Abstract
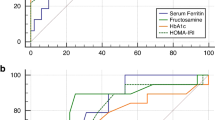
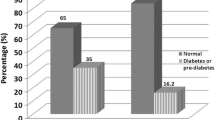
Insulin resistance (IR) underlies some glucose metabolism abnormalities in thalassemia major. Recently, triglyceride glucose index (TyG) has been proposed for evaluating insulin resistance as a simple, low cost, and accessible tool. In this study, the TyG index were studied for IR monitoring in beta-thalassemia major (βTM) patients. The participants were 90 βTM patients on chronic regular transfusion therapy. The TyG index was computed based on fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and triglyceride (TG). The time gap between the first and the second TyG index survey (TyG.1 and TyG.2) was 2 years. The agreement between TyG and HOMA-IR were studied with the extension of limit of agreement (LOA). We included 90 patients 53.3 % men (n = 48). Among them, 14.4 % (14.6 % male, 14.3 % female) had impaired fasting glucose level (e.g., 100–125 mg/dl) at first test. It rose to 37.8 % (27.1 % male, 50 % female) during 2 years. Based on TyG.1, the 34.4 % of patients was detected as IR cases. After 2 years, the percent of IR based on TyG.2 was 82.2 %. The mean differences between TyG.1 and TyG.2 and their differences from the considered cutoff values were significant (P < 0.001). The prediction limits between TyG and HOMA-IR had good agreement. These data may suggest the use of TyG index for detection/monitoring of IR in βTM patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhat KG, Periasamy PK. Effect of long-term transfusion therapy on the glycometabolic status and pancreatic Beta cell function in patients with beta thalassemia major. J Family Med Prim Care. 2014;3(2):119–23.
Balkau B, Eschwège E. Insulin resistance: an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease? Diabetes Obes Metab. 1999;1 Suppl 1:S23–31.
Godsland IF, Lecamwasam K, Johnston DG. A systematic evaluation of the insulin resistance syndrome as an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease mortality and derivation of a clinical index. Metabolism. 2011;60(10):1442–8.
Kuusisto J, Lempiainen P, Mykkanen L, Laakso M. Insulin resistance syndrome predicts coronary heart disease events in elderly type 2 diabetic men. Diabetes Care. 2001;24(9):1629–33.
Hafez M, Youssry I, El-Hamed FA, Ibrahim A. Abnormal glucose tolerance in beta-thalassemia: assessment of risk factors. Hemoglobin. 2009;33(2):101–8.
Chatterjee R, Bajoria R. New concept in natural history and management of diabetes mellitus in thalassemia major. Hemoglobin. 2009;33(1):S127–30.
Borali A, Livingstone C, Kaddam I, Ferns G. Selection of the appropriate method for the assessment of insulin resistance. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2011;11:158–68.
Simental-Mendia LE, Rodriguez-Moran M, Guerrero-Romero F. The product of fasting glucose and triglycerides as surrogate for identifying insulin resistance in apparently healthy subjects. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2008;6(4):299–304.
Guerrero-Romero F, Simental-Mendia LE, Gonzalez-Ortiz M, Martinez-Abundis E, Ramos-Zavala MG, Hernandez-Gonzalez SO, Jacques-Camarena O, Rodriguez-Moran M. The product of triglycerides and glucose, a simple measure of insulin sensitivity. Comparison with the euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamp. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2010; 95(7):33 47–51.
Abbasi F, Reaven GM. Comparison of two methods using plasma triglyceride concentration as a surrogate estimate of insulin action in nondiabetic subjects: triglycerides × glucose versus triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Metabolism. 2011;60(12):1673–6.
Vasques AC, Novaes FS, de Oliveira Mda S, Souza JR, Yamanaka A, Pareja JC, et al. TyG index performs better than HOMA in a Brazilian population: a hyperglycemic clamp validated study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011;93(3):e98–100.
Irace C, Carallo C, Scavelli FB, De Franceschi MS, Esposito T, Tripolino C, et al. Markers of insulin resistance and carotid atherosclerosis. A comparison of the homeostasis model assessment and triglyceride glucose index. Int J Clin Pract. 2013;67(7):665–72.
Petta S, Di Marco V, Di Stefano R, Cabibi D, Cammà C, Marchesini G, et al. TyG index, HOMA score and viral load in patients with chronic hepatitis C due to genotype 1. J Viral Hepat. 2011;18(7):e372–80.
Lucatello F, Vigna L, Carugno M, Tirelli AS, Bertazzi PA, Riboldi L. Comparison of indexes for assessing insulin resistance for the health surveillance among workers. G Ital Med Lav Ergon. 2012;34(3 Suppl):748–9.
Ivovic M, Marina LV, Vujovic S, Tancic-Gajic M, Stojanovic M, Radonjic NV, et al. Nondiabetic patients with either subclinical cushing’s or nonfunctional adrenal incidentalomas have lower insulin sensitivity than healthy controls: clinical implications. Metabolism. 2013;62(6):786–92.
