Abstract
Introduction
Seborrheic dermatitis (SEBD) is a chronic, recurrent skin disorder that typically occurs as an inflammatory response to fungi of the genus Malassezia. The development of an ex vivo model that mimics the fungal proliferation and skin inflammation of SEBD would play an important role in screening formulations for their efficacy in treating SEBD.
Methods
An ex vivo model for SEBD using human skin explants that had been mechanically manipulated to facilitate colonization of Malassezia furfur was developed. This model was used to evaluate the efficacy of a novel non-steroidal facial cream (NSFC) in inhibiting M. furfur proliferation and reducing inflammatory cytokine levels.
Results
This model reproduced some of the key pathological features of SEBD, including M. furfur proliferation and inflammatory cytokine production. Topical application of NSFC facial cream reduced M. furfur counts by 92% (p < 0.05) and levels of interleukin 8 (IL-8) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) by 82% and 40%, respectively (p < 0.05, both).
Conclusion
The proposed ex vivo model for SEBD could be a useful tool to evaluate topical antifungal treatments. The novel NSFC tested in this study reduced M. furfur proliferation and inflammatory cytokine levels following topical application and may be helpful in the management of SEBD.
Funding
ISDIN.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Seborrheic dermatitis (SEBD) is a commonly occurring, chronic papulosquamous dermatosis characterized by red skin, dry white scales, and rash that affect sebaceous gland-rich areas of the face, scalp, and the upper chest, with a reported prevalence between 1% and 3% in the adult population [1, 2]. The etiology of SEBD is complex, involving interplay between genetic, hormonal, immune, and environmental factors [3]. A key pathogenic component of SEBD is believed to be proliferation of yeast of the genus Malassezia that concentrate in hair follicles and sebum-rich areas of the body [1, 3, 4]. Malassezia are lipid-dependent fungi, requiring free fatty acids (FFAs) generated from the hydrolysis of sebaceous triglycerides [5,6,7,8,9]. FFAs irritate the skin and damage the stratum corneum, thereby disrupting epithelial barrier function and inducing abnormal keratinization [10,11,12,13]. Inflammatory cytokines have been reported in skin biopsies from SEBD lesions in patients, suggesting that an inflammatory response is also involved [8].
Standard treatment options for SEBD include topical therapy with antifungal and anti-inflammatory agents such as ketoconazole or corticosteroids [14]. Non-steroidal treatment options that help maintain skin free of Malassezia may help prevent flare-ups and can be helpful in the management of the disease. However, as a result of the complex nature of SEBD, no in vitro models currently exist to screen products for possible efficacy in the management of SEBD. Here we describe the development of an ex vivo model for SEBD using human skin explants infected with Malassezia spp. fungi. This model reproduces the fungal proliferation and inflammatory responses of SEBD. Following its validation, we tested the efficacy of a novel non-steroidal facial cream (NSFC), containing stearyl glycyrrhetinate, piroctone olamine, and biosaccharide gum-2, that is designed to reinforce the skin barrier and reduce fungal proliferation and inflammation. Our data suggest that this SEBD model may prove useful for the future development of SEBD treatments.
Methods
Human Skin Explants
Human skin explants were obtained, with informed consent from healthy female donors undergoing abdominoplasty, under authorization granted by the French government ethical committee according to French law L.1245 CSP. The explants were sourced from Biopredic, France. Within 2 h of surgery, skin was cut into 0.8 cm2 pieces and placed epidermis side up in 6-well Transwell plates containing 1.5 ml of Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM; GIBCO, Grand Island, NY, USA), supplemented with 2 mM l-glutamine (GIBCO) and antibiotics (100 IU/ml penicillin G and 100 lU/ml streptomycin; GIBCO). Explants were incubated at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2 for 48 h prior to study initiation.
Malassezia furfur
M. furfur (DSM 6170) was obtained from Leibniz Institute DSMZ-German Collection of Microorganisms and Cell Cultures (Brunswick, Germany) and cultivated in specific modified Dixon medium (m-Dixon; Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, USA). Fungal cultures were incubated at 30 °C for 42–48 h.
Topical Products
The investigational product tested was an NSFC containing stearyl glycyrrhetinate, piroctone olamine, and biosaccharide gum-2 (full composition in Table 1). NSFC without anti-inflammatory ingredients (NSFC-AI) had a similar composition to NSFC, with the exception of ingredients with known or suspected anti-inflammatory effects (Table 1). Petrolatum (Vaselina pura filante Acofarderm), ketoconazole 2% cream (Fungarest 20 mg/g®), and hydrocortisone (HC) 1% cream (Cortaid Hydrocortisone Maximum Strength Anti-Itch Cream) were purchased at a local pharmacy.
