Abstract
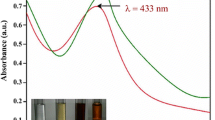
The green route of transition metal nanoparticle (NPs) synthesis by the single-step method has more attraction for multifunctional applications. The study aimed to demonstrate the use of Pandanus canaranus leaf extract, as an apposite substrate for the bio-synthesis of silver (Ag) NPs and Gold (Au) NPs. The UV–Vis spectrum of AgNPs and AuNPs showed an absorption peak at 450 and 520 nm, respectively. FT-IR revealed the respective functional groups (carboxylic acids and phenols) involved in the reduction of Ag + and Au + ions to nanoparticles. The XRD findings confirmed the crystalline nature of Ag and AuNPs with face-centered cubic structures, respectively. SEM images showed spherical and agglomerated morphology. Furthermore, EDX results confirmed the presence of Ag and Au metals. HRTEM images determined the sizes of AgNPs (6.33 to 24.43 nm) and AuNPs (37.44 nm) with spherical morphology. High hatching efficiency and less mortality of Artemia salina nauplii were observed in the treatment of AuNPs (93% and 26%) than AgNPs (91 and 55%). As the concentration of AgNPs and AuNPs increased, the findings of cell viability reduced (36 and 50%) in the lung cancer cells (A549 cells), respectively. The early and late apoptosis induced by the NPs in A549 cells were evidenced through AO/EtBr staining. To sum up, the PCLE-mediated NPs synthesis was very rapid and they significantly induced the apoptosis in A549 cells. With these promising potentials, P. canaranus can progress as a good candidate for cancer therapy.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data and other materials involved in this study can be shared upon request to the authors.
Abbreviations
- % :
-
Percentage
- °C :
-
Degree Celsius
- µg :
-
Microgram
- µL :
-
Microliter
- µm :
-
Micrometer
- AgNO 3 :
-
Silver nitrate
- AgNPs :
-
Silver nanoparticles
- ANOVA :
-
Analysis of variance
- AO :
-
Acridine orange
- AuNPs :
-
Gold nanoparticles
- cm :
-
Centimeter
- CO 2 :
-
Carbon-dioxide
- DAPI :
-
4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole
- H 2 O :
-
Water
- DLS :
-
Dynamic light scattering
- DMEM :
-
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium
- DMRT :
-
Duncan’s multiple range test
- DNA :
-
Deoxyribo nucleic acids
- EDS :
-
Energy dispersive studies
- ELISA :
-
Enzyme-linked immune-sorbent assay
- EtBr :
-
Ethidium bromide
- FBS :
-
Foetal bovine serum
- fcc :
-
Face centered cubics
- FTIR :
-
Fourier Transform Infra-Red
- HAuCl 4 . 3 H 2 O :
-
Hydrogen tetrachloroaurate (III) trihydrate
- IC :
-
Inhibitory concentration
- JCPDS :
-
Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards
- KBr :
-
Potassium bromide
- kV :
-
KiloVolt
- L :
-
Liter
- LC :
-
Lethal concentration
- mg :
-
Milligram
- ml :
-
Milliliter
- mm :
-
Millimeter
- mM :
-
Millimolar
- MTT :
-
3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
- mV :
-
Millivolt
- NaOCl :
-
Sodium hypochlorite
- NCCS :
-
National Centre for Cell Science
- NPs :
-
Nanoparticles
- PBS :
-
Phosphate buffered saline
- ppt :
-
Parts per thousands
- RH :
-
Relative humidity
- ROS :
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SEM :
-
Scanning electron microscopy
- SPSS :
-
Statistical package for the social sciences
- HRTEM :
-
High resolution transmission electron microscopy
- UK :
-
United Kingdom
- USA :
-
United States of America
- UV-Vis :
-
Ultraviolet and visible
- XRD :
-
X-ray diffraction
- ZP :
-
Zeta potential
References
Hosny M, Eltaweil AS, Mostafa M et al (2022) Facile synthesis of gold nanoparticles for anticancer, antioxidant applications, and photocatalytic degradation of toxic organic pollutants. ACS Omega 7:3121–3133. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c06714
Xu ZP, Zeng QH, Lu GQ, Yu AB (2006) Inorganic nanoparticles as carriers for efficient cellular delivery. Chem Eng Sci 61:1027–1040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2005.06.019
Chand K, Abro MI, Aftab U et al (2019) Green synthesis characterization and antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus of silver nanoparticles using extracts of neem, onion and tomato. RSC Adv 9:17002–17015. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA01407A
Alharbi NS, Alsubhi NS (2022) Green synthesis and anticancer activity of silver nanoparticles prepared using fruit extract of Azadirachta indica. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 15:335–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2022.08.009
Tian S, Saravanan K, Mothana RA et al (2020) Anti-cancer activity of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles using Avicennia marina against A549 lung cancer cells through ROS/mitochondrial damages. Saudi J Biol Sci 27:3018–3024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.08.029
Khatik N (2022) Green synthesis of nanomaterials and their utilization as potential vehicles for targeted cancer drug delivery. Adv Pharmacol Pharm 10:114–121. https://doi.org/10.13189/app.2022.100205
Patra JK, Das G, Fraceto LF et al (2018) Nano based drug delivery systems: recent developments and future prospects. J Nanobiotechnology 16:71. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-018-0392-8
