Abstract
Background
The incidence of type 1 diabetes (T1D) is showing a rising trend all over the world, and these patients are living longer than before. With increasing longevity, they are at increased risk of chronic complications including fractures. However, the bone mineral density (BMD) data in T1D patients are conflicting and variable across the studies. Here, we aimed to study the BMD in adult patients with T1D and delineate its predictors.
Material and methods
We recruited 40 T1D patients and equal number of age- and sex-matched control subjects. Clinical, biochemical, hormonal, and densitometric assessments were performed for each of the participants and compared between the two groups.
Results
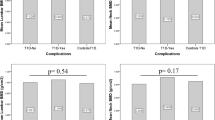
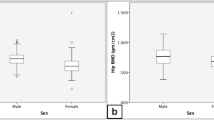
The median age of T1D and control subjects was 23.5 (21–27.75) years and 24 (22–26) years, respectively. The median duration of diabetes in T1D patients was 12.5 (9–15.75) years with a mean HbA1C of 8.7 ± 1.9%. The serum corrected calcium, phosphorous, alkaline phosphatase, creatinine, and plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D and iPTH levels were comparable between the groups. In T1D subjects, the mean lumbar spine and left hip BMD were 0.876 ± 0.154 gm/cm2 and 0.780 ± 0.112 gm/cm2, respectively, which corresponded to mean Z-scores of -1.5 ± 1.4 and -1.4 ± 0.9, respectively, which were significantly lower compared to control group. Multiple linear regression analyses showed that BMI and serum albumin were significant determinant of lumbar spine and hip BMD, respectively, in patients with T1D.
Conclusion
Patients of T1D have apparently reduced BMD, which is being influenced by BMI and serum albumin level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
International Diabetes Federation. IDF diabetes atlas. 8th ed. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation; 2017.
Onkamo P, Vaananen S, Karvonen M, Tuomilehto J. Worldwide increase in incidence of type I diabetes–the analysis of the data on published incidence trends. Diabetologia. 1999;42:1395–403.
Hough FS, Pierroz DD, Cooper C, Ferrari SL. Mechanisms in endocrinology: mechanisms and evaluation of bone fragility in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Eur J Endocrinol. 2016;174:R127–38.
Saha MT, Sievanen H, Salo MK, Tulokas S, Saha HH. Bone mass and structure in adolescents with type 1 diabetes compared to healthy peers. Osteoporos Int. 2009;20:1401–6.
Hadjidakis DJ, Raptis AE, Sfakianakis M, Mylonakis A, Raptis SA. Bone mineral density of both genders in type 1 diabetes according to bone composition. J Diabetes Complicat. 2006;20:302–7.
Dhaon P, Shah VN. Type 1 diabetes and osteoporosis: a review of literature. Ind J Endocrinol Metab. 2014;18:159–65.
Vestergaard P. Discrepancies in bone mineral density and fracture risk in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int. 2007;18:427–44.
Alhuzaim ON, Lewis EJ, Lovblom LE, Cardinez M, Scarr D, Boulet G, Weisman A, Lovshin JA, Lytvyn Y, Keenan HA, Brent MH. Bone mineral density in patients with longstanding type 1 diabetes: results from the Canadian study of longevity in type 1 diabetes. J Diabetes Complicat. 2019;33: 107324.
Aggarwal A, Ram S, Garg A, Pal R, Bhansali A, Singh P, Sharma S, Thakur JS, Sachdeva N, Bhadada SK. Metabolic bone profile of healthy adult North Indian population from Chandigarh Urban Bone Epidemiological Study (CUBES). Indian J Clin Biochem. 2019;28:1–7.
Pal R, Aggarwal A, Singh T, Sharma S, Khandelwal N, Garg A, Bhansali A, Kumar A, Yadav U, Singh P, Dhiman V. Diagnostic cut-offs, prevalence, and biochemical predictors of sarcopenia in healthy Indian adults: the Sarcopenia-Chandigarh Urban Bone Epidemiological Study (Sarco-CUBES). Eur Geriatr Med. 2020;11:725–36.
Aggarwal A, Pal R, Bhadada SK, Ram S, Garg A, Bhansali A, Singh P, Thakur JS, Singh T, Sachdeva N, Rao SD. Bone mineral density in healthy adult Indian population: the Chandigarh Urban Bone Epidemiological Study (CUBES). Arch Osteoporos. 2021;16:1–9.
