Abstract
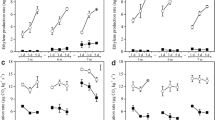
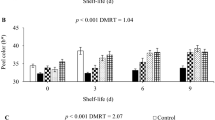
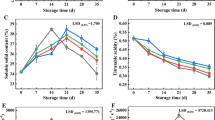
We investigated the possibility of prolonging the freshness of persimmons (Diospyros kaki) for overseas export. Previous studies aimed at improving the shelf life of harvested persimmons focused on the synthetic gas 1-MCP, an inhibitor of ethylene perception. In this study, the natural lipid compound lysophosphatidylethanolamine (LPE) was applied to prolong the freshness of persimmons. LPE significantly delayed persimmon softening when applied not only during fruit growth, but also after harvest, or after a long period of post-harvest cold storage, simulating conditions of overseas export. LPE suppressed the expression of the softening-related genes ACS1, ACO1, ERF24, DkUGD1, DkCHI3, and DkB-CHI1. These results reveal the effects of LPE on persimmon softening and the related molecular mechanisms and provide evidence that LPE can be used to delay persimmon softening.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed ZF, Palta JP (2015) A postharvest dip treatment with lysophosphatidylethanolamine, a natural phospholipid, may retard senescence and improve the shelf life of banana fruit. HortScience 50:1035–1040
Ahmed S, Thompson A, Perviez M, Ullah H, Chatha Z (2006) Effect of polyethylene film thickness and exposure time of ethylene on the ripening behavior and quality of banana. Int J Agric Biol 8:381–386
Ahmed M, Yousef AR, Sarrwy S (2011) Modified atmosphere packaging for maintaining quality and shelf life extension of persimmon fruits. Asian J Agric Sci 3:308–316
Alexander L, Grierson D (2002) Ethylene biosynthesis and action in tomato: a model for climacteric fruit ripening. J Exp Bot 53:2039–2055. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erf072
Bhushan S, Tripathi S, Thakur N (2002) Effect of different modified atmosphere packaging on the quality of kiwifruit stored at room temperature. J Food Sci Technol 39:279–283
Butt MS, Sultan MT, Aziz M, Naz A, Ahmed W, Kumar N, Imran M (2015) Persimmon (Diospyros kaki) fruit: hidden phytochemicals and health claims. EXCLI J 14:542. https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2015-159
Çandir E, Özdemir AE, Kaplankiran M, Demirkeser TH, Yildiz E (2010) Storage life of non-astringent persimmons grown in the eastern Mediterranean. N Z J Crop Hortic Sci 38:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1080/01140671003619266
Choi H-S, Jung S-K, Kim Y-K (2013) Storage ability of non-astringent ‘Fuyu’ persimmon fruit is affected by various concentrations of 1-methylcyclopropene and/or modified atmosphere packaging. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 88:195–200. https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.2013.11512956
Cutillas-Iturralde A, Zarra I, Fry SC, Lorences EP (1994) Implication of persimmon fruit hemicellulose metabolism in the softening process. Importance of xyloglucan endotransglycosylase. Physiol Plant 91:169–176. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1994.tb00415.x
Dal Cin V, Rizzini FM, Botton A, Tonutti P (2006) The ethylene biosynthetic and signal transduction pathways are differently affected by 1-MCP in apple and peach fruit. Postharvest Biol Technol 42:125–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2006.06.008
Fan L, Zheng S, Wang X (1997) Antisense suppression of phospholipase D alpha retards abscisic acid-and ethylene-promoted senescence of postharvest Arabidopsis leaves. Plant Cell 9:2183–2196. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.9.12.2183
Farag KM, Palta JP (1991) Improving postharvest keeping quality of vine-ripened tomato fruits with a natural lipid. HortScience 26:778
Farag KM, Palta JP (1993) Use of lysophosphatidylethanolamine, a natural lipid, to retard tomato leaf and fruit senescence. Physiol Plant 87:515–521. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1993.tb02501.x
