Abstract
Acne is a very common non-infectious skin condition that is frequently treated in dermatological practices. Because acne is often chronic and may persist for years, safe and effective long-term maintenance therapy is often required. Given the increasing frequency of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and the gravity of the consequences of this trend, it behooves dermatologists to maximize use of non-antimicrobial therapy when treating acne. In this review of the literature we present data regarding the efficacy and appropriate use of non-antimicrobial treatments for acne. A variety of topical and oral treatment options exist that can be used in a step-wise manner according to the patients’ severity and therapeutic response. Non-antimicrobial treatments can be highly efficacious at controlling acne, especially when used as maintenance therapy. While antibiotics have a role in acne treatment, they should not be used as monotherapy, and lengthy courses of antibiotic use are discouraged.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Antibiotic overuse and the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, coupled with a dearth of new antimicrobial agents, have resulted in a serious domestic and global threat [1]. The scale and magnitude of this threat is severe. A recent statement issued from the Centers for Disease Control reported that roughly 23,000 deaths occur annually in the USA alone as a direct result of antibiotic-resistant bacteria [1]. The trend of increasingly antibiotic-resistant bacteria is ongoing; even last-resort antibiotics, such as colistin, which are used to treat multidrug-resistant infections, are becoming ineffective. For example, E. coli harboring the MCR-1 plasmid, which confers resistance to colistin, has recently been discovered for the first time in a human in the USA [2].
Dermatologists are in a unique position to respond to the rising threat of antibiotic-resistant bacteria: dermatologists make up just 1% of all physicians but are responsible for 4.9% of antibiotic prescriptions [3]. Dermatologists primarily prescribe antibiotics for the treatment of acne, and this prescribing practice may have contributed to the rise of antibiotic resistance. Responsible antibiotic stewardship is increasingly becoming recognized as an important principle to incorporate into dermatology practices.
Acne is one of the most common skin disorders treated by dermatologists, affecting between 40–50 million Americans [4]. While acne is highly prevalent in youth with around 85% of teenagers affected at some point in time, its occurrence is not uncommon in adults [5, 6].
The pathogenesis of acne is a multifactorial process that involves the pilosebaceous unit and results in a combination of non-inflammatory (open and closed comedones) and inflammatory (papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts) lesions. Several distinct processes contribute to the development of acne, including the colonization of the skin with Propionibacterium acnes, heightened levels of inflammation, increased sebum production and abnormal keratinization. Inflammation is especially important in the disease process, and several syndromes that are characterized by profound systemic inflammation and concurrent severe acne have been described: pyogenic arthritis, pyoderma gangrenosum, acne (PAPA syndrome); pyoderma gangrenosum, acne, suppurative hidradenitis (PASH syndrome); pyogenic arthritis, pyoderma gangrenosum, acne, suppurative hidradenitis (PAPASH syndrome); synovitis, acne, pustulosis palmoplantaris, hyperostosis, osteitis (SAPHO syndrome).
Acne can be successfully treated using a multipronged approach by targeting its underlying key mechanisms. Although acne is not caused by an overabundance of P. acnes, antibiotics have long played a central role in acne therapy and have often been used as monotherapy. Systemic antibiotics used for acne treatment include tetracyclines (tetracycline, doxycycline and minocycline), macrolides (erythromycin and less often clindamycin) and occasionally sulfonamides (trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole). The therapeutic effect of systemic antibiotics is thought to be due primarily to their anti-inflammatory properties, and this is especially true for the tetracyclines. Topical antibiotics include clindamycin and erythromycin.
Antibiotic overuse in the treatment of acne has led to changing resistance patterns in P. acnes. While only 20% of P. acnes showed antibiotic resistance in 1978, roughly 2/3 are resistant today [7–9]. Both systemic and topical antibiotics are capable of changing the antibiotic-resistance patterns in bacteria. Topical erythromycin has been shown to produce overgrowth of antibiotic resistance bacteria both locally and at distant sites [10, 11]. Similar resistance trends are also likely to result from topical clindamycin monotherapy.
Collateral damage to normal skin flora also occurs as a result of antibiotic use. The normal skin biome serves as an innate defense, and changes in the skin biome brought on by antibiotics can increase the risk of colonization by pathologic organisms [12]. For example, long courses of tetracycline induce gram-negative bacterial overgrowth in the nares, and this is associated with gram-negative folliculitis [13, 14]. Antibiotics used in the treatment of acne are also associated with the overgrowth of Streptococcus pyogenes and Staphylococcus aureus in the oral pharynx, and these changes may be linked to clinical pharyngitis [15–17]. Furthermore, increased rates of antibiotic-resistant bacteria colonization is seen in family members of acne patients who are treated with antibiotics [18].
Given the risk associated with antibiotic use, careful consideration must be given to the use of this class of medications when treating acne. In this systematic review of the literature we present the efficacy data from randomized clinical trials investigating non-antimicrobial treatments for acne, highlighting the appropriate use of these treatments as alternatives to long courses of systemic antibiotics.
Methods
Search Strategies
A comprehensive search of the English-language literature was performed on PubMed using the following search terms: “acne,” “treatment” and “randomized” as well as “photodynamic therapy,” “blue light” and “zinc” or “peel”. Bibliographies of select publications were reviewed for eligible studies.
Data Sources
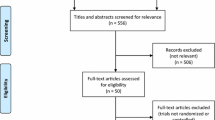
We included randomized clinical studies published before April 2016 that evaluated presently available first- and second-line topical, oral and physical treatment modalities for acne. Inclusion criteria required a numeric report of either the change in total lesion count (TLC) for topical and oral treatments or the change in inflammatory lesion count (ILC) for studies evaluating physical treatment modalities. Only studies that provided the number of patients in each treatment group were included in our final review. Studies examining investigational treatments or therapies not currently available in the USA were excluded. Similarly, studies that solely examined antimicrobial dosing of antibiotics or studies that did not meet the above criteria were excluded from this review. This article is based on previously conducted studies and does not involve any new studies of human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Data Extraction
Data collection included the number of patients per treatment group, details of treatment regimens, severity and location of acne, change in TLC or ILC following treatment, and tolerability of treatment.
Results
A total of 192 studies were found, of which 57 met the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Study size ranged from 10 to 3010 patients, and treatment duration ranged from 6 weeks to 6 months. When applicable, efficacy results from trials examining matching treatment regiments were reviewed together using a weighted average. The majority of acne treatment studies included either patients with mild to moderate acne or those with moderate to severe acne. Mild to moderate acne is characterized by a predominance of open and closed comedones, some papules and pustules, and few to no cysts or nodules. Patients with predominantly inflammatory lesions, several nodules or cystic lesions or patients who have scarring acne are considered to have moderate or severe acne. The results below are grouped either based on the trend of acne severity included in the associated studies or based on select adjuvant treatment modalities such as hormonal or physical treatment therapies.
Mild to Moderate Acne Treatment
First-line treatment options for mild to moderate acne include a variety of topical monotherapies and combination products: retinoids, benzoyl peroxide (BPO), clindamycin, clindamycin combined with BPO and adapalene combined with BPO (Table 1). Because clindamycin monotherapy is discouraged, its efficacy will be reviewed here primarily because it is used in combination treatment regimens or combination products. Alternative topical treatments include salicylic acid, azelaic acid and dapsone. Low-dose isotretinoin and oral zinc represent alternative systemic treatment options.
Studies examining first-line treatment options for mild to moderate acne reported a range of efficacies, as measured by TLC reductions, with the most impressive outcomes often seen in combination therapies treatment arms (Fig. 1) [19]. Clindamycin 1% plus BPO 3% gel was the most efficacious combination treatment (68.9% decrease in TLC at 12 weeks) [20, 21]. Similarly, adapalene 0.1% and BPO 2.5% combination gel was highly efficacious (65.4% TLC reduction at 12 weeks) [22].
Comparison of efficacy of first-line mild to moderate acne treatments in reducing total acne lesion count. BPO benzoyl peroxide. Clindamycin 1% + BPO 3% gel: Schaller et al. [20], Eichenfield et al. [21]; clindamycin 1% + BPO 5% gel BID: Langner et al. [30], Jackson et al. [38]; clindamycin 1% + tretinoin 0.025% lotion: Jackson et al. [38], NilFroushzadeh et al. [39]; clindamycin 1% + BPO 5% gel: Langner et al. [30]; clindamycin 1% lotion + adapalene 0.1% gel: Wolf et al. [40]. BPO 3% gel: Eichenfield et al. [28]; BPO 2.5% gel: Gollnick et al. [22], Babaeinejad and Fouladi [29]. Tretinoin 0.1% cream: Webster et al. [36]; tretinoin 0.025% gel: Cunliffe et al. [35], Webster [36]; tretinoin 0.025% cream: Webster [36]; tretinoin 0.1% gel: Webster et al. [36]; tretinoin 0.05% gel: Webster et al. [31], Tirado-Sánchez and Ponce-Olivera [33]; tretinoin 0.04% microsphere gel: Berger et al. [32]; adapalene 0.1% + BPO 2.5% combo gel: Gollnick et al. [22]; adapalene 0.3% gel: Thiboutot et al. [23], Pariser et al. [24], Tanghetti et al. [25], Tirado-Sánchez and Ponce-Olivera [33]; adapalene 0.1% lotion: Eichenfield et al. [28]; adapalene 0.1% gel: Gollnick et al. [22], Thiboutot et al. [23], Pariser et al. [24], Babaeinejad and Fouladi [29], Langner et al. [30], Tirado-Sánchez and Ponce-Olivera [33], Cunliffe et al. [35]; adapalene 0.1% cream: Shalita et al. [26], Lucky et al. [34]; tazarotene 1% cream: Tanghetti et al. [25], Shalita et al. [26]; tazarotene 1% foam: Feldman et al. [27]; tazarotene 0.1% gel: Shalita et al. [37]; tazarotene 0.05% gel: Shalita et al. [37]. Asterisk Treatment length varied from 12 weeks to 16 weeks. Double dagger symbol Treatment length varied from 8 to 12 weeks. Dagger symbol Treatment length varied from 12 weeks to 90 days
Topical retinoids are a mainstay of acne treatment and have been in use since they were first approved by the FDA in 1971. Although thousands of retinoids have been synthesized or described, only three are approved for acne treatment in the USA: tretinoin, adapalene and tazarotene. The first retinoid to become available was a highly concentrated tretinoin solution whose use was limited by excessive skin irritation. With the development of new vehicles, such as creams and gels, the tolerability of tretinoin improved. In an effort to further reduce treatment-associated skin irritation, tretinoin can now also be delivered as a large polymer gel or cream or as a microsphere gel. Adapalene and tazarotene are third-generation retinoids, and each has distinct properties. Adapalene, which is available as a gel, lotion, cream or pledgets, has the unique property of being stable in the presence of light and BPO. Tazarotene, which is available as a cream, foam or gel, is also approved for treating psoriasis.
