Abstract
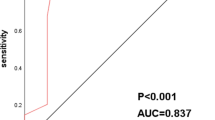
The detection of biomarkers in blood macrophages is a new non-invasive cancer screening method, but its performance in early stage lung cancer screening remains undetermined. We evaluated the Apo10 and TKTL1 levels in blood macrophages of 156 early-stage lung cancer patients and 153 controls. APT (combination of Apo10 and TKTL1) level was significantly higher in the lung cancer group than that in the control group (P < 0.001). AUROC analysis showed that APT has high diagnostic value in differentiating early-stage lung cancer (AUC = 0.9132) and can be considered a biomarker for screening lung cancer patients from individuals with lung nodules.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Chuanbo Xie, Yuying Liu, and Musheng Zeng had full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. The data used for the analyses are available by request to the corresponding author (Chuanbo Xie).
References
M.J. Stagno, A. Schmidt, J. Bochem et al., Epitope detection in monocytes (EDIM) for liquid biopsy including identification of GD2 in childhood neuroblastoma-a pilot study. Brit. J. Cancer 127(7), 1324-1331 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-022-01855-x.
J.F. Coy, EDIM-TKTL1/Apo10 blood test: an Innate Immune System based Liquid Biopsy for the early detection, characterization and targeted treatment of Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18(4) (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040878
S. Saman, M.J. Stagno, S.W. Warmann et al., Biomarkers Apo10 and TKTL1: epitope-detection in monocytes (EDIM) as a new diagnostic approach for cholangiocellular, pancreatic and colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 27(1), 129–137 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3233/CBM-190414
M. Grimm, O. Feyen, J.F. Coy et al., Analysis of circulating CD14+/CD16 + monocyte-derived macrophages (MDMs) in the peripheral blood of patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 121(3), 301–306 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oooo.2015.10.024. pmid:26747736.
M. Grimm, S. Hoefert, M. Krimmel et al., Monitoring carcinogenesis in a case of oral squamous cell carcinoma using a panel of new metabolic blood biomarkers as liquid biopsies. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 20(3), 295–302 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10006-016-0549-2
C. Urla, M.J. Stagno, A. Schmidt et al., Epitope Detection in Monocytes (EDIM) As a New Method of Liquid Biopsy in Pediatric Rhabdomyosarcoma. Biomedicines 10(8), 1812 (2022) https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10081812
D.R. Aberle, A.M. Adams, C.D. Berg et al., Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. New Engl. J. Med. 365(5), 395–409 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1102873
A. McWilliams, M.C. Tammemagi, J.R. Mayo et al., Probability of cancer in pulmonary nodules detected on first screening CT. New Engl. J. Med. 369(10), 910–919 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1214726
S. Maldonado, S. Gonzalez, A. Delorme, Husing et al., Evaluation of Prediction Models for identifying malignancy in pulmonary nodules detected via low-dose computed Tomography. JAMA Netw. Open. 3(2), e1921221 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.21221
S. Burg, A. Grust et al., Blood-test based targeted visualization enables early detection of Premalignant and malignant tumors in asymptomatic individuals. J. Clin. Med. Images 6(9) 2022
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the participants who participated in this diagnostic study. Registration of this study ChiCTR2000040302.
Funding
This study was supported by the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2022A1515011329).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Chuanbo Xie, Shuqing Wang, Yuying Liu and Chi Guo were responsible for data acquisition and analysis. Chuanbo Xie was responsible for preparing the first draft of the manuscript. Chuanbo Xie and Yuying Liu were responsible for recruiting study participants. Chi Guo was responsible for Apo10 and TKTL1 testing. Musheng Zeng supported the study design development and interpretation of the data. All authors had an opportunity to review and revise the manuscript and approved its final submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the institutional review board of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center (SYSUCC, ID: G2022-005-01), and all procedures were conducted according to the principles expressed in the Declaration of Helsinki. The authors enrolled the participants using a chart review blinded to their personal identifying information (name, address, etc.). Therefore, this study did not violate the right and welfare of the subjects. All participants provided written consent for the anonymous use of their data for their research purposes.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, C., Wang, S., Guo, C. et al. Apo10 and TKTL1 in blood macrophages as biomarkers for differentiating lung cancer from benign lung lesions: a comparative study with conventional biomarkers. Cell Oncol. 46, 1725–1729 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-023-00838-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-023-00838-1