Gross KC, Wallner SJ (1979) Degradation of cell wall polysaccharides during tomato fruit ripening. Plant Physiol 63:117–120. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.63.1.117
Harima S, Nakano R, Yamauchi S, Kitano Y, Kubo Y, Inaba A, Tomita E (2002) Inhibition of fruit softening in forcing-cultured ‘Tonewase’ Japanese persimmon by packaging in perforated and non-perforated polyethylene bags. J Jpn Soc Hortic Sci 71:284–291. https://doi.org/10.2503/jjshs.71.284
Harima S, Nakano R, Yamauchi S, Kitano Y, Yamamoto Y, Inaba A, Kubo Y (2003) Extending shelf-life of astringent persimmon (Diospyros kaki Thunb.) fruit by 1-MCP. Postharvest Biol Technol 29:319–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-5214(03)00058-9
Hong JH (2012) Lysophosphatidylethanolamine treatment delays leaf senescence and improve fruit storability in melon (Cucumis melo L.). Korean J Hortic Sci Technol 30:158–161. https://doi.org/10.7235/hort.2012.12046
Itamura H, Ohno Y, Yamamura H (1997) Characteristics of fruit softening in Japanese persimmon ‘Saijo’. International Society for Horticultural Science (ISHS), Leuven, pp 179–188
Jiang Y, Joyce D (2000) Effects of 1-methylcyclopropene alone and in combination with polyethylene bags on the postharvest life of mango fruit. Ann Appl Biol 137:321–327. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7348.2000.tb00073.x
Jiang Y, Joyce DC, Macnish AJ (1999) Extension of the shelf life of banana fruit by 1-methylcyclopropene in combination with polyethylene bags. Postharvest Biol Technol 16:187–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-5214(99)00009-5
Jiang N, Rao J, Fu R, Suo J (2010) Effects of propylene and 1-methylcyclopropene on PG activities and expression of DkPG1 gene during persimmon softening process. Acta Hortic Sin 37:1507–1512
Jung S-K, Choi H-S (2015) Effects of 1-MCP or packaging film on the quality and gas composition of ‘Fuji’ apple fruit during long-term storage. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 90:344–348. https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.2015.11513193
Jung J, Choi SC, Jung S, Cho B-K, Ahn G-H, Ryu SB (2017) A transcriptome approach toward understanding fruit softening in persimmon. Front Plant Sci 8:1556. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01556
Kaur N, Palta JP (1997) Postharvest dip in a natural lipid, lysophosphatidylethanolamine, may prolong vase life of snapdragon flowers. HortScience 32:888–890
Kim Y-K, Lee J-M (2004) Extension of storage and shelf-life of sweet persimmon with 1-MCP. In: III International Symposium on Persimmon, vol 685, pp 165–175
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lownds N, Banaras M, Bosland P (1994) Postharvest water loss and storage quality of nine pepper (Capsicum) cultivars. HortScience 29:191–193
Nakano R, Harima S, Ogura E, Inoue S, Kubo Y, Inaba A (2001) Involvement of stress-induced ethylene biosynthesis in fruit softening of ‘Saijo’ persimmon. J Jpn Soc Hortic Sci 70:581–585. https://doi.org/10.2503/jjshs.70.581
Nakano R, Ogura E, Kubo Y, Inaba A (2003) Ethylene biosynthesis in detached young persimmon fruit is initiated in calyx and modulated by water loss from the fruit. Plant Physiol 131:276–286. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.010462
Nishiyama K, Guis M, Rose JK, Kubo Y, Bennett KA, Wangjin L, Kato K, Ushijima K, Nakano R, Inaba A (2007) Ethylene regulation of fruit softening and cell wall disassembly in Charentais melon. J Exp Bot 58:1281–1290. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erl283
Özgen M, Farag KM, Ozgen S, Palta JP (2005) Lysophosphatidylethanolamine accelerates color development and promotes shelf life of cranberries. HortScience 40:127–130
Özgen M, Serçe S, Akça Y, Hong JH (2015) Lysophosphatidylethanolamine (LPE) improves fruit size, color, quality and phytochemical contents of Sweet Cherry cv ‘0900 Ziraat’. Korean J Hortic Sci Technol 33:196–201. https://doi.org/10.7235/hort.2015.13195