We reviewed efficacy data for the three retinoids currently used in the USA, and all were effective at decreasing the TLC when used as monotherapy (Fig. 1) [22–37]. Webster et al. reported a 71% TLC reduction with tretinoin 0.1% cream, which was the highest average TLC reduction reported for all of the retinoids [36]. TLC reductions were similar among tretinoin 0.05% gel, tretinoin 0.025% gel and cream, tretinoin 0.01% gel, tazarotene 1% foam, cream and gel, tazarotene 0.05% gel as well as adapalene 0.03% gel and adapalene 0.1% lotion and gel. Lower TLC reductions were seen with tretinoin 0.04% microsphere gel and adapalene 0.1% cream. Efficacies varied with the vehicle: adapalene 0.1% lotion and 0.1% gel were similarly efficacious (53.7% and 53.6% TLC reduction, respectively), and both were more efficacious than adapalene 0.1% cream (32.9% decrease in TLC). Similarly, tretinoin 0.025% gel was more efficacious than 0.025% cream (54.7% and 52.5% TLC reduction). Topical retinoids were overall well tolerated with the most commonly reported adverse reactions being local skin irritation, erythema and dryness. Retinoids will be discussed further in the “Discussion.”
BPO is an antimicrobial topical medication that is a common component of acne treatment regimens. There is no known bacterial resistance to BPO, and it is available over the counter as a cream, lotion, gel or wash at concentrations ranging from 2.5% to 10%. When evaluated as monotherapy, BPO was moderately efficacious in decreasing acne lesions [21, 22, 29]. Higher concentrations of BPO were noted to result in larger TLC reductions (61.8% vs. 50.3% for 3% gel and 2.5% gel, respectively) [21, 22, 29]. BPO was also well tolerated with common side effects including erythema and skin irritation.
Although topical clindamycin is not recommended as monotherapy because of the risk of antibiotic resistance, its efficacy as a single agent has been evaluated in clinical trials [20, 21, 30, 38–40]. Both clindamycin 1% nanoemulsion gel and conventional clindamycin gel were highly efficacious at decreasing TLC (69.3% vs. 51.9%, respectively), while clindamycin lotion only produced a modest improvement (28.6%) [39–41]. Clindamycin’s efficacy was enhanced with the addition of salicylic acid: clindamycin 1% combined with 2% salicylic acid lotion resulted in a TLC reduction of 77.9% [39]. Topical clindamycin was very well tolerated, with side effects including mild burning, stinging and scaling.
Azelaic acid is a non-antibiotic topical acne treatment that is available as a 20% cream and a 15% gel or foam, and it is often used as an adjuvant acne treatment. Azelaic acid has comedolytic, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. Twice daily application of azelaic acid 20% cream was found to be moderately effective at treating mild to moderate acne with a 53.9% decrease in TLC reported at 12 weeks [20]. Azelaic acid 15% and 20% formulations will be discussed further in the “Discussion.”
Second-line therapies showed modest to moderate improvement in TLC, with combination treatments resulting in the highest efficacies. Dapsone 5% gel alone resulted in a modest TLC reduction (39.0% at week 12), and this was enhanced with the addition of adapalene 0.1% gel (51.0% at week 12) [42, 43]. Topical dapsone was very well tolerated with common side effects including mild pruritus and burning at the application site, especially when combined with adapalene. Erythromycin 4% with zinc acetate 1.2% has been reported to produce moderate decreases in TLC (64.5% in 12 weeks) [44]. A seaweed-derived oligosaccharide complexed to 0.1% zinc pyrrolidone cream was also moderately effective (61.2% decrease in TLC in 8 weeks) [45].
Low-dose isotretinoin has been evaluated as a second-line systemic treatment for mild to moderate acne. Isotretinoin used at low and intermittent dosing (0.5 mg/kg daily for 1 out of every 4 weeks for 24 weeks) was shown to be highly efficacious (80.5% TLC reduction at week 24) [46]. This dosing regimen, however, is uncommonly used because of the prescribing restrictions that have resulted from the iPLEDGE system.
Oral zinc sulfate has also been evaluated as a second-line systemic treatment option for mild to moderate acne; 220 mg of zinc sulfate dosed three times daily produced a moderate TLC reduction (45.5% at 12 weeks) [47]. This treatment, however, was very poorly tolerated with 40% of subjects reporting nausea or vomiting.
Moderate to Severe Acne Treatment
Historically, long courses of antibiotics have been used as first-line therapy for patients with moderate to severe acne. Given the trend of increasing antibiotic resistance, antibiotic treatment as monotherapy is discouraged. In lieu of long courses of antibiotics, other first-line treatment options for moderate to severe acne include oral isotretinoin or a subantimicrobial oral antibiotic combined with the topical therapies used for mild to moderate acne.
Isotretinoin dosed at 0.5–1.0 mg/kg daily was more efficacious than doxycycline 200 mg plus adapalene 0.1%/benzoyl peroxide 2.5% gel at reducing TLC (92.9% vs. 78.2%) [48]. Low-dose isotretinoin (20 mg daily) combined with a 20% salicylic acid peel applied every 2 weeks was more efficacious than low-dose isotretinoin alone (92.5% vs. 73.4% TLC reduction at week 16) [49].
The tolerability of isotretinoin will be discussed further in the “Discussion.” Briefly, isotretinoin dosed at 1 mg/kg has been generally well tolerated, with patients commonly reporting xerosis, cheilitis, myalgias and gastrointestinal upset. Laboratory abnormalities such as hypertriglyceridemia are also common. The most serious risk associated with isotretinoin pertains to its teratogenic effects.
Subantimicrobial doxycycline has been evaluated in the treatment of moderate to severe acne; 20 mg of doxycycline twice daily was more efficacious than either 40 mg modified release or 100 mg doxycycline once daily (52.3%, 41.7% and 35.9% TLC reduction, respectively) [50, 51]. The subantimicrobial properties of doxycycline 40 mg modified-release capsules were demonstrated in a recent pharmacokinetics study: subjects treated with doxycycline 40 mg failed to achieve a mean steady-state doxycycline plasma concentration that surpassed the antimicrobial threshold, while those treated with doxycycline 50 mg daily had steady-state plasma concentrations that exceeded this threshold [52]. Low-dose antibiotics will be discussed further in the Discussion section. Doxycycline was well tolerated with a minority of patients reporting headache and nausea.
Hormonal Therapies
Unique therapeutic options are available when treating women with acne. Hormonal therapies, such as combined oral contraceptive pills (COCs) as well as spironolactone, are known to improve female acne even in the absence of concurrent hirsutism. Four COCs have been approved by the FDA for acne treatment, while spironolactone is used off label for this purpose in women.
COCs have been evaluated for efficacy in treating women with persistent acne and have been found to have mild to moderate efficacy; 20 μg ethinyl estradiol/100 μg levonorgestrel resulted in a mild decrease in TLC (31.1%) after treatment for six cycles of 28 days [53, 54]; 20 μg ethinyl estradiol/3 mg drospirenone was moderately effective in decreasing facial and truncal TLC (46.3% and 57.3%, respectively) [55, 56]. COCs were well tolerated, with low incidence of adverse events. Reported side effects include metrorrhagia, vomiting and allergic reaction.
Spironolactone, which is an aldosterone receptor antagonist approved for the treatment of hypertension, is known to have potent antiandrogen properties and is used in clinical practice off label for adult female acne. Although well-designed randomized controlled trials are lacking, expert opinion supports the use of this overall well-tolerated and safe treatment in select women [19]. Possible side effects include breast tenderness, irregular menses and gastrointestinal upset. Because of the risk of developing gynecomastia, men are excluded from using this off-label treatment.
Physical Therapies
While not currently considered first-line therapy for acne, physical therapies can be useful in select patients with moderate to severe acne who have primarily inflammatory acne lesions. Physical therapies for the treatment of acne include phototherapy, photodynamic therapy (PDT) and chemical peels. Photo therapy involves exposing affected skin to a specific light source such as long pulsed dye laser (LPDL), intense pulsed laser (IPL) or various wavelengths of light. Often, a photosensitizer, such as aminolevulinic acid (ALA) or methyl-ALA (MAL), is applied to the skin and left on the skin for a certain time prior to treatment with light. The combination of a photosensitizer with light therapy is called PDT.
