Abstract
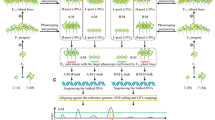
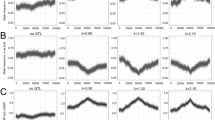
BSA (bulked-segregant analysis) can be defined as a rapid procedure for identifying genomic regions responsible for complex traits in crops. The method involves comparing two bulked DNA samples generated from a segregating population originating from a single cross. With the improvement of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology, BSA combined with next-generation sequencing (NGS-BSA) has been widely applied to QTL mapping due to its high efficiency. Following a summary of widely used NGS-BSA methods, we present a novel strategy of NGS-BSA application, called as Modified QTL-seq. For Modified QTL-seq, QTL-seq analysis is performed on paired bulks,followed by multiple comparison analysis, which can significantly narrow the candidate intervals. Besides, F4:5 progeny used for additional QTL-seq analysis are only polymorphic at the target locus, which diminishs the heterosis influence on construction of bulked DNA, thus further narrowing candidate regions. Therefore, Modified QTL-seq is another optimization of NGS-BSA application. Compared with previous BSA methods, Modified QTL-seq is potential and cost-effective, and will accelerate QTL-mapping in crops.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BSA:
-
Bulked segregant analysis
- NILs:
-
Near-isogenic lines
- NGS:
-
Next-generation sequencing
- NGS-BSA:
-
Bulked-segregant analysis combined with next-generation sequencing
- QTLs:
-
Quantitative trait loci
- MAS:
-
Marker-assisted selection
- RFLP:
-
Restriction fragment polymorphism
- RAPD:
-
Random amplified polymorphic DNA
- NGM:
-
Next generation mapping
- LD:
-
Linkage disequilibrium
- GPS:
-
Graded Pool-Seq
- PCAMP:
-
Pair-wise Comparison Analysis for Multiple Pool-seq
- SSR:
-
Simple sequence repeat
- SNP:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism
- X-QTL:
-
Extreme QTL mapping
- RF:
-
Reference
- SV:
-
Structural variation
- WGS:
-
Whole genome sequencing
- ceX-QTL:
-
C. elegans X-QTL
- RIAILs:
-
Recombinant inbred advanced intercross lines
- IDMAS:
-
InDel markers-assisted selection
References
Abe A, Kosugi S, Yoshida K, Natsume S, Takagi H, Kanzaki H, Matsumura H, Yoshida K, Mitsuoka C, Tamiru M, Innan H, Cano L, Kamoun S, Terauchi R (2012) Genome sequencing reveals agronomically important loci in rice using MutMap. Nat Biotechnol 30:174–178. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2095
Austin RS, Vidaurre D, Stamatiou G, Breit R, Provart NJ, Bonetta D, Zhang J, Fung P, Gong Y, Wang PW, McCourt P, Guttman DS (2011) Next-generation mapping of Arabidopsis genes. Plant J 67:715–725. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04619.x
Burga A, Ben-David E, Lemus Vergara T, Boocock J, Kruglyak L (2019) Fast genetic mapping of complex traits in C. elegans using millions of individuals in bulk. Nat Commun 10:2680. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10636-9
Darvasi A, Soller M (1994) Selective DNA pooling for determination of linkage between a molecular marker and a quantitative trait locus. Genetics 138:1365–1373. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.8.23.2928
Dong W, Wu D, Li G, Wu D, Wang Z (2018) Next-generation sequencing from bulked segregant analysis identifes a dwarfsm gene in watermelon. Sci Rep 8:2908. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-21293-1
Ehrenreich M, Torabi N, Jia Y, Kent J, Martis S, Shapiro JA, Gresham D, Caudy AA, Kruglyak L (2010) Dissection of genetically complex traits with extremely large pools of yeast segregants. Nature 464:1039–1042. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08923
Fekih R, Takagi H, Tamiru M, Abe A, Natsume S, Yaegashi H, Sharma S, Sharma S, Kanzaki H, Matsumura H, Saitoh H, Mitsuoka C, Utsushi H, Uemura A, Kanzaki E, Kosugi S, Yoshida K, Cano L, Kamoun S, Terauchi R (2013) MutMap+: genetic mapping and mutant identification without crossing in rice. PLoS One 8: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0068529
Godfray HC, Beddington JR, Crute IR, Haddad L, Lawrence D, Muir JF, Pretty J, Robinson S, Thomas SM, Toulmin C (2010) Food security: the challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science 327:812–818. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1185383
Huo H, Henry IM, Coppoolse ER, Verhoef-Post M, Schut JW, de Rooij H, Vogelaar A, Joosen RV, Woudenberg L, Comai L, Bradford KJ (2016) Rapid identification of lettuce seed germination mutants by bulked segregant analysis and whole genome sequencing. Plant J 88:345–360. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13267
Jia Q, Wang J, Zhu J, Hua W, Shang Y, Yang J, Liang Z (2017) Toward identification of black lemma and pericarp gene Blp1 in barley combining bulked segregant analysis and specific-locus amplified fragment sequencing. Front Plant Sci 8:1414. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01414
Kumar R, Janila P, Vishwak arma MK, Khan AW, Manohar SS, Gangurde SS, Variath MT, Shasidhar Y, Pandey MK, Varshney RK (2019) Whole-genome resequencing based QTL-Seq identified candidate genes and molecular markers for fresh seed dormancy in groundnut. Plant Biotechnol J 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13266
Lu H, Lin T, Klein J, Wang S, Qi J, Zhou Q, Sun J, Zhang Z, Weng Y, Huang S (2014) QTL-seq identifies an early flowering QTL located near Flowering Locus T in cucumber. Theor Appl Genet 127:1491–1499. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-014-2313-z