Franco F, Rettenmaier C, Jeon HS, Roldan Cuenya B (2020) Transition metal-based catalysts for the electrochemical CO 2 reduction: from atoms and molecules to nanostructured materials. Chem Soc Rev 49:6884–6946. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CS00835D
Laban B, Ralević U, Petrović S et al (2020) Green synthesis and characterization of nontoxic L-methionine capped silver and gold nanoparticles. J Inorg Biochem 204:110958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2019.110958
Perera M, Wijenayaka LA, Siriwardana K et al (2020) Gold nanoparticle decorated titania for sustainable environmental remediation: green synthesis, enhanced surface adsorption and synergistic photocatalysis. RSC Adv 10:29594–29602. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA05607C
Moradi S, Khaledian S, Abdoli M et al (2018) Nano-biosensors in cellular and molecular biology. Cell Mol Biol 64:85–90. https://doi.org/10.14715/cmb/2018.64.5.14
Castillo-Henríquez L, Alfaro-Aguilar K, Ugalde-Álvarez J et al (2020) Green synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles from plant extracts and their possible applications as antimicrobial agents in the agricultural area. Nanomaterials 10:1763. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091763
Abdoli M, Mohammadi G, Mansouri K et al (2022) A review on anticancer, antibacterial and photo catalytic activity of various nanoparticles synthesized by probiotics. J Biotechnol 354:63–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2022.06.005
Khaledian S, Nikkhah M, Shams-bakhsh M, Hoseinzadeh S (2017) A sensitive biosensor based on gold nanoparticles to detect Ralstonia solanacearum in soil. J Gen Plant Pathol 83:231–239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-017-0721-z
Peralta-Videa JR, Huang Y, Parsons JG et al (2016) Plant-based green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles: scientific curiosity or a realistic alternative to chemical synthesis? Nanotechnol Environ Eng 1:4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41204-016-0004-5
Slepička P, Slepičková Kasálková N, Siegel J et al (2019) Methods of gold and silver nanoparticles preparation. Materials (Basel) 13:1. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010001
Abdoli M, Arkan E, Shekarbeygi Z, Khaledian S (2021) Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Centaurea behen leaf aqueous extract and investigating their antioxidant and cytotoxic effects on acute leukemia cancer cell line (THP-1). Inorg Chem Commun 129:108649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2021.108649
Kuppusamy P, Yusoff MM, Maniam GP, Govindan N (2016) Biosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant derivatives and their new avenues in pharmacological applications - An updated report. Saudi Pharm J 24:473–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2014.11.013
Adkar PP, Bhaskar VH (2014) Pandanus odoratissimus (Kewda): A review on ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, and nutritional aspects. Adv Pharmacol Sci 2014:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/120895
Jose B, Harikumar K, Krishnan PN, Satheeshkumar K (2016) In vitro mass multiplication of screw pines (Pandanus spp.) - an important costal bio- resource. J Coast Conserv 20:443–453. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11852-016-0458-4
Balamurugan V, Raja K, Selvakumar S, Vasanth K (2022) Phytochemical screening, antioxidant, anti-diabetic and cytotoxic activity of leaves of Pandanus canaranus Warb. Mater Today Proc 48:322–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.07.603
Ibrahim HMM (2015) Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using banana peel extract and their antimicrobial activity against representative microorganisms. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 8:265–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2015.01.007
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63
Ramalingam V, Revathidevi S, Shanmuganayagam TS et al (2017) Gold nanoparticle induces mitochondria-mediated apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in nonsmall cell lung cancer cells. Gold Bull 50:177–189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13404-017-0208-x
Kuppusamy P, Ichwan SJA, Al-Zikri PNH et al (2016) In vitro anticancer activity of Au, Ag nanoparticles synthesized using Commelina nudiflora L. aqueous extract against HCT-116 colon cancer cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 173:297–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0666-7
Yallappa S, Manjanna J, Peethambar SK et al (2013) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Acacia farnesiana (sweet acacia) seed extract under microwave irradiation and their biological assessment. J Clust Sci 24:1081–1092
Hosny M, Fawzy M, Eltaweil AS (2022) Phytofabrication of bimetallic silver-copper/biochar nanocomposite for environmental and medical applications. J Environ Manag 316:115238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115238
Shukurov I, Mohamed MS, Mizuki T et al (2022) Biological synthesis of bioactive gold nanoparticles from Inonotus obliquus for dual chemo-photothermal effects against human brain cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci 23:2292
