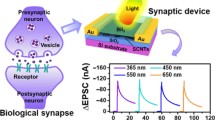
Abstract
Layered two-dimensional materials are promising candidates for next-generation semiconductor platforms owing to their atomically thin bodies, and it is crucial to develop a method for their large-scale synthesis for integrating these materials into the fabrication process. Here, we report the synthesis of a centimeter-scale HfS2 ingot using the molten salt flux method (MSFM). The structure, crystallinity, and uniformity of the synthesized HfS2 sample were verified using X-ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. The chemical properties were investigated using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. A HfS2 synaptic field effect transistor (FET) was fabricated to confirm its electrical uniformity and semiconducting nature, with an average mobility of 10.6 cm2 V-1 s-1. The synaptic plasticity of the HfS2 synaptic FET was investigated by applying light pulses (405 nm) in different modulation configurations. Paired-pulse facilitation was achieved by applying a continuous light pulse with a negative gate bias voltage. The modulation of synaptic weight was demonstrated under different stimulation conditions, which emulates the human brain. Furthermore, the linearity of the HfS2 synaptic device was optimized based on the frequency of the pulses to enhance learning accuracy. The approach reported here encourages the large-scaled production of transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) for use in artificial synaptic transistors.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data supporting the plots and other findings are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Beck, M.E., Hersam, M.C.: Emerging opportunities for Electrostatic Control in Atomically Thin devices. ACS Nano. 14, 6498–6518 (2020)
Fang, N., Nagashio, K.: Accumulation-Mode two-Dimensional Field-Effect Transistor: Operation mechanism and thickness scaling rule. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 10, 32355–32364 (2018)
Zhang, M., Fan, Z.H., Jiang, X.X., Zhu, H., Chen, L., Xia, Y.D., Yin, J., Liu, X.K., Sun, Q.Q.: Zhang.: MoS-based charge-trapping synaptic device with electrical and optical modulated conductance. Nanophotonics-Berlin. 9, 2475–2486 (2020)
Wang, C., Liu, H., Chen, L., Zhu, H., Ji, L., Sun, Q.Q., Zhang, D.W.: Ultralow-Power synaptic Transistor based on Wafer-Scale MoS Thin Film for Neuromorphic Application. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 42, 1555–1558 (2021)
Arnold, A.J., Razavieh, A., Nasr, J.R., Schulman, D.S., Eichfeld, C.M.: Das.: Mimicking Neurotransmitter Release in Chemical synapses Hysteresis Engineering in MoS transistors. Acs Nano. 11, 3110–3118 (2017)
Xiong, H., Xu, L.P., Gao, C.F., Zhang, Q., Deng, M.H., Wang, Q.F., Zhang, J.Z., Fuchs, D., Li, W.W., Cui, A.Y., Shang, L.Y., Jiang, K., Hu, Z.G.: Chu.: Optically modulated HfS-Based synapses for Artificial Vision systems. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 13, 50132–50140 (2021)
Wang, Q.F., Jiang, R.Q., Gao, Z.T., Deng, M.H., Chen, J.H., Zhu, L.Q., Shang, L.Y., Li, Y.W., Fuchs, D., Zhang, J.Z., Hu, Z.G.: A HfS-based photoelectronic synaptic transistor with tunable synaptic plasticity for emotional memory. Appl. Surf. Sci. 613, 156148 (2023)
Wang, S.Y., Zhang, D.W., Zhou, P.: Two-dimensional materials for synaptic electronics and neuromorphic systems. Sci. Bull. 64, 1056–1066 (2019)
Susarla, S., Kutana, A., Hachtel, J.A., Kochat, V., Apte, A., Vajtai, R., Idrobo, J.C., Yakobson, B.I., Tiwary, C.S., Ajayan, P.M.: Quaternary 2D transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) with Tunable Bandgap. Adv. Mater. 29, 1702457 (2017)
Ramasubramaniam, A., Naveh, D., Towe, E.: Tunable band gaps in bilayer transition-metal dichalcogenides. Phys. Rev. B. 84, 2053215 (2011)
Chaves, A., Azadani, J.G., Alsalman, H., da Costa, D.R., Frisenda, R., Chaves, A.J., Song, S.H., Kim, Y.D., He, D.W., Zhou, J.D., Castellanos-Gomez, A., Peeters, F.M., Liu, Z., Hinkle, C.L., Oh, S.H., Ye, P.D., Koester, S.J., Lee, Y.H., Avouris, P., Wang, X.R.: Bandgap engineering of two-dimensional semiconductor materials. Npj 2d Mater. Appl. 4, 1–21 (2020)