Although there was significant inter-study heterogeneity with respect to acne severity, number and frequency of treatments, PDT occlusion time, and study design, efficacy trends can be appreciated when comparing the various treatment modalities. Treatment with IPL, which uses wavelengths of 400–1200 nm, was found to have some of the most impressive ILC reductions for treating mild to severe acne (up to 90% decrease), and this efficacy may be increased when treatment is combined with a suction device to flatten the skin during treatment (up to 90% decrease) [57–65]. IPL efficacy did not appear to be significantly enhanced when combined with PDT [62, 64–68]. IPL’s efficacy may be due in part to its longer wavelengths, which have the ability to produce selective photothermolysis of sebaceous glands; sebum has an absorption peak at 1210 nm [69]. LPDL, which uses a wavelength of 595 nm, was more effective at decreasing ILC in patients with mild to severe acne when combined with PDT (67% vs. 100%) [70, 71]. Treatment with red (620–660 nm) and blue (400–500 nm) light are both moderately effective at decreasing ILC (up to 66% and up to 77%, respectively), and these efficacies can be enhanced when combined with PDT [58, 64, 67, 72–82]. Red light PDT appears to be more effective when the photosensitizer is incubated under occlusion compared to no occlusion (59.4% and 31.7% ILC reduction, respectively) [80]. Blue-red (400–500 plus 620–660 nm) light therapy may be superior to either blue or red light alone, with ILC reductions of up to 90% reported [58, 83–85].
Side effects related to light therapy limit its use. The incidence of adverse events, such as pain and burning, is relatively high in patients using PDT. Patients have also reported significant cutaneous erythema lasting for several days post treatment. Postinflammatory pigmentation alteration can also be associated with PDT treatment.
Treatment of acne with chemical peels involves application of a keratolytic agent such as salicylic acid or glycolic acid to promote desquamation. Glycolic acid and amino fruit acid peels used at increasing concentration applied over 24 weeks at 2-week intervals were moderately effective in decreasing non-inflammatory TLC (62.7% and 62.4%, respectively, at 6 months) [86]. Lipohydroxy acid and salicylic acid peels applied over 12 weeks at 2-week intervals were also moderately effective in decreasing non-inflammatory TLC (55.6% and 48.5%, respectively, at 98 days) [87].
Discussion
Acne is a chronic, multifactorial skin disease that is very common and can lead to disfiguring scars. Because the pilosebaceous unit is the primary structure involved, acne most frequently occurs in areas of high pilosebaceous unit density such as the face, neck, chest and back [88].
Acne pathogenesis is complex, and our understanding of this disease process continues to evolve. Comedogenesis is thought to be triggered by a combination of abnormal desquamation of lipid-laden keratinocytes within the sebaceous follicle plus sebaceous gland hyperactivity. Androgens, which control sebum production, are known to contribute to the disease process. Increased production and cohesion of the corneocytes narrow the pilosebaceous opening to the skin and result in a bottleneck phenomenon, thereby producing a microcomedone. As the comedone develops and expands, there can be disruption of the follicular epithelium with extrusion of sebum and corneocytes into the interstitium, thereby leading to an inflammatory response. P. acnes, which is a ubiquitous commensal gram-positive rod, is found in higher concentrations on acne-affected skin. P. acnes is also known to stimulate an inflammatory response and facilitate comedone rupture. While P. acnes is involved in the disease process, its density is not correlated with acne severity and acne may occur even without its presence. For example, microcomedones are known to form in children with early acne prior to P. acnes colonization [89]. Furthermore, eradicating P. acnes may improve acne but will not produce a “cure” of the disease [90].
A plethora of non-antibiotic topical and systemic acne treatment options are available and include topical retinoids, BPO, combination products, azelaic acid, isotretinoin, subantimicrobial dosed antibiotics, hormonal therapies and physical modalities. These treatment options can be used in a step-wise manner depending on the disease severity, patient characteristics and patient’s therapeutic response.
In the mild to moderate acne group, combination topical treatment is often effective for both induction and maintenance therapy. A variety of different monotherapy or combination treatment options exist that target distinct key aspects of the acne disease process.
Topical retinoids, which are vitamin A derivatives, are one of the mainstays of acne treatment. This class of medication targets the initial step of comedogenesis by normalizing follicular keratinization, thereby preventing the development of new comedones and hastening the resolution of existing lesions. Topical retinoids also have anti-inflammatory properties and are not antimicrobial. Monotherapy with a topical retinoid is an excellent choice for patients with predominantly comedonal acne [19].
A variety of topical retinoids are available in differing strengths and vehicles: tretinoin 0.025–0.1% as a cream, gel or microsphere; adapalene 0.1–0.3% cream or 0.1% lotion; tazarotene 0.05–0.1% cream, gel or foam. As each of these products targets different combinations of retinoic acid receptors in the skin, there are slight differences in terms of efficacy and tolerability between these medications (Fig. 1). Several head-to-head studies have been conducted evaluating the efficacy of topical retinoids; however because different concentrations and vehicles were used it is difficult to make meaningful comparisons between these medications [23, 24, 31, 91, 92].
A range of efficacies have been reported for topical retinoids with the majority of studies reporting a TLC reduction of between 40–60% (Fig. 1) [23, 24, 26–28, 31, 92]. As expected, increasing strength was on average correlated with increased efficacy for each of the three retinoids. The vehicle was also found to play an important role in determining efficacy; with few exceptions, gels conferred a larger TLC reduction when compared to creams. Two notable exceptions to this trend were tretinoin 0.05% gel, which was found to be less efficacious than tretinoin 0.025% cream, and tretinoin 0.04% microsphere gel, which was less effective than tretinoin 0.025% cream. Because these comparisons are not from head-to-head studies, the results must be interpreted with caution. More head-to-head studies are needed to further define the individual efficacies of each of the topical retinoids in relation to each other.
Topical retinoid use is limited by skin irritation, erythema and peeling, all of which can be mitigated with the use of a less potent retinoid for initial therapy and by starting treatment with alternate evening use. Tolerability can also be enhanced by using tretinoin-impregnated microsphere gel, which was specifically formulated to have decreased depth of penetration [93]. Improved tolerability is likely to increase patient compliance with treatment. Tretinoin and adapalene are pregnancy category C, while tazarotene is category X and must be avoided in pregnant patients.
Because retinoids improve the abnormal keratinization seen in acne, they also enhance the delivery and efficacy of other topical treatments such as benzoyl peroxide and topical antibiotics (Fig. 1). Topical retinoids are thus an excellent choice for patients with mixed or inflammatory acne as these products can be used concurrently with other topical treatments or can be used in one of the combination products [19]. Combination therapy using a topical retinoid can be highly efficacious, and currently available combination products containing retinoids include adapalene 0.1%/BP 2.5% and tretinoin 0.025%/clindamycin [22, 38, 94].
BPO is a topical bactericidal and mildly comedolytic OTC product. Similar to topical retinoids, BPO is a cornerstone of maintenance therapy for mild to moderate acne and is commonly used as part of a combination treatment regimen. While few head-to-head studies examining the efficacy of BPO monotherapy have been done, a recent meta-analysis found that 5% BPO plus salicylic acid was similar in efficacy to BPO plus topical clindamycin [95]. BPO alone or in combination with topical erythromycin has been reported to be as efficacious as oral minocycline 100 mg once daily, thus making this a compelling alternative treatment regimen to long courses of systemic antibiotics [96].
BPO’s mechanism of action is through the release of free oxygen radicals. No resistance in P. acnes has been reported to date. A variety of strengths and concentrations are available, ranging from 2.5–10% in creams, foams, gels and washes. Side effects result from skin irritation and include erythema and dryness. In addition, fabric bleaching can result when clothing and linens come into contact with BPO.
Salicylic acid is also an over-the-counter product that has mild comedolytic and anti-inflammatory properties. Available in concentrations of up to 2%, salicylic acid can be delivered in an array of vehicles including washes, creams, foams and gels. Clinical trials evaluating the efficacy of salicylic acid are lacking.
Macrolides are the most commonly used topical antibiotics for treating acne, of which topical clindamycin is the preferred agent because of high levels of resistance to erythromycin [11]. Clindamycin has both anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. In order to prevent resistance in P. acnes, topical antimicrobials are most appropriately used either in conjunction with other topical treatments or as part of a combination product [19]. Clindamycin combination products include clindamycin 1% with either BPO 3.75% or 5% [20, 21, 30, 38]. Clindamycin is available as a 1% gel, lotion or solution and is very well tolerated.
Dapsone is an alternative topical antibiotic that treats acne primarily via its anti-inflammatory properties. When used as a monotherapy, dapsone is modestly efficacious with TLC reductions reported around 40%; however, the efficacy can be enhanced when dapsone is used concurrently with either BPO or tretinoin [42, 43]. Inflammatory lesions and adult female acne respond best to dapsone, which is available as a 5% gel [97, 98]. Topical dapsone is well tolerated, and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase levels do not need to be checked prior to use [19].