SEBD Model Development and Product Testing
Skin explants were stripped using D-squame tapes (Clinical and Derm LLC, Dallas, USA) to remove approximately 40% of the stratum corneum (confirmed by tape absorbance measurement). Control skin samples were not stripped. At 48 h after stripping, skin explants were inoculated with 1 × 106 colony forming units (CFU) of M. furfur and incubated at 37 °C, 5% CO2, and 95% humidity. At 24 h after inoculation, test products (dose 2 mg/cm2) were applied topically to explants using a micropipette and spread with a microspatula. Control explants were not treated. Two independent studies and at least three replicates for each product were performed.
Determination of Skin Viability
Skin viability was determined using a commercially available lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) assay kit (CytoTox 96® Non-Radioactive Cytotoxicity Assay, Promega, WI, USA) according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Skin viability was additionally measured using a resazurin assay. Briefly, skin explants were treated with 6 µM of resazurin NaCl solution (Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, USA) for 1 h, and the concentration of resorufin (RES) formed was quantified in a fluorometer plate reader (530 nm excitation wavelength and 590 nm emission wavelength).
Malassezia furfur Quantification and Visual Analysis
Viable fungal cells were recovered from skin explants by tape stripping. Tape strips were immersed in a solution of physiological buffered saline and 0.1% Triton X-100 and the number of CFUs determined by serial dilution in m-Dixon followed by direct plating. Plates were incubated at 30 °C for 42–48 h. Presence of M. furfur on skin explants was visualized by staining with Crystal Violet (0.5%; Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, USA).
Cytokine Quantification
Cytokine levels (TNF-α, IL-8, and IL-6) in explant culture media were determined using a commercially available ELISA kit according to the manufacturer’s specifications (Thermo Fisher Scientific, MA, USA). Results were expressed as average interleukin concentration (picograms per milliliter).
Statistical Analyses
Results are reported as mean ± standard deviation (SD). The homogeneity of variance was confirmed by the Levene’s test and the normality confirmed by the Anderson–Darling test. Unpaired t tests and one-factor analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Bonferroni–Dunn’s correction were performed to assess differences between groups. A p value less than 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
Model Development
Although Malassezia spp. are part of normal skin microbiota, they manifest themselves pathogenically only in some individuals, suggesting that compromised skin integrity may be responsible for facilitating colonization by Malassezia spp. in SEBD. Considering this, we decided to mechanically disrupt the integrity of the skin by tape stripping to facilitate fungal invasion. To confirm that stripping the skin did not negatively impact skin viability, we quantified LDH levels in the culture media and RES levels in skin tissue. LDH and RES levels in tape-stripped skin were higher and lower, respectively, than those of unstripped control skin at 24 h but had returned to normal by 48 h (Supplementary Table S1). Levels of IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α were higher at 24 h but had returned to normal by 48 h (Supplementary Table S2). Together these data suggest that by 48 h the skin had recovered sufficiently from the process of tape stripping to examine its impact upon M. furfur colonization.
At 48 h after tape stripping, explants were inoculated with M. furfur and colonies counted 24 h later. Fungal colony counts in tape-stripped skin were increased by 204.35% compared to non-inoculated skin. This was significantly more than non-tape-stripped skin (+61.24%, p < 0.05), confirming that skin surface damage was necessary to achieve the high fungal counts representative of SEBD. Levels of inflammatory cytokines were also increased in response to fungal inoculation (Supplementary Table S3), confirming the inflammatory effect of fungal infection in SEBD. TNF-α, IL-8, and IL-6 levels, however, did not differ between stripped and unstripped skin (Supplementary Table S3), suggesting that inflammation is a direct result of M. furfur colonization and not tape stripping.
Model Validation
Next, we sought to determine the reproducibility of the model by performing multiple infection replicates in different explant samples. On the basis of four separate studies, fungal colony counts did not significantly differ (92–105% of mean) up to 96 h post-inoculation (Supplementary Table S4), indicating good repeatability and reproducibility of the model, and suggesting that M. furfur proliferates in a controlled manner in human skin explants.
Having developed and validated our model, we sought to test its utility to screen topical agents for their antifungal activity. Topical treatment with ketoconazole 2% (a product with known antifungal properties [15]) reduced fungal CFUs by 76.3%. Petroleum jelly, however, did not decrease CFUs.
NSFC Antifungal Effect
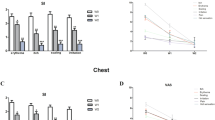
We then used our model to test the antifungal activity of a novel NSFC for treating SEBD. NSFC contains stearyl glycyrrhetinate, piroctone olamine, and biosaccharide gum-2, and is designed to reinforce the skin barrier and reduce fungal proliferation and inflammation. At 24 h after application, NSFC reduced the number of M. furfur colonies by 92% compared to non-treated control skin (p < 0.05; Fig. 1). To demonstrate that this was a direct result of the antifungal activity of NSFC rather than its anti-inflammatory properties, we also treated M. furfur-infected skin explants with NSFC-AI (NSFC without its anti-inflammatory components) and HC 1% (a known anti-inflammatory agent). NSFC-AI reduced M. furfur numbers by 91.5% compared to non-treated control skin. The HC 1% cream did not reduce colony counts, however. Together these data suggest that the ability of NSFC to reduce M. furfur numbers in skin is directly attributable to its antifungal properties.