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: A rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:9828–9832. https://doi.org/10.2307/2357899
Nelson WJ, Lee BC, Gasperini FA, Hair DM (2012) Meeting the challenge of feeding 9 billion people safely and securely. J Agromedicine 174:347–350. https://doi.org/10.1080/1059924X.2012.726161
Nicholas FW, Wade CM, Ollivier L, Sölkner J (2015) Quantitative genetics, spread of genes and genetic improvement: papers in honour of John James. 132: 85–88. https://doi.org/10.1111/jbg.12158
Pardue SL (2010) Food, energy, and the environment. Poult Sci 89:797–802. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.2009-00565
Qi L, Ding Y, Zheng X, Xu R, Zhang L, Wang Y, Wang X, Zhang L, Cheng Y, Qiao W, Yang Q (2018) Fine mapping and identification of a novel locus qGL12.2 control grain length in wild rice (Oryza rufpogon Grif.). Theor Appl Genet 131:1497–1508. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-018-3093-7
Schneeberger K, Ossowski S, Lanz C, Juul T, Petersen AH, Nielsen KL, Jørgensen JE, Weigel D, Andersen SU (2009) SHOREmap: simultaneous mapping and mutation identification by deep sequencing. Nat Methods 6:550–1. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth0809-550
Song J, Li Z, Liu Z, Guo Y, Qiu L (2017) Next-generation sequencing from bulked-segregant analysis accelerates the Simultaneous identification of two qualitative genes in soybean. Front Plant Sci 8:919. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00919
Takagi H, Uemura A, Yaegashi H, Tamiru M, Abe A, Mitsuoka C, Utsushi H, Natsume S, Kanzaki H, Matsumura H, Saitoh H, Yoshida K, Cano LM, Kamoun S, Terauchi R (2013a) MutMap-Gap: whole-genome resequencing of mutant F2 progeny bulk combined with de novo, assembly of gap regions identifies the rice blast resistance gene Pii. New Phytol 200:276–283. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12369
Takagi H, Abe A, Yoshida K, Kosugi S, Natsume S, Mitsuoka C, Uemura A, Utsushi H, Tamiru M, Takuno S, Innan H, Cano LM, Kamoun S, Terauchi R (2013b) QTL-seq: rapid mapping of quantitative trait loci in rice by whole genome resequencing of DNA from two bulked populations. Plant J 74:174–183. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12105
Takagi H, Tamiru M, Abe A, Yoshida K, Uemura A, Yaegashi H, Obara T, Oikawa K, Utsushi H, Kanzaki E, Mitsuoka C, Natsume S, Kosugi S, Kanzaki H, Matsumura H, Urasaki N, Kamoun S, Terauchi R (2015) MutMap accelerates breeding of a salt-tolerant rice cultivar. Nat Biotechnol 5:445–449. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3188
Tao Y, Niu Y, Wang Y, Chen T, Naveed SA, Zhang J, Xu J, Li Z (2018) Genome-wide association mapping of alumin umtoxicity tolerance and fine mapping of a candidate gene for Nrat1 in rice. PLoS One 13:e0198589. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12369
Wang C, Tang S, Zhan Q, Hou Q, Zhao Y, Zhao Q, Feng Q, Zhou C, Lyu D, Cui L, Li Y, Miao J, Zhu C, Lu Y, Wang Y, Wang Z, Zhu J, Shangguan Y, Gong J, Yang S, Wang W, Zhang J, Xie H, Huang X, Han B (2019) Dissecting a heterotic gene through GradedPool-Seq mapping informs a rice-improvement strategy. Nat Commun 10:2982. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1537-2995.1993.331194182236.x
Win KT, Vegas J, Zhang C, Song K, Lee S (2017) QTL mapping for downy mildew resistance in cucumber via bulked segregant analysis using next-generation sequencing and conventional methods. Theor Appl Genet 130:199–211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-016-2806-z
Xu X, Chao J, Cheng X, Wang R, Sun B, Wang H, Luo S, Xu X, Wu T, Li Y (2016) Mapping of a novel race specific resistance gene to phytophthora root rot of pepper (Capsicum annuum) using bulked segregant analysis combined with specific length amplified fragment sequencing strategy. PLoS One 11:e0151401. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0151401
Yang H, Zhao T, Jiang J, Wang S, Wang A, Li J, Xu X (2017) Mapping and screening of the tomato Stemphylium lycopersici resistance gene, Sm, based on bulked segregant analysis in combination with genome resequencing. BMC Plant Biol 17:266. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-017-1215-z
Yang X, Xia X, Zhang Z, Nong B, Zeng Y, Wu Y, Xiong F, Zhang Y, Liang H, Pan Y, Dai G, Deng G, Li D (2019) Identification of anthocyanin biosynthesis genes in rice pericarp using PCAMP. Plant Biotechnol J 17:1700–1702. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13133
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by Key Research Project of Specialty Industry (YCX2019T05) of Shanxi Academy of Agricultural Sciences and was conceived by Genquan Wang. On the basis of consulting a large number of scientific literatures, Xiaoyu Wang is responsible for summary, innovation and paper writing. All authors agree on the final manuscript.
Funding
Key Research Project of Specialty Industry of Shanxi Academy of Agricultural Sciences.
Number: YCX2019T05.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Wang, G. Application of NGS-BSA and proposal of Modified QTL-seq. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 32, 31–39 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-022-00778-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-022-00778-1