Azelaic acid, which is a non-antibiotic, has mild comedolytic and anti-inflammatory properties and is bactericidal against a range of gram-negative and -positive organisms including P. acnes [99, 100]. The anti-inflammatory properties of azelaic acid are twofold: azelaic acid downregulates inflammatory cytokines and scavenges reactive oxygen species [101–104]. Because azelaic acid also has skin-lightening properties, it is often the preferred agent for treating patients with post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation from acne lesions. Azelaic acid is available as a 20% cream and a 15% gel and foam, all of which are well tolerated. Although the gel and foam formulations have a lower concentration of active ingredient, these vehicles provide enhanced skin penetration and thus improved efficacy when compared to the cream, and patients may prefer these vehicles over the cream [105–107]. The 15% azelaic acid strength is FDA approved for inflammatory rosacea but is commonly used off label for acne treatment, especially in pregnant women [108]. More studies are needed evaluating the use of azelaic acid as a single agent or as part of a combination regimen for the treatment of acne.
Two novel topical acne treatments are currently in clinical trials: SB204 gel as well as DRM01 gel. SB204, which is the first in its class as a topical nitric oxide-releasing medication, has both anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties [109, 110]. Phase 2 studies show SB204 to be a promising acne treatment that is well tolerated and effective against inflammatory and non-inflammatory lesions. SB204 is currently in phase 3 trials. DRM01 is a small molecule that targets acetyl coenzyme-A carboxylase, which is an important enzyme in the synthesis of sebum. DRM01 has demonstrated good efficacy and safety results in phase 2 studies, and it has been selected to undergo further evaluation in an upcoming phase 3 trials [111].
Topical treatment modalities alone are often inadequate in patients with moderate to severe acne; these patients will often require systemic therapy for their acne. Antibiotics have long played a principal role in acne treatment in this group of patients. The efficacy of antibiotics in treating acne may be due more to their anti-inflammatory properties than their antimicrobial effects [112, 113]. Although topical and systemic antibiotics continue to have an important and appropriate role in acne pharmacotherapy, especially for moderate to severe acne, their overuse is associated with significant population-wide risks, and there are numerous non-antimicrobial treatments available. Because acne is a chronic disease spanning from adolescence well into adulthood, many patients are treated continuously for years with oral and/or topical antibiotics. Antibiotic consumption is also increasing worldwide, which is a concerning trend given the increasing prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and the lack of novel antibiotics [114]. There is mounting pressure to use antibiotics more judiciously and decrease unnecessary prescribing, with the CDC now recommending the use and expansion of antibiotic stewardship programs that aim to change prescribing habits [115–117].
Induction therapy for moderate to severe acne with systemic antibiotics is currently considered appropriate, however in order to minimize the risk of promoting antibiotic resistance these medications should not be used as monotherapy, and their duration should be limited to 3 months or less [118–121]. Prior to starting antibiotics, bacterial culture and sensitivity can be obtained as this information can help direct treatment choice and length [122]. The risks of antibiotic treatment, including dyschromia, pseudotumor cerebri and allergic reactions, should be discussed with patients and their families as the public is often uninformed about the risks of and alternatives to antibiotics. If induction therapy is required again in the future because of a flare in the disease, re-treatment should be done using the same antibiotic that was used initially if it was effective in order to avoid exposing the patient to numerous antibiotics and reduce the risk of developing resistant bacteria [90].
In addition to systemic treatment with antibiotics, alternative treatments exist such as subantimicrobial dosing of doxycycline. Systemic doxycycline, when dosed at 20 mg twice daily or 40 mg daily, exerts a therapeutic anti-inflammatory effect without the untoward effect of producing antibiotic resistance [50, 51]. Subantimicrobial dosing of doxycycline has been shown to be superior at decreasing TLC when compared to doxycycline 100 mg dosed once daily [50]. Further research into the area of subantimicrobial dosing of other antibiotics may prove fruitful and deliver new systemic treatment options for patients with moderate to severe acne.
Isotretinoin is also an important non-antibiotic therapeutic option for patients with moderate to severe acne. This group of patients is often treated for excessive lengths of time with systemic antibiotics prior to being treated with isotretinoin [123]. Patients who are unable to transition off of oral antibiotics after 3 months of induction treatment or patients with active scarring acne should be considered for isotretinoin [19, 123].
Isotretinoin, which is highly effective at producing long-lasting remission in patients with severe acne, works by shrinking sebaceous glands [124]. A typical starting dose is around 0.5 mg/kg/day, and this is increased, as tolerated by the patient, to a goal dose of 1.0 mg/kg/day [125]. Because there is an inverse relationship between a patient’s cumulative dose and risk of relapse, it is recommended that patients reach a cumulative dose of 120–150 mg/kg before cessation of therapy [126]. Some authors have advocated for even higher cumulative doses up to 220 mg/kg as this appears to significantly decrease the risk of relapse without increasing serious treatment-related adverse events [127].
Isotretinoin is known to have numerous side effects, the majority of which are temporary and resolve with discontinuation of therapy. Musculoskeletal aches, cheilitis, hypertriglyceridemia and ophthalmic symptoms are most common. While it has been suggested that there is a relationship between isotretinoin treatment and both inflammatory bowel disease and depression, the majority of studies have not found evidence to support any causal association [128–131]. The most serious established risk of isotretinoin is that which is posed to the fetus. Because of the highly teratogenic effects of isotretinoin, all patients treated with isotretinoin must participate in the iPLEDGE system, and female patients of child-bearing potential must use effective contraception.
The treatment of acne in women requires important consideration, as women comprise over 60% of clinic visits for acne and have a higher incidence than men of late-onset acne developing after age 25 [132, 133]. Moreover, acne in women can be difficult to treat and can become persistent, and women are four times more likely to have severe acne than men [5]. Cosmetics or skin care products used by women do not appear to be responsible for the increased prevalence of acne in women, and the microflora of the skin in women with late onset acne compared to adolescents with acne is essentially the same, indicating that the pathogenesis of acne is likely not related to microflora differences [133, 134].
Androgens play a role in the development of acne through stimulation of sebaceous glands. The importance of androgens in the pathogenesis of acne can be appreciated by the fact that androgen-insensitive subjects neither produce sebum nor develop acne and by the fact that hyperandrogenic states such as polycystic ovarian disease produce acne that is highly responsive to anti-androgen agents [135, 136]. Conditions such as polycystic ovarian syndrome can cause elevated androgen levels leading to acne development, and such conditions should be considered in women with late-onset acne that is resistant to conventional treatments. While most women with acne have normal levels of serum androgens, there may still be a hormonal acne trigger such as menstrual cycle- associated flares. This phenomenon can be explained by an increased androgen sensitivity in these individuals [137].
COCs treat acne through their anti-androgenic properties. COCs contain estrogen and progestin, which cause an increase in sex hormone-binding globulin, which binds free androgens and also exerts a negative feedback to decrease ovarian androgen production. There are four currently FDA approved COCs: ethinyl estradiol/norgestimate, ethinyl estradiol/norethindrone acetate/ferrous fumarate, ethinyl estradiol/drospirenone and ethinyl estradiol/drospirenone/levomefolate. Drospirenone is a unique progestin with structural similarities to spironolactone. While COCs have been shown to be superior at reducing moderate acne compared to placebo, no conclusive data exist to suggest that one COC is superior over another [19, 138]. COCs can be used to treat acne in women with or without signs of hyperandrogenism, and COCs also provide the added benefits of contraception and regulation of heavy periods. Side effects include increased risk for thromboembolic events, myocardial infarction and a controversial association with cervical and breast cancer. There is no conclusive evidence supporting weight gain in association with COCs.
Spironolactone is an aldosterone receptor antagonist that also has anti-androgenic properties by blocking cutaneous androgen receptors [19]. Spironolactone may also inhibit androgen synthesis and decrease steroid hormone-binding globulin [139]. While randomized controlled trials evaluating spironolactone in treating acne are lacking, this medication can be used in select women as monotherapy or can be combined with other drugs. Men should not be treated for acne with spironolactone because of the risk of gynecomastia. This medication should specifically be considered in women with hirsutism, those with hormonally triggered acne, women with severe acne recalcitrant to standard therapies or women with late-onset acne vulgaris. Spironolactone dosing for acne treatment ranges from 25–200 mg daily and is usually well tolerated; side effects are usually dose dependent. Usually the 25–50 mg daily dose does not cause significant side effects; higher doses can cause diuresis, menstrual irregularities, and breast tenderness and enlargement [140]. A recent paper reported that there is no need for routine potassium monitoring for hyperkalemia in healthy young women taking spironolactone for acne [141]. Spironolactone has a black box warning, as it has been implicated as being a possible teratogen and thus should be avoided in pregnancy.
Topical anti-androgens, though not available for use in clinical practice, are an exciting area of clinical research and potential future treatment option for men. These investigational products have been the subject of intense research given that they have promising efficacy results for treating acne and they minimize systemic side effects of anti-androgens. Cortexolone 17α-propionate 1% cream applied daily for 8 weeks decreased TLC in men by 65.7%, with no serious adverse effects [142]. Topical 5% spironolactone gel applied for 6 weeks was also shown to be effective in reducing TLC by 70.9% in mild to moderate acne [143].
Select patients with a predominance of inflammatory lesions may benefit from treatment with physical modalities. Physical therapies include chemical peels, light therapy with or without accompanying photosensitizer, comedo removal and intralesional steroids.
Comedo removal is the process of extracting acne lesions through application of pressure close to the acne pore or through incision and expression of contents. Such a practice can offer immediate relief for the patient, but it can result in scarring and incomplete evacuation of lesion contents. This practice is also not supported by extensive evidence in peer-reviewed papers evaluating its efficacy; hence, it should only be used when comedones persist after other therapies are ineffective [19].
