Abstract
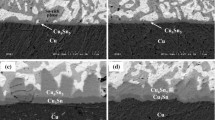
Efficient diffusion barriers are necessary to prevent the formation of copper-tin intermetallic compounds (IMCs) in advanced packaging for Sn/Cu micro-bumps. This study investigated the interfacial properties of solder and Ni, Co-9W, Co-20W, Co-20Fe-10W, and Co-36Fe-17W barriers and determined the thickness of IMCs formed between Sn and these barriers after up to 15 reflows. Among the five barriers, Co-36Fe-17W proved to be the most effective in inhibiting the reaction of liquid Sn solder. At the Sn/Co-W interface, CoSn3 IMC was formed, while at the Sn/Co-Fe-W interface, CoSn3 IMC and FeSn2 IMC were observed. The contact angles of these layers were measured and found to be 18°, 22°, 25°, 29°, and 27°, respectively. The results showed that an increase in W content in Co-W led to an increase in the contact angle, while the intrinsic wettability of Co-Fe-W decreased with an increase in Fe content. The shear strengths of the five joints were 27 MPa, 31 MPa, 25 MPa, 25 MPa, and 26 MPa, respectively, with different fracture modes observed. The Co-Fe-W-Sn layer was partially peeling from the diffusion barriers in SAC305/Co-20Fe-10W, and the fracture surfaces exhibited an irregular and rough state, which was attributed to the increasing Fe and W contents. These findings offer valuable insights for enhancing the reliability of electronic packages.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun, L., Chen, M., Zhang, L., He, P., Xie, L.: Recent progress in SLID bonding in novel 3D-IC technologies. J. Alloys Compd. 818, 152825 (2020)
Lau, J.H.: Recent advances and trends in advanced packaging. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packaging Manuf. Technol. 12, 228–252 (2022)
Lim, G.T., Kim, B.J., Lee, K., et al.: Temperature effect on intermetallic compound growth kinetics of Cu pillar/Sn bumps. J. Electron. Mater. 38, 2228–2233 (2009)
Liashenko, O.Y., Lay, S., Hodaj, F.: On the initial stages of phase formation at the solid Cu/liquid Sn-based solder interface. Acta Mater. 117, 216–227 (2016)
Hu, X., Li, Y., Liu, Y., et al.: Microstructure and shear strength of Sn37Pb/Cu solder joints subjected to isothermal aging[J]. Microelectron. Reliab. 54(8), 1575–1582 (2014)
Borgesen, P., Yin, L., Kondos, P.: Assessing the risk of Kirkendall voiding in Cu3Sn. Microelectron. Reliab. 51(4), 837–846 (2011)
Kannojia, H.K., Dixit, P.: A review of intermetallic compound growth and void formation in electrodeposited Cu–Sn layers for microsystems packaging[J]. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 6742–6777 (2021)
Liu, Y.X., Chu, Y.C., Tu, K.N.: Scaling effect of interfacial reaction on intermetallic compound formation in Sn/Cu pillar down to 1 µm diameter. Acta Mater. 117, 146–152 (2016)
Shen, J., Chan, Y.C., Liu, S.Y.: Growth mechanism of Ni3Sn4 in a Sn/Ni liquid/solid interfacial reaction. Acta Mater. 57, 5196–5206 (2009)
Ghosh, G.: Thermodynamic modeling of the nickel-lead-tin system. Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 30, 1481–1494 (1999)
Chen, K., Ling, H., Guo, F., et al.: Effect of Ni barrier layer thickness on IMCs evolution in Ф5µm Cu/Ni/Sn pillar bumps. 19th International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology (ICEPT 2018), 190–194 (2018)
Chen, C.M., Chen, S.W.: Electromigration effect upon the Sn/Ag and Sn/Ni interfacial reactions at various temperatures. Acta Mater. 50, 2461–2469 (2002)
Chen, S., Tan, L., Yang, C., et al.: Effects of amorphous CoW and NiW barrier layers on the evolution of Sn/Cu interface. Mater. Charact. 181, 111448 (2021)
Chen, S., Yang, C., Tan, L., et al.: Effects of W contents on the solid-state interfacial reactions of Sn/Co-W. J. Mater. Sci. 1–13. (2022)