Pal R, Bhadada SK, Aggarwal A, Singh T. The prevalence of sarcopenic obesity in community-dwelling healthy Indian adults-the Sarcopenic Obesity-Chandigarh Urban Bone Epidemiological Study (SO-CUBES). Osteoporosis and Sarcopenia. 2021;7:24–9.
Shah VN, Harrall KK, Shah CS, Gallo TL, Joshee P, Snell-Bergeon JK, Kohrt WM. Bone mineral density at femoral neck and lumbar spine in adults with type 1 diabetes: a meta-analysis and review of the literature. Osteoporos Int. 2017;28:2601–10.
Pan H, Wu N, Yang T, He W. Association between bone mineral density and type 1 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of cross-sectional studies. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2014;7:531–42.
Leidig-Bruckner G, Grobholz S, Bruckner T, Scheidt-Nave C, Nawroth P, Schneider JG. Prevalence and determinants of osteoporosis in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Endocr Disord. 2014;14:1–3.
Novak D, Forsander G, Kristiansen E, Svedlund A, Magnusson P, Swolin-Eide D. Altered cortical bone strength and lean mass in young women with long-duration (19 years) type 1 diabetes. Sci Rep. 2020;10:1–9.
Joshi A, Varthakavi P, Chadha M, Bhagwat N. A study of bone mineral density and its determinants in type 1 diabetes. J Osteoporos. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/397814.
Roggen I, Gies I, Vanbesien J, Louis O, De Schepper J. Trabecular bone mineral density and bone geometry of the distal radius at completion of pubertal growth in childhood type 1 diabetes. Horm Res Paediatr. 2013;79:68–74.
Karagüzel G, Akçurin S, Özdem S, Boz A, Bircan I. Bone mineral density and alterations of bone metabolism in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2006;19:805–14.
Völzke H, Krohn U, Wallaschofski H, Lüdemann J, John U, Kerner W. The spectrum of thyroid disorders in adult type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2007;23:227–33.
Tahirović H, Dućić V, Smajić A. Euthyroid sick syndrome in type I diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents. Acta Paediatr Hung. 1991;31:67–73.
Radetti G, Paganini C, Gentili L, Barbin F, Pasquino B, Zachmann M. Altered adrenal and thyroid function in children with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Acta Diabetol. 1994;31:138–40.
Helmreich DL, Parfitt DB, Lu XY, Akil H, Watson SJ. Relation between the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid (HPT) axis and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis during repeated stress. Neuroendocrinology. 2005;81:183–92.
Mastorakos G, Pavlatou M. Exercise as a stress model and the interplay between the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal and the hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid axes. Horm Metab Res. 2005;37:577–84.
Hofbauer LC, Brueck CC, Singh SK, Dobnig H. Osteoporosis in patients with diabetes mellitus. J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22:1317–28.
Peavy DE, Taylor JM, Jefferson LS. Time course of changes in albumin synthesis and mRNA in diabetic and insulin-treated diabetic rats. Am J Physiol. 1985;248(6):E656–63.
Feo PD, Gaisano MG, Haymond MW. Differential effects of insulin deficiency on albumin and fibrinogen synthesis in humans. J Clin Investig. 1991;88:833–40.
Afshinnia F, Wong KK, Sundaram B, Ackermann RJ, Pennathur S. Hypoalbuminemia and osteoporosis: reappraisal of a controversy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101:167–75.
Abu-Amer Y. NF-κB signaling and bone resorption. Osteoporos Int. 2013;24:2377–86.
Cao X, Lin W, Liang C, et al. Naringin rescued the TNF-α-induced inhibition of osteogenesis of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by depressing the activation of NF-κB signaling pathway. Immunol Res. 2015;62:357–67.
Jimi E, Aoki K, Saito H, et al. Selective inhibition of NF-κB blocks osteoclastogenesis and prevents inflammatory bone destruction in vivo. Nat Med. 2004;10:617–24.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mukherjee, S., Pal, R., Bhadada, S.K. et al. Bone mineral density and its predictors in a cohort of adults with type 1 diabetes attending a tertiary care institute in North India. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries 44, 48–52 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-023-01185-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-023-01185-5