Antifungal effect. a M. furfur CFUs in SEBD model control vs. treated with NSFC, NSFC-AI, and HC 1% cream (*p < 0.05). b Macroscopic pictures of SEBD model taken after staining with Crystal Violet stain before M. furfur inoculation (i) No M. furfur inoculation; (ii) M. furfur control; (iii) M. furfur + NSFC; (iv) M. furfur + NSFC-AI; (v) M. furfur + hydrocortisone 1% cream; (vi) M. furfur + Petrolatum group
NSFC Anti-Inflammatory Effect
To examine the anti-inflammatory properties NSFC, we measured TNF-α and IL-8 levels in the culture media 24 h after product application. Both NSFC and NSFC-AI reduced TNF-α and IL-8 to levels equivalent to those of HC (Fig. 2). Since NSFC-AI does not contain any anti-inflammatory agents, this observation suggests that the reduction in inflammation by NSFC is a direct result of its antifungal effect rather than its anti-inflammatory properties.
Discussion
Here we report the development of a novel ex vivo model that reproduces a number of the salient pathological features of SEBD. This model, based on human skin explants inoculated with M. furfur, can be established in a relatively short time span (3 days) and is suitable for testing the efficacy of agents in treating SEBD. To our knowledge an ex vivo model of SEBD that mimics the fungal proliferation and cutaneous inflammation of SEBD has not been described previously.
In order to establish fungal colonies in pathologically relevant numbers in this model, the integrity of the skin first had to be compromised. Although stripping of the skin explants caused an inflammatory response that could potentially interfere with the testing of topical products, skin viability and cytokine levels had returned to their basal levels within 48 h, suggesting that skin homeostasis had been restored by this time. Although several species of the Malassezia genus have been associated with SEBD, M. furfur has been shown to be one of the predominant species in SEBD [16, 17] and thus was chosen to generate this model. Future models using different Malassezia species or even clinical isolates would further extend its suitability.
Our model demonstrated good reproducibility, with consistent M. furfur numbers between experimental replicates, making it highly suitable for preclinical testing. A potential limitation of this model, however, is that it uses skin derived from anatomical areas not normally affected by SEBD. Since skin-resident immune cell populations and skin-associated microbiota are influenced by skin region [18, 19], it is likely that differences exist in skin taken from regions normally affected by SEBD. Another limitation of the model is that it does not represent all aspects of pathogenesis of seborrheic dermatitis which is clearly very complex. However it represents part of it as MF colonization is a well-established component of seborrheic dermatitis pathogenesis, although aspects of why Malassezia is pathogenic in some individuals and commensal in others and the role played by the rest of the skin microbiota in pathogenesis are not clear today. Nevertheless, we believe that the simplicity of this model and the ready availability of abdominal skin make it suitable for screening. Indeed, the efficacy of the novel NSFC tested in this study is supported by results from clinical trials. Here, NSFC demonstrated significant effects on desquamation, erythema, and pruritus in subjects with mild-to-moderately inflamed facial SEBD [20].
Topical application of NSFC in this model led to a significant reduction in M. furfur counts and a subsequent reduction in inflammatory cytokine levels. Interestingly, anti-inflammatory effects were also observed with NSFC-AI. NSFC-AI comprises the same formulation as NSFC but without its anti-inflammatory ingredients, suggesting that skin inflammation in SEBD is predominantly secondary to fungal proliferation.
Conclusions
We have generated a novel ex vivo model for SEBD, based on human skin explants inoculated with M. furfur. The SEBD model was employed to test the antifungal efficacy of an NSFC that uses skin barrier enhancing properties to protect against fungal proliferation. The NSFC demonstrated remarkable efficacy in reducing fungal load and decreasing levels of cutaneous inflammation. This non-steroidal cream with skin barrier enhancing properties can be helpful in the management of SEBD and complement the current topical armamentarium for SEBD.
References
Gupta AK, Bluhm R. Seborrheic dermatitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2004;18:13–20.
Dessinioti C, Katsambas A. Seborrheic dermatitis: etiology, risk factors, and treatments: facts and controversies. Clin Dermatol. 2013;31:343–51.
Borda LJ, Wikramanayake TC. Seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff: a comprehensive review. J Clin Investig Dermatol. 2015;3(2):10.
Heng MC, Henderson CL, Barker DC, et al. Correlation of Pityosporum ovale density with clinical severity of seborrheic dermatitis as assessed by a simplified technique. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;23:82–6.