Paniagua A, East A, Hindmarsh J, Heyes J (2013) Moisture loss is the major cause of firmness change during postharvest storage of blueberry. Postharvest Biol Technol 79:13–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2012.12.016
Ryu SB, Wang X (1995) Expression of phospholipase D during castor bean leaf senescence. Plant Physiol 108:713–719. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.2.713
Ryu SB, Karlsson BH, Özgen M, Palta JP (1997) Inhibition of phospholipase D by lysophosphatidylethanolamine, a lipid-derived senescence retardant. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:12717–12721. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.94.23.12717
Salvador A, Cuquerella J, Martínez-Jávega J, Monterde A, Navarro P (2004) 1-MCP preserves the firmness of stored persimmon ‘Rojo Brillante’. J Food Sci 69:69–73. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2004.tb15516.x
Sitrit Y, Bennett AB (1998) Regulation of tomato fruit polygalacturonase mRNA accumulation by ethylene: a re-examination. Plant Physiol 116:1145–1150. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.116.3.1145
Sivertsvik M, Rosnes JT, Bergslien H (2002) Modified atmosphere packaging. In: Minimal processing technologies in the food industry. CRC, New York, pp 61–86
Tata SK, Jung JH, Kim YH, Choi JY, Jung JY, Lee IJ, Shin JS, Ryu SB (2016) Heterologous expression of chloroplast-localized geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase confers fast plant growth, early flowering and increased seed yield. Plant Biotechnol J 14:29–39. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12333
Vilas-Boas EVDB, Kader AA (2007) Effect of 1-methylcyclopropene (1-MCP) on softening of fresh-cut kiwifruit, mango and persimmon slices. Postharvest Biol Technol 43:238–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2006.09.010
Wan Zaliha WS, Singh Z (2012) Lysophosphatidylethanolamine improves fruit colour and accumulation of anthocyanin in ‘cripps pink’ apples. International Society for Horticultural Science (ISHS), Leuven, pp 227–232
Wang X (2005) Regulatory functions of phospholipase D and phosphatidic acid in plant growth, development, and stress responses. Plant Physiol 139:566–573. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.105.068809
Watkins CB (2006) The use of 1-methylcyclopropene (1-MCP) on fruits and vegetables. Biotechnol Adv 24:389–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2006.01.005
Win NM, Lee J, Yoo J, Ryu S, Kim K-O, Kim DH, Jung HY, Choung M-G, Park K-I, Cho Y-J, Kang I-K (2018) Effects of polyethylene film liner, 1-methylcyclopropene, and aminoethoxyvinylglycine treatments on fruit quality attributes of ‘tonewase’ persimmon fruits during cold storage. Hortic Sci Technol 36:256–265. https://doi.org/10.12972/kjhst.20180026
Zhong S, Fei Z, Chen Y-R, Zheng Y, Huang M, Vrebalov J, Mcquinn R, Gapper N, Liu B, Xiang J (2013) Single-base resolution methylomes of tomato fruit development reveal epigenome modifications associated with ripening. Nat Biotechnol 31:154. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2462
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 Program (Project Nos. PJ01348601 & PJ01368201), the Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea, and in part from the Korea Institute of Planning & Evaluation for Technology of Agriculture, Forestry, Fisheries and Food (IPET 112150-3), and the KRIBB Project Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Communicated by Eun Jin Lee, Ph.D.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, J., Lee, YP., Bae, SW. et al. Lysophosphatidylethanolamine delays fruit softening of persimmon (Diospyros kaki). Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 60, 491–499 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-019-00140-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-019-00140-w