Chemical peels are an effective alternative treatment option for patients with non-inflammatory acne lesions. Active ingredients in chemical peels, such as salicylic acid and glycolic acid, work by decreasing the connections between keratinocytes, thereby leading to desquamation [144]. Salicylic acid also decreases activity of the arachidonic acid pathway, thereby decreasing perilesional inflammation [145]. Evidence suggests that chemical peels may improve comedonal acne. However, multiple treatments are often necessary and may not produce lasting improvement; thus, there is little evidence to support its use in routine first-line acne treatment [19].
Light therapy is a moderately to highly effective method for treating inflammatory acne. Light therapy treats acne primarily through activation of porphyrins, leading to the destruction of P. acnes. The longer wavelengths used in IPL may also destroy sebaceous glands. Of the light therapies, IPL appears to have the greatest therapeutic effect. Both red and blue light are commonly used for acne treatment, and both appear to be more effective when combined with PDT. ALA, a commonly used photosensitizer, is taken up by sebaceous glands and produces reactive oxygen species (ROS) when activated by red or blue light [82]. These ROS then cause sebaceous gland damage and destruction of P. acnes. MAL, which is a commonly used photosensitizer outside of the US, has also been used in PDT for acne treatment and has demonstrated significant efficacy in decreasing ILC [146]. PDT shows great promise in treating acne ranging from mild to severe, but the optimal choice of photosensitizer and light source are topics still under investigation [19]. Moreover, the side effects associated with PDT, including moderate to severe pain during treatment and post-treatment erythema, limit its use, and more effective solutions to address these side effects are necessary for this treatment modality to become more widely used.
Intralesional steroid injection, using triamcinolone acetonide injected into the center of the acne lesion, can be useful in decreasing individual nodulocystic acne lesions, especially when desiring rapid resolution. However, steroid injections can cause local skin atrophy and telangiectasias; thus, care should be taken to use this treatment modality sparingly [147].
Microdermabrasion is a minimally invasive procedure that involves varying degrees of controlled abrasion of the skin to treat a variety of conditions. Although microdermabrasion is generally not used to treat acne vulgaris, it is a commonly employed technique for treating acne scars and can produce mild to moderate improvement in skin contour irregularities [148].
Conclusion
Overuse of antibiotics has resulted in antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and this development poses a major public health concern for the future. Dermatologists play a vital role in addressing this problem by practicing proper stewardship in prescribing antibiotics.
It is important to realize that while antibiotics play a crucial role in the treatment of acne, they should be used judiciously. Systemic antibiotics, when used as induction therapy for 3 months, are an appropriate component of treatment for moderate to severe acne patients. After induction therapy patients should be transitioned off of systemic antibiotics and onto a maintenance therapy regimen. If, however, they have not cleared or if they cannot successfully transition to maintenance therapy, the possibility of treatment failure should be considered, and next line therapy with isotretinoin may be required.
Non-antibiotic treatments have been shown to improve acne significantly and should be used in place of antibiotics when possible, especially for maintenance treatment. Benzoyl peroxide and topical retinoids should have a central role in acne maintenance treatment. Combination therapies, hormonal therapies, and physical treatment modalities are also effective in reducing acne lesions and should be considered in select patients when appropriate.
Further research is needed evaluating the efficacy of non-antimicrobial treatments for acne with a specific focus on optimizing combination products or treatments regimens and on optimizing the use of physical modalities for acne treatment. Research evaluating the efficacy of azelaic acid has primarily focused on the treatment of rosacea; however, this medication has significant therapeutic potential for acne treatment, especially if used in combination with other topical non-antimicrobial treatments. Research evaluating sub-antimicrobial dosing of antibiotics other than doxycycline may reveal new therapeutic options for acne treatment. Finally, novel and promising non-antibiotic treatments are currently in development for acne treatment, and we anticipate that these will ultimately enhance the non-antibiotic treatment options available for acne patients.
References
CDC. Get Smart about Antibiotics Week [Internet]. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2015 [cited 2016 Feb 28]. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/media/dpk/2015/dpk-antibiotics-week-2015.html.
McGann P, Snesrud E, Maybank R, Corey B, Ong AC, Clifford R, et al. Escherichia coli harboring MCR-1 and bla CTX-M on a novel IncF plasmid: first report of MCR-1 in the United States. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016;60(7):4420–1
Bowe WP. Antibiotic resistance and acne: where we stand and what the future holds. J Drugs Dermatol. 2014;13(6):s66–70.
White GM. Recent findings in the epidemiologic evidence, classification, and subtypes of acne vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;39(2 Pt 3):S34–7.
Goulden V, Stables GI, Cunliffe WJ. Prevalence of facial acne in adults. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;41(4):577–80.
Bhate K, Williams HC. Epidemiology of acne vulgaris. Br J Dermatol. 2013;168(3):474–85.
Rosen T. Antibiotic resistance: an editorial review with recommendations. J Drugs Dermatol. 2011;10(7):724–33.
Leyden JJ. In vivo antibacterial effects of tretinoin-clindamycin and clindamycin alone on Propionibacterium acnes with varying clindamycin minimum inhibitory. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11(12):1434–8.
Leyden JJ, Preston N, Osborn C, Gottschalk RW. In-vivo effectiveness of adapalene 0.1%/benzoyl peroxide 2.5% gel on antibiotic-sensitive and resistant Propionibacterium acnes. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2011;4(5):22–6.
Vowels BR, Feingold DS, Sloughfy C, Foglia AN, Konnikov N, Ordoukhanian E, et al. Effects of topical erythromycin on ecology of aerobic cutaneous bacterial flora. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1996;40(11):2598–604.
Mills O, Thornsberry C, Cardin CW, Smiles KA, Leyden JJ. Bacterial resistance and therapeutic outcome following three months of topical acne therapy with 2% erythromycin gel versus its vehicle. Acta Derm Venereol. 2002;82(4):260–5.
Gallo RL, Nakatsuji T. Microbial symbiosis with the innate immune defense system of the skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2011;131(10):1974–80.
Marples RR, Fulton JE, Leyden J, McGinley KJ. Effect of antibiotics on the nasal flora in acne patients. Arch Dermatol. 1969;99(6):647–51.
Leyden JJ, Marples RR, Mills OH, Kligman AM. Gram-negative folliculitis—a complication of antibiotic therapy in acne vulgaris. Br J Dermatol. 1973;88(6):533–8.
Levy RM, Huang EY, Roling D, Leyden JJ, Margolis DJ. Effect of antibiotics on the oropharyngeal flora in patients with acne. Arch Dermatol. 2003;139(4):467–71.
Margolis DJ, Fanelli M, Kupperman E, Papadopoulos M, Metlay JP, Xie SX, et al. Association of pharyngitis with oral antibiotic use for the treatment of acne: a cross-sectional and prospective cohort study. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148(3):326–32.
Margolis DJ, Bowe WP, Hoffstad O, Berlin JA. Antibiotic treatment of acne may be associated with upper respiratory tract infections. Arch Dermatol. 2005;141(9):1132–6.
Adams SJ, Cunliffe WJ, Cooke EM. Long-term antibiotic therapy for acne vulgaris: effects on the bowel flora of patients and their relatives. J Invest Dermatol. 1985;85(1):35–7.
Work Group, Zaenglein AL, Pathy AL, Schlosser BJ, Alikhan A, Baldwin HE, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74(5):945–73.e33.
Schaller M, Sebastian M, Ress C, Seidel D, Hennig M. A multicentre, randomized, single-blind, parallel-group study comparing the efficacy and tolerability of benzoyl peroxide 3%/clindamycin 1% with azelaic acid 20% in the topical treatment of mild-to-moderate acne vulgaris. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30(6):966–73.
Eichenfield LF, Alió Sáenz AB. Safety and efficacy of clindamycin phosphate 1.2%-benzoyl peroxide 3% fixed-dose combination gel for the treatment of acne vulgaris: a phase 3, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, active- and vehicle-controlled study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2011;10(12):1382–96.
Gollnick HPM, Draelos Z, Glenn MJ, Rosoph LA, Kaszuba A, Cornelison R, et al. Adapalene-benzoyl peroxide, a unique fixed-dose combination topical gel for the treatment of acne vulgaris: a transatlantic, randomized, double-blind, controlled study in 1670 patients. Br J Dermatol. 2009;161(5):1180–9.
Thiboutot D, Pariser DM, Egan N, Flores J, Herndon JH, Kanof NB, et al. Adapalene gel 0.3% for the treatment of acne vulgaris: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, controlled, phase III trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54(2):242–50.
Pariser DM, Thiboutot DM, Clark SD, Jones TM, Liu Y, Graeber M, et al. The efficacy and safety of adapalene gel 0.3% in the treatment of acne vulgaris: a randomized, multicenter, investigator-blinded, controlled comparison study versus adapalene gel 0.1% and vehicle. Cutis. 2005;76(2):145–51.
Tanghetti E, Dhawan S, Green L, Del Rosso J, Draelos Z, Leyden J, et al. Randomized comparison of the safety and efficacy of tazarotene 0.1% cream and adapalene 0.3% gel in the treatment of patients with at least moderate facial acne vulgaris. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9(5):549–58.
Shalita A, Miller B, Menter A, Abramovits W, Loven K, Kakita L. Tazarotene cream versus adapalene cream in the treatment of facial acne vulgaris: a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, parallel-group study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2005;4(2):153–8.
Feldman SR, Werner CP, Alió Saenz AB. The efficacy and tolerability of tazarotene foam, 0.1%, in the treatment of acne vulgaris in 2 multicenter, randomized, vehicle-controlled, double-blind studies. J Drugs Dermatol. 2013;12(4):438–46.