Chokkalingam M, Singh P, Huo Y et al (2019) Facile synthesis of Au and Ag nanoparticles using fruit extract of Lycium chinense and their anticancer activity. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 49:308–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2018.11.025
Vanaja M, Paulkumar K, Gnanajobitha G et al (2014) Herbal plant synthesis of antibacterial silver nanoparticles by Solanum trilobatum and its characterization. Int J Metal 692461:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/692461
Anandalakshmi K, Venugobal J, Ramasamy V (2016) Characterization of silver nanoparticles by green synthesis method using Pedalium murex leaf extract and their antibacterial activity. Appl Nanosci 6:399–408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-015-0449-z
Vijayan SR, Santhiyagu P, Singamuthu M et al (2014) Synthesis and characterization of silver and gold nanoparticles using aqueous extract of seaweed, Turbinaria conoides, and their antimicrofouling activity. Sci World J 2014:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/938272
Vanaja M, Gnanajobitha G, Paulkumar K et al (2013) Phytosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by Cissus quadrangularis: influence of physicochemical factors. J Nanostructure Chem 3:17. https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-8865-3-17
Rasmussen MK, Pedersen JN, Marie R (2020) Size and surface charge characterization of nanoparticles with a salt gradient. Nat Commun 11:2337. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15889-3
Rekulapally R, Murthy Chavali LN, Idris MM, Singh S (2019) Toxicity of TiO 2, SiO 2, ZnO, CuO, Au and Ag engineered nanoparticles on hatching and early nauplii of Artemia sp. PeerJ 6:e6138. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.6138
MacRae TH, Pandey AS (1991) Effects of metals on early life stages of the brine shrimp, Artemia: a developmental toxicity assay. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 20:247–252. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055911
Balalakshmi C, Gopinath K, Govindarajan M et al (2017) Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using a cheap Sphaeranthus indicus extract: Impact on plant cells and the aquatic crustacean Artemia nauplii. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 173:598–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2017.06.040
Nunes BS, Carvalho FD, Guilhermino LM, Van Stappen G (2006) Use of the genus Artemia in ecotoxicity testing. Environ Pollut 144:453–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2005.12.037
Mayorga P, Pérez KR, Cruz SM, Cáceres A (2010) Comparison of bioassays using the anostracan crustaceans Artemia salina and Thamnocephalus platyurus for plant extract toxicity screening. Rev Bras Farmacogn 20:897–903. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-695X2010005000029
Radhika Rajasree SR, Ganesh Kumar V, Stanley Abraham L, Indabakandan D (2010) Studies on the toxicological effects of engineered nanoparticles in environment—a review. Int J Appl Bioeng 4:44–53
Rodd AL, Creighton MA, Vaslet CA et al (2014) Effects of surface-engineered nanoparticle-based dispersants for marine oil spills on the model organism Artemia franciscana. Environ Sci Technol 48:6419–6427. https://doi.org/10.1021/es500892m
Arulvasu C, Jennifer SM, Prabhu D, Chandhirasekar D (2014) Toxicity effect of silver nanoparticles in brine shrimp Artemia. Sci World J 2014:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/256919
Karthika V, Arumugam A, Gopinath K et al (2017) Guazuma ulmifolia bark-synthesized Ag, Au and Ag/Au alloy nanoparticles: photocatalytic potential, DNA/protein interactions, anticancer activity and toxicity against 14 species of microbial pathogens. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 167:189–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2017.01.008
Ganeshkumar M, Sathishkumar M, Ponrasu T et al (2013) Spontaneous ultra fast synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Punica granatum for cancer targeted drug delivery. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 106:208–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.01.035
Sriram MI, Kanth SBM, Kalishwaralal K, Gurunathan S (2010) Antitumor activity of silver nanoparticles in Dalton’s lymphoma ascites tumor model. Int J Nanomedicine 5:753–762. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S11727
Shawkey AM, Rabeh MA, Abdulall AK, Abdellatif AO (2013) Green nanotechnology: anticancer activity of silver nanoparticles using Citrullus colocynthis aqueous extracts. Adv Life Sci Technol 13:60–70
Chairuangkitti P, Lawanprasert S, Roytrakul S et al (2013) Silver nanoparticles induce toxicity in A549 cells via ROS-dependent and ROS-independent pathways. Toxicol Vitr 27:330–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2012.08.021
Saravanakumar K, Chelliah R, MubarakAli D et al (2019) Unveiling the potentials of biocompatible silver nanoparticles on human lung carcinoma A549 cells and Helicobacter pylori. Sci Rep 9:5787. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-42112-1
Dipankar C, Murugan S (2012) The green synthesis, characterization and evaluation of the biological activities of silver nanoparticles synthesized from Iresine herbstii leaf aqueous extracts. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 98:112–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.04.006