Schwartz RA, Janusz CA, Janniger CK. Seborrheic dermatitis: an overview. Am Fam Physician. 2006;74:125–30.
Kim GK. Seborrheic dermatitis and malassezia species: how are they related? J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2009;2:14–7.
Faergemann J, Bergbrant IM, Dohse M, et al. Seborrhoeic dermatitis and Pityrosporum (Malassezia) folliculitis: characterization of inflammatory cells and mediators in the skin by immunohistochemistry. Br J Dermatol. 2001;144:549–56.
Bikowski J. Facial seborrheic dermatitis: a report on current status and therapeutic horizons. J Drugs Dermatol. 2009;8:125–33.
Trznadel-Grodzka E, Blaszkowski M, Rotsztejn H. Investigations of seborrheic dermatitis. Part I. The role of selected cytokines in the pathogenesis of seborrheic dermatitis. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2012;66:843–7.
Riciputo RM, Oliveri S, Micali G, et al. Phospholipase activity in Malassezia furfur pathogenic strains. Mycoses. 1996;39:233–5.
Plotkin LI, Squiquera L, Mathov I, et al. Characterization of the lipase activity of Malassezia furfur. J Med Vet Mycol. 1996;34:43–8.
Lee YW, Lee SY, Lee Y, et al. Evaluation of expression of lipases and phospholipases of Malassezia restricta in patients with seborrheic dermatitis. Ann Dermatol. 2013;25:310–4.
Ortiz G, Martin MC, Carrillo-Munoz AJ, et al. [Phospholipase and proteinase production by Malassezia pachydermatis isolated in dogs with and without otitis]. Rev Iberoam Micol. 2013;30:235–8.
Borda LJ, Perper M, Keri JE. Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis: a comprehensive review. J Dermatol Treat. 2019:30(2):158–69.
Dall’Oglio F, Lacarrubba F, Verzi AE, et al. Noncorticosteroid combination shampoo versus 1% ketoconazole shampoo for the management of mild-to-moderate seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp: results from a randomized, investigator-single-blind trial using clinical and trichoscopic evaluation. Skin Append Disord. 2016;1:126–30.
Lian C, Shen L, Gao Q, et al. Identification of Malassezia species in the facial lesions of Chinese seborrhoeic dermatitis patients based on DNA sequencing. Mycoses. 2014;57:759–64.
Bhatia N. Treating seborrheic dermatitis: review of mechanisms and therapeutic options. J Drugs Dermatol. 2013;12:796–8.
Tong PL, Roediger B, Kolesnikoff N, et al. The skin immune atlas: three-dimensional analysis of cutaneous leukocyte subsets by multiphoton microscopy. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:84–93.
Abdallah F, Mijouin L, Pichon C. Skin immune landscape: inside and outside the organism. Mediat Inflamm. 2017;2017:5095293.
Dall’Oglio F, Lacarrubba F, Luca M, et al. Clinical and instrumental evaluation of a new topical non-corticosteroid antifungal/anti- inflammatory/antiseborrheic combination cream for the treatment of mild-to-moderate facial seborrheic dermatitis. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2019;12:103–8.
Acknowledgements
Funding
This study and the Rapid Service Fee were funded by ISDIN, Barcelona, Spain. The authors would like to acknowledge the contribution of Ms. G. Martinez-Masana in management of the experimental work performed in this study. All authors had full access to all of the data in this study and take complete responsibility for the integrity of the data and accuracy of the data analysis.
Authorship
All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this article, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given their approval for this version to be published.
Author Contributions
F. Goñi-de-Cerio performed the research. C. Granger and A. Garre designed the research study. M. Narda and A.Garre analyzed the data. M. Narda wrote the paper.
Disclosures
Dr. C. Granger is an employee of ISDIN. Dr. A. Garre is an employee of ISDIN. Dr. M. Narda is an employee of ISDIN. Dr. A. Balato has given conferences in symposia sponsored by Abbvie, Janssen, Lilly, Sanofi, and has been a consultant for Abbvie, ISDIN, Novartis, Lilly. F. Goñi-de-Cerio has nothing to disclose.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
Human skin explants were obtained, with informed consent, from healthy female donors undergoing abdominoplasty, under authorization granted by French government ethical committee according to French law L.1245 CSP. The explants were sourced from Biopredic, France. The anonymity of patients is maintained and patients sign an informed consent form before donating their samples.
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article/as supplementary information files.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Enhanced digital features
To view enhanced digital features for this article go to https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.8307485.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ ), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Granger, C., Balato, A., Goñi-de-Cerio, F. et al. Novel Non-Steroidal Facial Cream Demonstrates Antifungal and Anti-Inflammatory Properties in Ex Vivo Model for Seborrheic Dermatitis. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) 9, 571–578 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13555-019-0311-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13555-019-0311-4