Eichenfield LF, Jarratt M, Schlessinger J, Kempers S, Manna V, Hwa J, et al. Adapalene 0.1% lotion in the treatment of acne vulgaris: results from two placebo-controlled, multicenter, randomized double-blind, clinical studies. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9(6):639–46.
Babaeinejad SH, Fouladi RF. The efficacy, safety, and tolerability of adapalene versus benzoyl peroxide in the treatment of mild acne vulgaris: a randomized trial. J Drugs Dermatol. 2013;12(7):790–4.
Langner A, Chu A, Goulden V, Ambroziak M. A randomized, single-blind comparison of topical clindamycin + benzoyl peroxide and adapalene in the treatment of mild to moderate facial acne vulgaris. Br J Dermatol. 2008;158(1):122–9.
Webster G, Cargill DI, Quiring J, Vogelson CT, Slade HB. A combined analysis of 2 randomized clinical studies of tretinoin gel 0.05% for the treatment of acne. Cutis. 2009;83(3):146–54.
Berger R, Barba A, Fleischer A, Leyden JJ, Lucky A, Pariser D, et al. A double-blinded, randomized, vehicle-controlled, multicenter, parallel-group study to assess the safety and efficacy of tretinoin gel microsphere 0.04% in the treatment of acne vulgaris in adults. Cutis. 2007;80(2):152–7.
Tirado-Sánchez A, Ponce-Olivera RM. Efficacy and tolerance of superoxidized solution in the treatment of mild to moderate inflammatory acne. A double-blinded, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, randomized, clinical trial. J Dermatol Treat. 2009;20(5):289–92.
Lucky A, Jorizzo JL, Rodriguez D, Jones TM, Stewart DM, Tschen EH, et al. Efficacy and tolerance of adapalene cream 0.1% compared with its cream vehicle for the treatment of acne vulgaris. Cutis. 2001;68(4 Suppl):34–40.
Cunliffe WJ, Poncet M, Loesche C, Verschoore M. A comparison of the efficacy and tolerability of adapalene 0.1% gel versus tretinoin 0.025% gel in patients with acne vulgaris: a meta-analysis of five randomized trials. Br J Dermatol. 1998;139(Suppl 52):48–56.
Webster GF. Safety and efficacy of Tretin-X compared with Retin-A in patients with mild-to-severe acne vulgaris. Skinmed. 2006;5(3):114–8.
Shalita AR, Chalker DK, Griffith RF, Herbert AA, Hickman JG, Maloney JM, et al. Tazarotene gel is safe and effective in the treatment of acne vulgaris: a multicenter, double-blind, vehicle-controlled study. Cutis. 1999;63(6):349–54.
Jackson JM, Fu J-JJ, Almekinder JL. A randomized, investigator-blinded trial to assess the antimicrobial efficacy of a benzoyl peroxide 5%/clindamycin phosphate 1% gel compared with a clindamycin phosphate 1.2%/tretinoin 0.025% gel in the topical treatment of acne vulgaris. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9(2):131–6.
NilFroushzadeh MA, Siadat AH, Baradaran EH, Moradi S. Clindamycin lotion alone versus combination lotion of clindamycin phosphate plus tretinoin versus combination lotion of clindamycin phosphate plus salicylic acid in the topical treatment of mild to moderate acne vulgaris: a randomized control trial. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2009;75(3):279–82.
Wolf JE, Kaplan D, Kraus SJ, Loven KH, Rist T, Swinyer LJ, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of combined topical treatment of acne vulgaris with adapalene and clindamycin: a multicenter, randomized, investigator-blinded study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49(3 Suppl):S211–7.
Bhavsar B, Choksi B, Sanmukhani J, Dogra A, Haq R, Mehta S, et al. Clindamycin 1% nano-emulsion gel formulation for the treatment of acne vulgaris: results of a randomized, active controlled, multicentre, phase IV clinical trial. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014;8(8):YC05–9.
Draelos ZD, Carter E, Maloney JM, Elewski B, Poulin Y, Lynde C, et al. Two randomized studies demonstrate the efficacy and safety of dapsone gel, 5% for the treatment of acne vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56(3):439.e1-10.
Fleischer AB, Shalita A, Eichenfield LF, Abramovits W, Lucky A, Garrett S, et al. Dapsone gel 5% in combination with adapalene gel 0.1%, benzoyl peroxide gel 4% or moisturizer for the treatment of acne vulgaris: a 12-week, randomized, double-blind study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9(1):33–40.
Langner A, Sheehan-Dare R, Layton A. A randomized, single-blind comparison of topical clindamycin + benzoyl peroxide (Duac) and erythromycin + zinc acetate (Zineryt) in the treatment of mild to moderate facial acne vulgaris. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2007;21(3):311–9.
Capitanio B, Sinagra JL, Weller RB, Brown C, Berardesca E. Randomized controlled study of a cosmetic treatment for mild acne. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2012;37(4):346–9.
Lee JW, Yoo KH, Park KY, Han TY, Li K, Seo SJ, et al. Effectiveness of conventional, low-dose and intermittent oral isotretinoin in the treatment of acne: a randomized, controlled comparative study. Br J Dermatol. 2011;164(6):1369–75.
Weimar VM, Puhl SC, Smith WH, tenBroeke JE. Zinc sulfate in acne vulgaris. Arch Dermatol. 1978;114(12):1776–8.
Tan J, Humphrey S, Vender R, Barankin B, Gooderham M, Kerrouche N, et al. A treatment for severe nodular acne: a randomized investigator-blinded, controlled, noninferiority trial comparing fixed-dose adapalene/benzoyl peroxide plus doxycycline vs. oral isotretinoin. Br J Dermatol. 2014;171(6):1508–16.
Kar BR, Tripathy S, Panda M. Comparative study of oral isotretinoin versus oral isotretinoin + 20% salicylic acid peel in the treatment of active acne. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2013;6(4):204–8.
Moore A, Ling M, Bucko A, Manna V, Rueda M-J. Efficacy and safety of subantimicrobial dose, modified-release doxycycline 40 mg versus doxycycline 100 mg versus placebo for the treatment of inflammatory lesions in moderate and severe acne: a randomized, double-blinded, controlled study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2015;14(6):581–6.
Skidmore R, Kovach R, Walker C, Thomas J, Bradshaw M, Leyden J, et al. Effects of subantimicrobial-dose doxycycline in the treatment of moderate acne. Arch Dermatol. 2003;139(4):459–64.
Fowler JF. Anti-inflammatory dose doxycycline for the treatment of rosacea. Expert Rev Dermatol. 2007;2(5):523–31.
Leyden J, Shalita A, Hordinsky M, Swinyer L, Stanczyk FZ, Weber ME. Efficacy of a low-dose oral contraceptive containing 20 microg of ethinyl estradiol and 100 microg of levonorgestrel for the treatment of moderate acne: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;47(3):399–409.
Thiboutot D, Archer DF, Lemay A, Washenik K, Roberts J, Harrison DD. A randomized, controlled trial of a low-dose contraceptive containing 20 microg of ethinyl estradiol and 100 microg of levonorgestrel for acne treatment. Fertil Steril. 2001;76(3):461–8.
Maloney JM, Dietze P, Watson D, Niknian M, Lee-Rugh S, Sampson-Landers C, et al. A randomized controlled trial of a low-dose combined oral contraceptive containing 3 mg drospirenone plus 20 microg ethinylestradiol in the treatment of acne vulgaris: lesion counts, investigator ratings and subject self-assessment. J Drugs Dermatol. 2009;8(9):837–44.
Palli MBA, Reyes-Habito CM, Lima XT, Kimball AB. A single-center, randomized double-blind, parallel-group study to examine the safety and efficacy of 3 mg drospirenone/0.02 mg ethinyl estradiol compared with placebo in the treatment of moderate truncal acne vulgaris. J Drugs Dermatol. 2013;12(6):633–7.
Shamban AT, Enokibori M, Narurkar V, Wilson D. Photopneumatic technology for the treatment of acne vulgaris. J Drugs Dermatol. 2008;7(2):139–45.
Liu L-H, Fan X, An Y-X, Zhang J, Wang C-M, Yang R-Y. Randomized trial of three phototherapy methods for the treatment of acne vulgaris in Chinese patients. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2014;30(5):246–53.
Gold MH, Biron J. Efficacy of a novel combination of pneumatic energy and broadband light for the treatment of acne. J Drugs Dermatol. 2008;7(7):639–42.
Wanitphakdeedecha R, Tanzi EL, Alster TS. Photopneumatic therapy for the treatment of acne. J Drugs Dermatol. 2009;8(3):239–41.
Elman M, Lask G. The role of pulsed light and heat energy (LHE) in acne clearance. J Cosmet Laser Ther Off Publ Eur Soc Laser Dermatol. 2004;6(2):91–5.
Yeung CK, Shek SY, Bjerring P, Yu CS, Kono T, Chan HH. A comparative study of intense pulsed light alone and its combination with photodynamic therapy for the treatment of facial acne in Asian skin. Lasers Surg Med. 2007;39(1):1–6.
Moftah NH, Ibrahim SM, Wahba NH. Intense pulsed light versus photodynamic therapy using liposomal methylene blue gel for the treatment of truncal acne vulgaris: a comparative randomized split body study. Arch Dermatol Res. 2016;308(4):263–8.