Mericq V, Salas P, Pinto V, Cano F, Reyes L, Brown K, et al. Steroid withdrawal in pediatric kidney transplant allows better growth, lipids and body composition: a randomized controlled trial. Horm Res Paediatr. 2013;79(2):88–96.
Carstensen B. Comparing methods of measurement: extending the LoA by regression. Stat Med. 2010;29:401–10.
Bendix Carstensen, Lyle Gurrin, Claus Ekstrom and Michal Figurski. MethComp: functions for analysis of agreement in method comparison studies. 2015 R package version 1.22.2. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=MethComp
R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. 2015 R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. URL http://www.R-project.org/.
Hintze, J. PASS 11. NCSS, LLC. 2011 Kaysville, Utah, USA. www.ncss.com.
Tsapas A, Vlachaki E, Christoforidis A, Sarigianni M, Bekiari E, Perifanis V, et al. Insulin sensitivity assessment with euglycemic insulin clamp in adult beta-thalassaemia major patients. Eur J Haematol. 2007;79(6):526–30.
Li MJ, Peng SS, Lu MY, Chang HH, Yang YL, Jou ST, et al. Diabetes mellitus in patients with thalassemia major. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2014;61(1):20–4.
Ghergherehchi R, Habibzadeh A. Insulin resistance and β cell function in patients with β-thalassemia major. Hemoglobin. 2015;39(1):69–73.
Tangvarasittichai S, Pimanprom A, Choowet A, Tangvarasittichai O. Association of iron overload and oxidative stress with insulin resistance in transfusion-dependent beta-thalassemia major and beta-thalassemia/HbE patients. Clin Lab. 2013;59(7–8):861–8.
Chern JP, Lin KH, Lu MY, Lin DT, Lin KS, Chen JD, et al. Abnormal glucose tolerance in transfusion-dependent beta thalassemic patients. Diabetes Care. 2001;24(5):850–4.
Arija V, Fernandez-Cao JC, Basora J, Bullo M, Aranda N, Estruch R, et al. Excess body iron and the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a nested case-control in the PREDIMED (PREventionwith MEDiterranean Diet) study. Br J Nutr. 2014;112(11):1896–904.
De Sanctis V, Soliman A, Yassin M. Iron overload and glucose metabolism in subjects with β-thalassaemia major: an overview. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2013;9(4):332–41.
Siklar Z, Citak FE, Uysal Z, Oçal G, Ertem M, Engiz O, et al. Evaluation of glucose homeostasis in transfusion-dependent thalassemic patients. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2008;25(7):630–7.
Suvarna J, Ingle H, Deshmukh CT. Insulin resistance and beta cell function in chronically transfused patients of thalassemia major. Indian Pediatr. 2006;43(5):393–400.
Soliman AT, Yasin M, El-Awwa A, De Sanctis V. Detection of glycemic abnormalities in adolescents with beta thalassemia using continuous glucose monitoring and oral glucose tolerance in adolescents and young adults with β-thalassemia major: pilot study. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2013;17(3):490–5.
Gamberini MR, De Sanctis V, Gilli G. Hypogonadism, diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, hypoparathyroidism: incidence and prevalence related to iron overload and chelation therapy in patients with thalassaemia major followed from 1980 to 2007 in the ferrara centre. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2008;6 Suppl 1:158–69.
De Sanctis V, Zurlo MG, Senesi E, Boffa C, Cavallo L, Di Gregorio F. Insulin dependent diabetes in thalassaemia. Arch Dis Child. 1988;63(1):58–62.
Mula-Abed WA, Al Hashmi H, Al Muslahi M, Al Muslahi H, Al LM. Prevalence of endocrinopathies in patients with Beta thalassaemia major—a cross-sectional study in Oman. Oman Med J. 2008;23(4):257–62.
Khalifa AS, Salem M, Mounir E, El-Tawil MM, El-Sawy M, Abd Al-Aziz MM. Abnormal glucose tolerance in Egyptian beta-thalassemic patients: possible association with genotyping. Pediatr Diabetes. 2004;5(3):126–32.
el-Hazmi MA, al-Swailem A, al-Fawaz I, Warsey AS, al-Swailem A. Diabetes mellitus in children suffering from beta-thalassaemia. J Trop Pediatr. 1994;40(5):261–6.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Golestan University of Medical Sciences for supporting the study setup. We would like to thank all the subjects for their participation and continued follow-up. The authors wish to thank all the survey personnel and the officers in Taleghani Pediatric hospital for their cooperation.
Funding
Deputy of research and technology of Golestan University of Medical Sciences
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jamshir, M., Fayaz, M., Mirbehbahani, N. et al. TyG index and insulin resistance in beta-thalassemia. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries 35 (Suppl 3), 529–534 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-015-0418-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-015-0418-9