Jiménez, D.: Drift-diffusion model for single layer transition metal dichalcogenide field-effect transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 243501 (2012)
Wang, D.G., Zhang, X.W., Wang, Z.G.: Recent advances in Properties, synthesis and applications of two-dimensional HfS. J. Nanosci. Nanotechno. 18, 7319–7334 (2018)
Yan, C.Y., Gan, L., Zhou, X., Guo, J., Huang, W.J., Huang, J.W., Jin, B., Xiong, J., Zhai, T.Y.: Li.: Space-confined Chemical Vapor Deposition synthesis of ultrathin HfS Flakes for Optoelectronic Application. Adv. Funct. Mater. 27, 1702918 (2017)
Cao, Y., Wähler, T., Park, H., Will, J., Prihoda, A., Moses Badlyan, N., Fromm, L., Yokosawa, T., Wang, B., Guldi, D.M., Görling, A., Maultzsch, J., Unruh, T., Spiecker, E., Halik, M., Libuda, J.: Area-Selective Growth of HfS2 Thin films via Atomic Layer deposition at low temperature. Adv. Mater. Interfaces. 7, 2001493 (2020)
Gupta, S.K., Mao., Y.: Recent developments on molten salt synthesis of Inorganic nanomaterials: A review. J. Phys. Chem. C. 125, 6508–6533 (2021)
Zhang, L.Z., Chen, C., Zhou, J.D., Yang, G.L., Wang, J.M., Liu, D., Chen, Z.Q., Lei, W.W.: Solid phase exfoliation for producing Dispersible Transition Metal Dichalcogenides Nanosheets. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30, 2004139 (2020)
Gupta, S.K., Mao., Y.B.: A review on molten salt synthesis of metal oxide nanomaterials: Status, opportunity, and challenge. Prog Mater. Sci. 117, 100734 (2021)
Kanazawa, T., Amemiya, T., Ishikawa, A., Upadhyaya, V., Tsuruta, K., Tanaka, T., Miyamoto, Y.: Few-layer HfS transistors. Sci. Rep. 6, 1–9 (2016)
Feng, P., Xu, W.W., Yang, Y., Wan, X., Shi, Y., Wan, Q., Zhao, J.W.: Z. Cui.: Printed Neuromorphic devices based on printed Carbon Nanotube Thin-Film transistors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 27, 160447 (2017)
Guo, L.Q., Zhu, L.Q., Ding, J.N., Huang, Y.K.: Paired-pulse facilitation achieved in protonic/electronic hybrid indium gallium zinc oxide synaptic transistors. Aip Adv. 5, 087112 (2015)
Guo, T., Ge, J.W., Sun, B., Pan, K.Q., Pan, Z., Wei, L., Yan, Y., Zhou, Y.N.: Wu.: Soft Biomaterials Based Flexible Artificial Synapse for Neuromorphic Computing. Adv. Electron. Mater. 8, 2200449 (2022)
Castillo, P.E.: Presynaptic LTP and LTD of excitatory and inhibitory synapses. Csh Perspect. Biol. 4, a005728 (2012)
Zheng, B.J., Chen, Y.F., Wang, Z.G., Qi, F., Huang, Z.S., Hao, X., Li, P.J., Zhang, W.L., Li, Y.R.: Vertically oriented few-layered HfS nanosheets: Growth mechanism and optical properties. 2d Mater. 3, 035024 (2016)
Wang, D.G., Zhang, X.W., Guo, G.C., Gao, S.H., Li, X.X., Meng, J.H., Yin, Z.G., Liu, H., Gao, M.L., Cheng, L.K., You, J.B., Wang, R.Z.: Large-area synthesis of layered HfS Se alloys with fully tunable Chemical compositions and Bandgaps. Adv. Mater. 30, 1803285 (2018)
Gao, J., Li, L., Tan, J.W., Sun, H., Li, B.C., Idrobo, J.C., Singh, C.V., Lu, T.M.: Koratkar.: Vertically oriented arrays of ReS nanosheets for Electrochemical Energy Storage and Electrocatalysis. Nano Lett. 16, 3780–3787 (2016)
Yang, L.L., Liu, D.Y., Li, J., Yi, Q., Yi, J., Huang, B., Miao, L.L., Wu, M., Zhao, C.J.: Broadband optical response of layered nickel ditelluride towards the mid-infrared regime. Opt. Mater. Express. 10, 1335–1343 (2020)
Zhao, Q.Y., Guo, Y.H., Si, K.Y., Ren, Z.Y., Bai, J.T., Xu, X.L.: Elastic, electronic, and dielectric properties of bulk and monolayer ZrS, ZrSe, HfS, HfSe from Van Der Waals density-functional theory. Phys. Status Solidi B. 254, 1700033 (2017)
Hodul, D.T., Stacy, A.M.: Anomalies in the properties of Hf(S2 – xTex)1 – y and hf(Se2 – xTex)1 – y near the metal-insulator transition. J. Solid State Chem. 54, 438–446 (1984)
Lai, S., Byeon, S., Jang, S.K., Lee, J., Lee, B.H., Park, J.H., Kim, Y.H.: Lee.: HfO/HfS hybrid heterostructure fabricated controllable chemical conversion of two-dimensional HfS. Nanoscale. 10, 18758–18766 (2018)