Hong JS, Jung JY, Yoon JY, Suh DH. Acne treatment by methyl aminolevulinate photodynamic therapy with red light vs. intense pulsed light. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52(5):614–9.
Oh SH, Ryu DJ, Han EC, Lee KH, Lee JH. A comparative study of topical 5-aminolevulinic acid incubation times in photodynamic therapy with intense pulsed light for the treatment of inflammatory acne. Dermatol Surg Off Publ Am Soc Dermatol Surg Al. 2009;35(12):1918–26.
Taub AF. A comparison of intense pulsed light, combination radiofrequency and intense pulsed light, and blue light in photodynamic therapy for acne vulgaris. J Drugs Dermatol. 2007;6(10):1010–6.
Ma Y, Liu Y, Wang Q, Ren J, Xiang L. Prospective study of topical 5-aminolevulinic acid photodynamic therapy for the treatment of severe adolescent acne in Chinese patients. J Dermatol. 2015;42(5):504–7.
Mei X, Shi W, Piao Y. Effectiveness of photodynamic therapy with topical 5-aminolevulinic acid and intense pulsed light in Chinese acne vulgaris patients. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2013;29(2):90–6.
Paithankar DY, Sakamoto FH, Farinelli WA, Kositratna G, Blomgren RD, Meyer TJ, et al. Acne treatment based on selective photothermolysis of sebaceous follicles with topically delivered light-absorbing gold microparticles. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135(7):1727–34.
Haedersdal M, Togsverd-Bo K, Wiegell SR, Wulf HC. Long-pulsed dye laser versus long-pulsed dye laser-assisted photodynamic therapy for acne vulgaris: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58(3):387–94.
Alexiades-Armenakas M. Long-pulsed dye laser-mediated photodynamic therapy combined with topical therapy for mild to severe comedonal, inflammatory, or cystic acne. J Drugs Dermatol. 2006;5(1):45–55.
Gold MH, Sensing W, Biron JA. Clinical efficacy of home-use blue-light therapy for mild-to moderate acne. J Cosmet Laser Ther Off Publ Eur Soc Laser Dermatol. 2011;13(6):308–14.
Handler MZ, Bloom BS, Goldberg DJ. Energy-based devices in treatment of acne vulgaris. Dermatol Surg Off Publ Am Soc Dermatol Surg Al. 2016;42(5):573–85.
Na JI, Suh DH. Red light phototherapy alone is effective for acne vulgaris: randomized, single-blinded clinical trial. Dermatol Surg Off Publ Am Soc Dermatol Surg Al. 2007;33(10):1228–33 (discussion 1233).
Aziz-Jalali MH, Tabaie SM, Djavid GE. Comparison of red and infrared low-level laser therapy in the treatment of acne vulgaris. Indian J Dermatol. 2012;57(2):128–30.
de Arruda LHF, Kodani V, Bastos Filho A, Mazzaro CB. A prospective, randomized, open and comparative study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of blue light treatment versus a topical benzoyl peroxide 5% formulation in patients with acne grade II and III. An Bras Dermatol. 2009;84(5):463–8.
Pollock B, Turner D, Stringer MR, Bojar RA, Goulden V, Stables GI, et al. Topical aminolaevulinic acid-photodynamic therapy for the treatment of acne vulgaris: a study of clinical efficacy and mechanism of action. Br J Dermatol. 2004;151(3):616–22.
Taub AF. Photodynamic therapy for the treatment of acne: a pilot study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2004;3(6 Suppl):S10–4.
Akaraphanth R, Kanjanawanitchkul W, Gritiyarangsan P. Efficacy of ALA-PDT vs blue light in the treatment of acne. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2007;23(5):186–90.
Bissonnette R, Maari C, Nigen S, Provost N, Bolduc C. Photodynamic therapy with methylaminolevulinate 80 mg/g without occlusion improves acne vulgaris. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9(11):1347–52.
Wiegell SR, Wulf HC. Photodynamic therapy of acne vulgaris using 5-aminolevulinic acid versus methyl aminolevulinate. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54(4):647–51.
Wiegell SR, Wulf HC. Photodynamic therapy of acne vulgaris using methyl aminolaevulinate: a blinded, randomized, controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. 2006;154(5):969–76.
Papageorgiou P, Katsambas A, Chu A. Phototherapy with blue (415 nm) and red (660 nm) light in the treatment of acne vulgaris. Br J Dermatol. 2000;142(5):973–8.
Lee SY, You CE, Park MY. Blue and red light combination LED phototherapy for acne vulgaris in patients with skin phototype IV. Lasers Surg Med. 2007;39(2):180–8.
Kwon HH, Lee JB, Yoon JY, Park SY, Ryu HH, Park BM, et al. The clinical and histological effect of home-use, combination blue-red LED phototherapy for mild-to-moderate acne vulgaris in Korean patients: a double-blind, randomized controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. 2013;168(5):1088–94.
Ilknur T, Demirtaşoğlu M, Biçak MU, Ozkan S. Glycolic acid peels versus amino fruit acid peels for acne. J Cosmet Laser Ther Off Publ Eur Soc Laser Dermatol. 2010;12(5):242–5.
Levesque A, Hamzavi I, Seite S, Rougier A, Bissonnette R. Randomized trial comparing a chemical peel containing a lipophilic hydroxy acid derivative of salicylic acid with a salicylic acid peel in subjects with comedonal acne. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2011;10(3):174–8.
Leyden JJ. New understandings of the pathogenesis of acne. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32(5, Part 3):S15–25.
Lavker RM, Leyden JJ, McGinley KJ. The relationship between bacteria and the abnormal follicular keratinization in acne vulgaris. J Invest Dermatol. 1981;77(3):325–30.
Thiboutot D, Gollnick H, Bettoli V, Dréno B, Kang S, Leyden JJ, et al. New insights into the management of acne: an update from the Global Alliance to Improve Outcomes in Acne group. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60(5 Suppl):S1–50.
Ioannides D, Rigopoulos D, Katsambas A. Topical adapalene gel 0.1% vs. isotretinoin gel 0.05% in the treatment of acne vulgaris: a randomized open-label clinical trial. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147(3):523–7.
Leyden JJ, Tanghetti EA, Miller B, Ung M, Berson D, Lee J. Once-daily tazarotene 0.1% gel versus once-daily tretinoin 0.1% microsponge gel for the treatment of facial acne vulgaris: a double-blind randomized trial. Cutis. 2002;69(2 Suppl):12–9.
Kircik LH. Microsphere technology: hype or help? J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2011;4(5):27–31.
Poulin Y, Sanchez NP, Bucko A, Fowler J, Jarratt M, Kempers S, et al. A 6-month maintenance therapy with adapalene-benzoyl peroxide gel prevents relapse and continuously improves efficacy among patients with severe acne vulgaris: results of a randomized controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. 2011;164(6):1376–82.
Seidler EM, Kimball AB. Meta-analysis comparing efficacy of benzoyl peroxide, clindamycin, benzoyl peroxide with salicylic acid, and combination benzoyl peroxide/clindamycin in acne. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63(1):52–62.
Ozolins M, Eady EA, Avery AJ, Cunliffe WJ, Po ALW, O’Neill C, et al. Comparison of five antimicrobial regimens for treatment of mild to moderate inflammatory facial acne vulgaris in the community: randomised controlled trial. Lancet Lond Engl. 2004;364(9452):2188–95.
Del Rosso JQ, Kircik L, Gallagher CJ. Comparative efficacy and tolerability of dapsone 5% gel in adult versus adolescent females with acne vulgaris. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2015;8(1):31–7.
Lucky AW, Maloney JM, Roberts J, Taylor S, Jones T, Ling M, et al. Dapsone gel 5% for the treatment of acne vulgaris: safety and efficacy of long-term (1 year) treatment. J Drugs Dermatol. 2007;6(10):981–7.
Skinoren Cream—Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC)-(eMC) [Internet]. (cited 2016 Jun 11). Available from: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/medicine/19239/SPC/Skinoren+Cream/.
Sieber MA, Hegel JKE. Azelaic acid: properties and mode of action. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2014;27(Suppl 1):9–17.
Mastrofrancesco A, Ottaviani M, Aspite N, Cardinali G, Izzo E, Graupe K, et al. Azelaic acid modulates the inflammatory response in normal human keratinocytes through PPARgamma activation. Exp Dermatol. 2010;19(9):813–20.
Briganti S, Flori E, Mastrofrancesco A, Kovacs D, Camera E, Ludovici M, et al. Azelaic acid reduced senescence-like phenotype in photo-irradiated human dermal fibroblasts: possible implication of PPARγ. Exp Dermatol. 2013;22(1):41–7.
Akamatsu H, Komura J, Asada Y, Miyachi Y, Niwa Y. Inhibitory effect of azelaic acid on neutrophil functions: a possible cause for its efficacy in treating pathogenetically unrelated diseases. Arch Dermatol Res. 1991;283(3):162–6.
Passi S, Picardo M, De Luca C, Breathnach AS, Nazzaro-Porro M. Scavenging activity of azelaic acid on hydroxyl radicals “in vitro”. Free Radic Res Commun. 1991;11(6):329–38.
Draelos ZD. The rationale for advancing the formulation of azelaic acid vehicles. Cutis. 2006;77(2 Suppl):7–11.
Draelos ZD, Elewski BE, Harper JC, Sand M, Staedtler G, Nkulikiyinka R, et al. A phase 3 randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled trial of azelaic acid foam 15% in the treatment of papulopustular rosacea. Cutis. 2015;96(1):54–61.
