Kumari R, Ramteke PW (2011) Studies on air pollution tolerance of selected plants in Allahabad City, India. J Environ Res Manag 2:42–46
Lohe RN, Tyagi B, Singh V, Tyagi PK, Khanna DR, Bhutiani R (2015) A comparative study for air pollution tolerance index of some terrestrial plant species. Glob J Environ Sci Manag 1:315–324
Miria A, Anisa BK (2013) Air pollution tolerance index and carbon storage of selected urban trees—a comparative study. Intl J Appl Res Stud 2:1–7
Panigrahi T, Satpathy JK, Panda RB (2014) Effect of air pollutants on different plant species found in ITR Complex, Chandipur. Int J Green Herbal Chem 3:29–34
Pravin US, Madhumita ST (2013) Physiological responses of some plant species as a bio-indicator of roadside automobile pollution stress using the air pollution tolerance index approach. Int J Plant Res 3:9–16
Rai PK, Panda LLS, Chutia BM, Singh MM (2013) Comparative assessment of air pollution tolerance index (APTI) in the industrial (Rourkela) and nonindustrial area (Aizawl) of India: an eco-management approach. Afr J Environ Sci Technol 7:944–948
Ram SS, Chaudhuri P, Chanda S, Santra SCC, Chakraborty A, Sudarshan M (2015) A review on air pollution monitoring and management using plants with special reference to foliar dust adsorption and physiological stress responses. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 45:2489–2522
Roy RK, Singh S (2014) Urban landscape and amelioration of environment by trees: method and approaches. Int J Latest Res Sci Technol 3:98–104
Sabri SNAM, Ahmad MI, Naim DM (2015a) Plants as bio-indicators based on APTI approach. In: Naim DM, Ahmad MI (eds) Natural resources and technology. Penerbit USM, Penang
Sabri SNAM, Ahmad MI, Yusup Y (2015b) Assessment of air pollution tolerance index of selected plant species commonly found along roadsides in Palau Pinang, Malaysia. Int J Sci Res 4:1914–1918
Sasmita D, Pramila P (2010) Seasonal variation in air pollution tolerance indices and selection of plants species for industrial areas of Rourkela. Indian J Environ Protec 30:978–988
Schlemmer MR, Francis DD, Shanahan JF, Schepers JS (2005) Remotely measuring chlorophyll content in corn leaves with differing nitrogen levels and relative water content. Agron J 97:106
Setälä H, Viippola V, Rantalainen A, Pennanen A, Yli-Pelkonen V (2013) Does urban vegetation mitigate air pollution in northern conditions. Environ Pollut 183:104–112
Sharma SC, Srivastava R, Roy RK (2005) Role of bougainvilleas in mitigation of environmental pollution. J Environ Sci Eng 47:131–134
Sharma P, Jain R, Ghosh C (2016) Role of ascorbic acid in imparting tolerance to plants against oxidizing pollutants. Int J Sci Technol Res 5:43–47
Singh SK, Rao DN (1983) Evaluation of plants for their tolerance to air pollution. In: Proceedings of the symposium on air pollution control, pp 218–224
Teiri H, Pourzamani H, Hajizadeh Y (2018) Phytoremediation of VOCs from indoor air by ornamental potted plants: a pilot study using a palm species under the controlled environment. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.01.078
Wellburn AR (1994) The spectral determination of chlorophylls a and b, as well as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometers of different resolution. J Plant Physiol 144:307–313
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to acknowledge the support of Nasar Amjad, Kainat Ilyas and Saira Mushtaq, graduate students in the Institute of Horticultural Sciences, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan, and Ms. Nawal Mehmood, graduate student, Department of Biochemistry, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, for technical support during biochemical analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by So-Young Park, Ph.D.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, I., Abdullah, B., Dole, J.M. et al. Evaluation of the air pollution tolerance index of ornamentals growing in an industrial area compared to a less polluted area. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 60, 595–601 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-019-00141-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-019-00141-9