Rorvik, P.M., Lyngdal, T., Sæterli, R., van Helvoort, A.T.J., Holmestad, R., Grande, T., Einarsrud, M.A.: Influence of volatile chlorides on the molten salt synthesis of ternary oxide nanorods and nanoparticles. Inorg. Chem. 47, 3173–3181 (2008)
Wang, X.Y., Huang, K.K., Yuan, L., Li, S., Ma, W., Liu, Z.Y., Feng, S.H.: Molten salt flux synthesis, Crystal Facet Design, characterization, electronic structure, and Catalytic Properties of Perovskite Cobaltite. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 10, 28219–28231 (2018)
Youssef, M., Keshavan, S., Dante, S.: Induced inhomogeneity in graphene work function due to graphene - TiO 2 /Ag/glass substrate interaction. Thin Solid Films. 628, 43–49 (2017)
Chae, S.H., Jin, Y., Kirn, T.S., Chung, D.S., Na, H., Nam, H., Kim, H., Perello, D.J., Jeong, H.Y., Ly, T.H.: Lee.: Oxidation Effect in Octahedral Hafnium Disulfide Thin Film. Acs Nano. 10, 1309–1316 (2016)
Nie, X.R., Sun, B.Q., Zhu, H., Zhang, M., Zhao, D.H., Chen, L., Sun, Q.Q., Zhang, D.W.: Impact of metal contacts on the performance of Multilayer HfS Field-Effect transistors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 9, 26996–27003 (2017)
Gao, C.F., Lee, M.P., Li, M.J., Lee, K.C., Yang, F.S., Lin, C.Y., Watanabe, K., Taniguchi, T., Chiu, P.W., Lien, C.H., Wu, W.W., Lin, S.P., Li, W.W., Lin, Y.F.: Chu.: Mimic Drug Dosage Modulation for Neuroplasticity based on charge-trap layered Electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2005185 (2021)
Kanazawa, T., Amemiya, T., Upadhyaya, V., Ishikawa, A., Tsuruta, K., Tanaka, T., Miyamoto, Y.: Performance improvement of HfS transistors by Atomic Layer Deposition of HfO. Ieee T Nanotechnol. 16, 582–587 (2017)
Xu, K., Huang, Y., Chen, B., Xia, Y., Lei, W., Wang, Z.X., Wang, Q.S., Wang, F., Yin, L.: Toward high-performance top-gate ultrathin HfS Field-Effect transistors by Interface Engineering. Small. 12, 3106–3111 (2016)
Das, S., Chen, H.Y., Penumatcha, A.V.: High performance Multilayer MoS transistors with Scandium contacts. Nano Lett. 13, 100–105 (2013)
Su, B.W., Zhang, X.L., Xin, W., Guo, H.W., Zhang, Y.Z., Liu, Z.B., Tian, J.G.: Laser-assisted two dimensional material electronic and optoelectronic devices. J. Mater. Chem. C. 9, 2599–2619 (2021)
Wang, I.T., Chang, C.C., Chiu, L.W., Chou, T.Y.: Hou.: 3D Ta/TaO/TiO/Ti synaptic array and linearity tuning of weight update for hardware neural network applications. Nanotechnology. 27, 365204 (2016)
Kumar, S., Kumbhar, D.D., Park, J.H., Kamat, R.K., Dongale, T.D.: Mukherjee.: YO-Based crossbar array for Analog and Neuromorphic Computation. Ieee T Electron. Dev. 70, 473–477 (2023)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grants funded by the Government of the Republic of Korea (2021R1C1C1012209 and RS-2023-00275300) and by the Korea Institute of Ceramic Engineering and Technology (KPP22002). This results was also supported by “Regional Innovation Strategy (RIS)” through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (MOE) (2021RIS-003). Following are results of a study on the “Leaders in INdustry-university Cooperation 3.0” Project, supported by the Ministry of Education and National Research Foundation of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M. J. K. and N. V. B. prepared the materials for most of the experimental measurements and analyzed the results. M. J. K., J.Y.C., and J. H. P. conceived and designed the study. S. C., S. B. S., S. H. R., and Y. J. J. assisted with material characterization and W. H. N conducted the XPS analysis. M. J. K. fabricated the devices and analyzed the results. M. J. K., N. V. B., J. Y. C., and J. H. P. wrote the manuscript. All the authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript. All authors revised the manuscript. J. H. P. supervised the study.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kwon, M.J., Binh, N.V., Cho, Sy. et al. Optoelectronic Synapse Behaviors of HfS2 Grown via Molten Salt Flux Method. Electron. Mater. Lett. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-024-00494-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-024-00494-z