Finacea (azelaic acid) Foam [Internet]. (cited 2016 Jun 29). Available from: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2015/207071Orig1s000TOC.cfm.
Gollnick HPM, Graupe K, Zaumseil R-P. Azelaic acid 15% gel in the treatment of acne vulgaris. Combined results of two double-blind clinical comparative studies. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges J Ger Soc Dermatol. 2004;2(10):841–7.
Novan Therapeutics:: Novan’s Phase 2b Results to be Presented at AAD [Internet]. (cited 2016 Jun 12). Available from: http://www.novantherapeutics.com/investors-media/press-releases/novans-phase-2b-results-be-presented-aad/.
PowerPoint Presentation - Novan_Phase_2b_AAD_2016.pdf [Internet]. (cited 2016 Jun 12). Available from: http://www.novantherapeutics.com/files/1114/6040/2416/Novan_Phase_2b_AAD_2016.pdf.
DRM01: Dermira [Internet]. (cited 2016 Jun 12). Available from: http://dermira.com/pipeline/drm01/.
Walsh TR, Efthimiou J, Dréno B. Systematic review of antibiotic resistance in acne: an increasing topical and oral threat. Lancet Infect Dis. 2016;16(3):e23–33.
Elewski BE, Lamb BA, Sams WM, Gammon WR. In vivo suppression of neutrophil chemotaxis by systemically and topically administered tetracycline. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983;8(6):807–12.
Van Boeckel TP, Gandra S, Ashok A, Caudron Q, Grenfell BT, Levin SA, et al. Global antibiotic consumption 2000 to 2010: an analysis of national pharmaceutical sales data. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14(8):742–50.
McCaig LF, Hughes JM. Trends in antimicrobial drug prescribing among office-based physicians in the United States. JAMA. 1995;273(3):214–9.
Watson RL, Dowell SF, Jayaraman M, Keyserling H, Kolczak M, Schwartz B. Antimicrobial use for pediatric upper respiratory infections: reported practice, actual practice, and parent beliefs. Pediatrics. 1999;104(6):1251–7.
Meeker D, Linder JA, Fox CR, et al. Effect of behavioral interventions on inappropriate antibiotic prescribing among primary care practices: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2016;315(6):562–70.
Gollnick H, Cunliffe W, Berson D, Dreno B, Finlay A, Leyden JJ, et al. Management of acne: a report from a global alliance to improve outcomes in acne. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49(1 Suppl):S1–37.
Dréno B. Bacteriological resistance in acne: A call to action. Eur J Dermatol EJD. 2015.
Dréno B, Bettoli V, Ochsendorf F, Layton A, Mobacken H, Degreef H, et al. European recommendations on the use of oral antibiotics for acne. Eur J Dermatol. 2004;14(6):391–9.
Nast A, Dréno B, Bettoli V, Degitz K, Erdmann R, Finlay AY, et al. European evidence-based (S3) guidelines for the treatment of acne. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012;26(Suppl 1):1–29.
Thiboutot D. Rethinking treatment of acne in the severe patient. J Drugs Dermatol. 2011;10(6):s8–12.
Nagler AR, Milam EC, Orlow SJ. The use of oral antibiotics before isotretinoin therapy in patients with acne. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74(2):273–9.
Peck GL, Olsen TG, Butkus D, Pandya M, Arnaud-Battandier J, Gross EG, et al. Isotretinoin versus placebo in the treatment of cystic acne. A randomized double-blind study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1982;6(4 Pt 2 Suppl):735–45.
Goldsmith LA, Bolognia JL, Callen JP, Chen SC, Feldman SR, Lim HW, et al. American Academy of Dermatology Consensus Conference on the safe and optimal use of isotretinoin: summary and recommendations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50(6):900–6.
Lehucher-Ceyrac D, de La Salmonière P, Chastang C, Morel P. Predictive factors for failure of isotretinoin treatment in acne patients: results from a cohort of 237 patients. Dermatol Basel Switz. 1999;198(3):278–83.
Blasiak RC, Stamey CR, Burkhart CN, Lugo-Somolinos A, Morrell DS. High-dose isotretinoin treatment and the rate of retrial, relapse, and adverse effects in patients with acne vulgaris. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149(12):1392–8.
Rubinow DR, Peck GL, Squillace KM, Gantt GG. Reduced anxiety and depression in cystic acne patients after successful treatment with oral isotretinoin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987;17(1):25–32.
Etminan M, Bird ST, Delaney JA, Bressler B, Brophy JM. Isotretinoin and risk for inflammatory bowel disease: a nested case-control study and meta-analysis of published and unpublished data. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149(2):216–20.
Chia CY, Lane W, Chibnall J, Allen A, Siegfried E. Isotretinoin therapy and mood changes in adolescents with moderate to severe acne: a cohort study. Arch Dermatol. 2005;141(5):557–60.
Cohen J, Adams S, Patten S. No association found between patients receiving isotretinoin for acne and the development of depression in a Canadian prospective cohort. Can J Clin Pharmacol. 2007;14(2):e227–33.
Yentzer BA, Hick J, Reese EL, Uhas A, Feldman SR, Balkrishnan R. Acne vulgaris in the United States: a descriptive epidemiology. Cutis. 2010;86(2):94–9.
Goulden V, Clark SM, Cunliffe WJ. Post-adolescent acne: a review of clinical features. Br J Dermatol. 1997;136(1):66–70.
Till AE, Goulden V, Cunliffe WJ, Holland KT. The cutaneous microflora of adolescent, persistent and late-onset acne patients does not differ. Br J Dermatol. 2000;142(5):885–92.
Imperato-McGinley J, Gautier T, Cai LQ, Yee B, Epstein J, Pochi P. The androgen control of sebum production. Studies of subjects with dihydrotestosterone deficiency and complete androgen insensitivity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993;76(2):524–8.
Lolis MS, Bowe WP, Shalita AR. Acne and systemic disease. Med Clin North Am. 2009;93(6):1161–81.
Thiboutot D, Chen W. Update and future of hormonal therapy in acne. Dermatol Basel Switz. 2003;206(1):57–67.
Lucky AW, Koltun W, Thiboutot D, Niknian M, Sampson-Landers C, Korner P, et al. A combined oral contraceptive containing 3-mg drospirenone/20-microg ethinyl estradiol in the treatment of acne vulgaris: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study evaluating lesion counts and participant self-assessment. Cutis. 2008;82(2):143–50.
Muhlemann MF, Carter GD, Cream JJ, Wise P. Oral spironolactone: an effective treatment for acne vulgaris in women. Br J Dermatol. 1986;115(2):227–32.
Kim GK, Del Rosso JQ. Oral spironolactone in post-teenage female patients with acne vulgaris: practical considerations for the clinician based on current data and clinical experience. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2012;5(3):37–50.
Plovanich M, Weng QY, Mostaghimi A. Low usefulness of potassium monitoring among healthy young women taking spironolactone for acne. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151(9):941–4.
Trifu V, Tiplica G-S, Naumescu E, Zalupca L, Moro L, Celasco G. Cortexolone 17α-propionate 1% cream, a new potent antiandrogen for topical treatment of acne vulgaris. A pilot randomized, double-blind comparative study vs. placebo and tretinoin 0.05% cream. Br J Dermatol. 2011;165(1):177–83.
Afzali BM, Yaghoobi E, Yaghoobi R, Bagherani N, Dabbagh MA. Comparison of the efficacy of 5% topical spironolactone gel and placebo in the treatment of mild and moderate acne vulgaris: a randomized controlled trial. J Dermatol Treat. 2012;23(1):21–5.
Dréno B, Fischer TC, Perosino E, Poli F, Viera MS, Rendon MI, et al. Expert opinion: efficacy of superficial chemical peels in active acne management—what can we learn from the literature today? Evidence-based recommendations. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011;25(6):695–704.
Lee H-S, Kim I-H. Salicylic acid peels for the treatment of acne vulgaris in Asian patients. Dermatol Surg Off Publ Am Soc Dermatol Surg Al. 2003;29(12):1196–9 (discussion 1199).
Pariser DM, Eichenfield LF, Bukhalo M, Waterman G, Jarratt M. PDT Study Group. Photodynamic therapy with methyl aminolaevulinate 80 mg g(−1) for severe facial acne vulgaris: a randomized vehicle-controlled study. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174(4):770–7.
Potter RA. Intralesional triamcinolone and adrenal suppression in acne vulgaris. J Invest Dermatol. 1971;57(6):364–70.
Karimipour DJ, Karimipour G, Orringer JS. Microdermabrasion: an evidence-based review. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;125(1):372–7.
Acknowledgments
No funding or sponsorship was received for this study or publication of this article. All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this manuscript, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given final approval for the version to be published.
Disclosures
T. N. Canavan and E. Chen have nothing to disclose. B. E. Elewski has received clinical research support from the following companies: Amgen, Abbvie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Incyte, Lilly, Merck, Novan, Novartis, Pfizer, Viamet and Valeant; all funds have gone to the dermatology department. B. E. Elewski also has received honorarium from the following companies: Anacor, Celgene, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer and Valeant.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
This article is based on previously conducted studies and does not involve any new studies of human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Enhanced content
To view enhanced content for this article go to http://www.medengine.com/Redeem/5CE4F06041B4C7A5.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0), which permits use, duplication, adaptation, distribution, and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Canavan, T.N., Chen, E. & Elewski, B.E. Optimizing Non-Antibiotic Treatments for Patients with Acne: A Review. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) 6, 555–578 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13555-016-0138-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13555-016-0138-1