Sun B, Hu N, Han L et al (2019) Anticancer activity of green synthesised gold nanoparticles from Marsdenia tenacissima inhibits A549 cell proliferation through the apoptotic pathway. Artif Cells Nanomedicine Biotechnol 47:4012–4019. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2019.1575844
Zheng Y, Zhang J, Zhang R et al (2019) Gold nano particles synthesized from Magnolia officinalis and anticancer activity in A549 lung cancer cells. Artif Cells Nanomedicine Biotechnol 47:3101–3109. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2019.1645152
Vijayan R, Joseph S, Mathew B (2018) Indigofera tinctoria leaf extract mediated green synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles and assessment of their anticancer, antimicrobial, antioxidant and catalytic properties. Artif Cells Nanomedicine Biotechnol 46:861–871. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2017.1345930
Muthukumar T, Sudhakumari SB et al (2016) Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles and their enhanced synergistic antitumor activity using HepG2 and MCF7 cells and its antibacterial effects. Process Biochem 51:384–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2015.12.017
Patil MP, Ngabire D, Thi HHP et al (2017) Eco-friendly synthesis of gold nanoparticles and evaluation of their cytotoxic activity on cancer cells. J Clust Sci 28:119–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-016-1051-6
Rajeshkumar S (2016) Anticancer activity of eco-friendly gold nanoparticles against lung and liver cancer cells. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 14:195–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgeb.2016.05.007
Taylor U, Barchanski A, Garrels W et al (2012) Toxicity of gold nanoparticles on somatic and reproductive cells. In: Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. pp 125–133
Batchelor-McAuley C, Tschulik K, Neumann CCM et al (2014) Why are silver nanoparticles more toxic than bulk silver? Towards understanding the dissolution and toxicity of silver nanoparticles. Int J Electrochem Sci 9:1132–1138
Yaqoob SB, Adnan R, Rameez Khan RM, Rashid M (2020) Gold, silver, and palladium nanoparticles: a chemical tool for biomedical applications. Front Chem 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.00376
Kumar H, Bhardwaj K, Kuča K et al (2020) Flower-based green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles: applications beyond fragrance. Nanomaterials 10:766. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10040766
Han G, Ghosh P, Rotello VM (2007) Functionalized gold nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nanomedicine 2:113–123. https://doi.org/10.2217/17435889.2.1.113
Jeyaraj M, Renganathan A, Sathishkumar G et al (2015) Biogenic metal nanoformulations induce Bax/Bcl2 and caspase mediated mitochondrial dysfunction in human breast cancer cells (MCF 7). RSC Adv 5:2159–2166. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA11686K
Gurunathan S, Lee K-J, Kalishwaralal K et al (2009) Antiangiogenic properties of silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials 30:6341–6350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.08.008
Adebayo IA, Gagman HA, Balogun WG et al (2019) Detarium microcarpum, Guiera senegalensis, and Cassia siamea induce apoptosis and cell cycle arrest and inhibit metastasis on MCF7 breast cancer cells. Evidence-Based Complement Altern Med 2019:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6104574
Gurunathan S, Han J, Park JH, Kim J-H (2014) A green chemistry approach for synthesizing biocompatible gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res Lett 9:248. https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-9-248
Patil MP, Jin X, Simeon NC et al (2018) Anticancer activity of Sasa borealis leaf extract-mediated gold nanoparticles. Artif Cells Nanomedicine Biotechnol 46:82–88. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2017.1293675
Namazi Sarvestani N, Sepehri H, Delphi L, Moridi Farimani M (2018) Eupatorin and salvigenin potentiate doxorubicin-induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in HT-29 and SW948 human colon cancer cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 19:131–139. https://doi.org/10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.1.131
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the Department of Botany, Periyar University, Salem, for accessing the lab facilities to carry out this research successfully.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Venkatachalam Balamurugan: conceptualization, data curation, methodology, visualization, writing—original draft, and writing—review and editing.
Govindasamy Balasubramani: conceptualization, data curation, methodology, visualization, writing—original draft, and writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The study does not require any ethical approval, where no test animals employed against ethical guidelines
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Balamurugan, V., Balasubramani, G. Green synthesis and cytotoxicity evaluation of silver and gold nanoparticles using Pandanus canaranus leaf extract on Artemia salina and A549 lung cancer cells. Biomass Conv. Bioref. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-03586-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-03586-8