Abstract
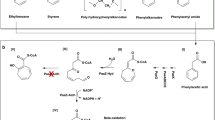
The phenolic acid decarboxylase (PAD) is a 44 kDa homodimeric, thermolabile and acid-resistant enzyme that some bacteria have developed as a detoxification system against phenolic acids produced by plants. It seems that the specificity of the PAD for their different substrates may be determined by an initial binding of the substrate to a cavity located in the vicinity of the active site. In order to test this hypothesis, PAD structures from Lactobacillus plantarum and 10 phylogenetically related bacteria were modeled and used for blind docking assays with p-coumaric acid as well as with 3 p-coumaric analogs and 42 property-matched decoys, to evaluate both the efficiency as the specificity with which the substrate can bind to the cavity. We show that both the efficiency and the specificity are low with raw models (not optimized) of the protein structures, but they are significantly increased when an equilibrium molecular dynamics simulation of the model of the protein in explicit solvent is previously conducted to the docking assay. The docking results showed that the binding efficiencies for the cis and trans conformations of the p-coumaric acid are different and suggest that the affinity of this substrate in the PADs from different bacteria may depend on the presence of charged amino acid residues in the cavity.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EMD:
-
Equilibrium molecular dynamics
- FAD:
-
Ferulic acid decarboxylase
- MSA:
-
Multiple sequence alignment
- PAD:
-
Phenolic acid decarboxylase
- PDC:
-
p-Coumaric acid decarboxylase
- RMSD:
-
Root median square deviation
- QMEAN4:
-
Qualitative model energy analysis
- GMQE:
-
Global model quality estimation
References
Acharya KR, Lloyd MD (2005) The advantages and limitations of protein crystal structures. Trends Pharmacol Sci 26(1):10–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2004.10.011
Adcock SA, McCammon JA (2006) Molecular dynamics: survey of methods for simulating the activity of proteins. Chem Rev 106(5):1589–1615. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr040426m
Avello M, Suwalsky M (2006) Radicales libres, antioxidantes naturales y mecanismos de protección. Atenea (Concepc) [online](n.494):161–172
Awad R, Gans P, Reiser JB (2017) Structural insights into the substrate recognition and reaction specificity of the PLP-dependent fold-type I isoleucine 2-epimerase from Lactobacillus buchneri. Biochimie 137:165–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2017.03.015
Barthelmebs L, Divies C, Cavin JF (2000) Knockout of the p-coumarate decarboxylase gene from Lactobacillus plantarum reveals the existence of two other inducible enzymatic activities involved in phenolic acid metabolism. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(8):3368–3375
Benkert P, Tosatto SC, Schomburg D (2008) QMEAN: a comprehensive scoring function for model quality assessment. Proteins 71(1):261–277. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.21715
Biasini M, et al. (2014) SWISS-MODEL: modelling protein tertiary and quaternary structure using evolutionary information. Nucleic Acids Res 42(Web Server issue):W252-8 https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku340
Brunger AT, Adams PD (2002) Molecular dynamics applied to X-ray structure refinement. Acc Chem Res 35(6):404–412
Cavasotto CN, Phatak SS (2009) Homology modeling in drug discovery: current trends and applications. Drug Discov Today 14(13–14):676–683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2009.04.006
Chen VB et al (2010) MolProbity: all-atom structure validation for macromolecular crystallography. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 66(Pt 1):12–21. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444909042073
de Beer TA, Berka K, Thornton JM, Laskowski RA (2014) PDBsum additions. Nucleic Acids Res 42(Database issue):D292-6 https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt940
de las Rivas B, Rodriguez H, Curiel JA, Landete JM, Munoz R (2009) Molecular screening of wine lactic acid bacteria degrading hydroxycinnamic acids. J Agric Food Chem 57(2):490–494. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf803016p
Frank A, Eborall W, Hyde R, Hart S, Turkenburg JP, Grogan G (2012) Mutational analysis of phenolic acid decarboxylase from Bacillus subtilis (BsPAD), which converts bio-derived phenolic acids to styrene derivatives. Catal Sci Technol 2(8):1568–1574. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CY20015E
Grosdidier A, Zoete V, Michielin O (2007) EADock: docking of small molecules into protein active sites with a multiobjective evolutionary optimization. Proteins 67(4):1010–1025. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.21367
Grosdidier A, Zoete V, Michielin O (2011a) Fast docking using the CHARMM force field with EADock DSS. J Comput Chem 32(10):2149–2159. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21797
Grosdidier A, Zoete V, Michielin O (2011b) SwissDock, a protein-small molecule docking web service based on EADock DSS. Nucleic Acids Res 39(Web Server issue):W270-7 https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr366
Gu W et al (2011) Structural basis of enzymatic activity for the ferulic acid decarboxylase (FADase) from Enterobacter sp. Px6-4. PLoS ONE 6(1):e16262. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0016262
Gury J et al (2009) Inactivation of PadR, the repressor of the phenolic acid stress response, by molecular interaction with Usp1, a universal stress protein from Lactobacillus plantarum, in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(16):5273–5283. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00774-09
Hu Y et al (2018) The catalytic activity for ginkgolic acid biodegradation, homology modeling and molecular dynamic simulation of salicylic acid decarboxylase. Comput Biol Chem 75:82–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2018.05.003
Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K (1996) VMD: visual molecular dynamics. J Mol Graph 14(1):33-8, 27-8
Irwin JJ, Shoichet BK (2005) ZINC–a free database of commercially available compounds for virtual screening. J Chem Inf Model 45(1):177–182. https://doi.org/10.1021/ci049714+
Jung DH et al (2013) Bioconversion of p-coumaric acid to p-hydroxystyrene using phenolic acid decarboxylase from B. amyloliquefaciens in biphasic reaction system. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(4):1501–1511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4358-8
Kalinin S et al (2017) Lucky switcheroo: dramatic potency and selectivity improvement of imidazoline inhibitors of human carbonic anhydrase VII. ACS Med Chem Lett 8(10):1105–1109. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.7b00300
Korendovych IV (2018) Rational and semirational protein design. In: Bornscheuer UT, Höhne M (eds) Protein engineering: methods and protocols. Springer, New York, pp 15–23
Kumar S, Pandey AK (2013) Chemistry and biological activities of flavonoids: an overview. Sci World J 2013:162750. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/162750
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33(7):1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Le SQ, Gascuel O (2008) An improved general amino acid replacement matrix. Mol Biol Evol 25(7):1307–1320. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msn067
Liu K, Watanabe E, Kokubo H (2017) Exploring the stability of ligand binding modes to proteins by molecular dynamics simulations. J Comput Aided Mol Des 31(2):201–211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-016-0005-2
Matte A, Grosse S, Bergeron H, Abokitse K, Lau PC (2010) Structural analysis of Bacillus pumilus phenolic acid decarboxylase, a lipocalin-fold enzyme. Acta Crystallogr, Sect F: Struct Biol Cryst Commun 66(Pt 11):1407–1414. https://doi.org/10.1107/S174430911003246X
Mulero J, Zafrilla P, Cayuela JM, Martinez-Cacha A, Pardo F (2011) Antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds in organic red wine using different winemaking techniques. J Food Sci 76(3):C436–C440. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3841.2011.02104.x
Mysinger MM, Carchia M, Irwin JJ, Shoichet BK (2012) Directory of useful decoys, enhanced (DUD-E): better ligands and decoys for better benchmarking. J Med Chem 55(14):6582–6594. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm300687e
Pettersen EF et al (2004) UCSF Chimera–a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25(13):1605–1612. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20084
Phillips JC et al (2005) Scalable molecular dynamics with NAMD. J Comput Chem 26(16):1781–1802. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20289
Radom F, Pluckthun A, Paci E (2018) Assessment of ab initio models of protein complexes by molecular dynamics. PLoS Comput Biol 14(6):e1006182. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006182
Rodriguez H et al (2010) p-Coumaric acid decarboxylase from Lactobacillus plantarum: structural insights into the active site and decarboxylation catalytic mechanism. Proteins 78(7):1662–1676. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.22684
Sakano T, Mahamood MI, Yamashita T, Fujitani H (2016) Molecular dynamics analysis to evaluate docking pose prediction. Biophys Physicobiol 13:181–194. https://doi.org/10.2142/biophysico.13.0_181
Salgado JM, Rodriguez-Solana R, Curiel JA, de las Rivas B, Munoz R, Dominguez JM (2012) Production of vinyl derivatives from alkaline hydrolysates of corn cobs by recombinant Escherichia coli containing the phenolic acid decarboxylase from Lactobacillus plantarum CECT 748T. Bioresour Technol 117:274–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.04.051
Shukla P (2018) Editorial: futuristic protein engineering: developments and avenues. Curr Protein Pept Sci 19(1):3–4. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920371901171121142734
Sievers F et al (2011) Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol Syst Biol 7:539. https://doi.org/10.1038/msb.2011.75
Sledz P, Caflisch A (2018) Protein structure-based drug design: from docking to molecular dynamics. Curr Opin Struct Biol 48:93–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2017.10.010
Winkler J, Kao KC (2011) Transcriptional analysis of Lactobacillus brevis to N-butanol and ferulic acid stress responses. PLoS ONE 6(8):e21438. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0021438
Xiang Z (2006) Advances in homology protein structure modeling. Curr Protein Pept Sci 7(3):217–227
Yadav R, Shukla P (2017) Probiotics for human health: current progress and applications. In: Shukla P (ed) Recent advances in Applied Microbiology. Springer Singapore, Singapore, pp 133–147
Yadav R, Singh PK, Puniya AK, Shukla P (2017) Catalytic interactions and molecular docking of bile salt hydrolase (BSH) from L. plantarum RYPR1 and its prebiotic utilization. Front Microbiol 7:2116 https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.02116
Zhao H, Caflisch A (2015) Molecular dynamics in drug design. Eur J Med Chem 91:4–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.08.004
Acknowledgement
To the memory of Ph. D. José Luis Muñoz-Sánchez, who started this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr. Parada-Fabián, Dr. Sánchez-Hernández and Dr. Méndez Tenorio have nothing to disclose.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parada-Fabián, J.C., Hernández-Sánchez, H. & Méndez-Tenorio, A. Substrate specificity of the phenolic acid decarboxylase from Lactobacillus plantarum and related bacteria analyzed by molecular dynamics and docking. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 28, 91–104 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-018-0466-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-018-0466-6