Liu, Y., Chen, P., Yan, P., et al.: Diffusion barrier property of Co-W layer compared with ni layer in fine pitch micro-bumps during high temperature storage. Mater. Lett. 347, 134572 (2023)
Liu, Y., Li, C., Chen, P., et al.: Effects of Electrodeposited Co–W and Co–Fe–W diffusion barrier layers on the evolution of Sn/Cu interface. Mater. Chem. Phys. 128761. (2023)
Derakhshandeh, J., Beyne, E., Beyer, G., et al.: Low temperature backside damascene processing on temporary carrier wafer targeting 7µm and 5µm pitch microbumps for N equal and greater than 2 die to wafer TCB stacking. 2022 IEEE 72nd Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC). IEEE. 1108–1113
Kyaw, T.T., Tunthawiroon, P., Kanlayasiri, K., et al.: A study on wettability and formation of intermetallic phase between Co–Cr–Mo alloy and Sn-Solder used as a potential under bump metallization for flip-chip packages. Intermetallics, 125. (2020)
Chen, L., Chen, S., Chen, P., et al.: Interface reliability and diffusion barrier property of Co-W barrier layer with modulated structure. Mater. Lett. 331, 133501 (2023)
Pan, H.C., Hsieh, T.E.: Diffusion barrier characteristics of electroless Co(W,P) thin films to lead-free SnAgCu solder. J. Electrochem. Soc., 158(11). (2011)
Chew, C.S., Durairaj, R., Haseeb A S M A, et al.: Mechanical properties of interfacial phases between Sn-3.5 Ag solder and Ni-18 at. % W barrier film by nanoindentation. Soldering Surf. Mt. Technol. 27(2), 90–94 (2015)
Pal, M.K., Gergely, G., Gácsi, Z.: Growth kinetics and IMCs layer analysis of SAC305 solder with the reinforcement of SiC during the isothermal aging condition. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 24, 8320–8331 (2023)
Pal, M.K., Gergely, G., Koncz-Horváth, D., et al.: Investigation of the electroless nickel plated sic particles in sac305 solder matrix. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 58(9–10), 529–537 (2020)
Pal, M.K., Gergely, G., Koncz-Horváth, D., et al.: Distribution and microstructure analysis of ceramic particles in the lead‐free solder matrix[J]. Cryst. Res. Technol. 55(12), 2000123 (2020)
Pal, M.K., Gergely, G., Koncz-Horváth, D., et al.: Investigation of microstructure and wetting behavior of Sn–3.0 Ag–0.5 cu (SAC305) lead-free solder with additions of 1.0 wt% SiC on copper substrate. Intermetallics. 128, 106991 (2021)
Görlich, J., Baither, D., Schmitz, G.: Reaction kinetics of Ni/Sn soldering reaction. Acta Mater. 58(9), 3187–3197 (2010)
Tian, S., Zhou, J., Xue, F., et al.: Microstructure, interfacial reactions and mechanical properties of Co/Sn/Co and Cu/Sn/Cu joints produced by transient liquid phase bonding. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29, 16388–16400 (2018)
Wang, C., Kuo, C., Huang, S., et al.: Temperature effects on liquid-state Sn/Co interfacial reactions. Intermetallics. 32, 57–63 (2013)
Fick, A.V.: On liquid diffusion. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philosophical Magazine J. Sci. 10(63), 30–39 (1855)
Amore, S., Ricci, E., Borzone, G., et al.: Wetting behaviour of lead-free Sn-based alloys on Cu and Ni substrates. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 495(1–2), 108–112 (2008)
Willis, B.: Reflow soldering processes and troubleshooting SMT, BGA, CSP and Flip Chip technologies, vol. 15. Soldering & Surface Mount Technology (2003). 1
Lu, M.H., Lauro, P., Goldsmith, C.: Study of interfacial reaction and electromigration reliability of Pb-free solders with nickel iron barrier layer. Proc. Asme Pac. Rim Tech. Conf. Exhib. Packaging Integr. Electron. Photonic Syst. Mems Nems 2011. 1, 453 (2012)
Chen, H., Tsai, Y.L., Chang, Y.T., et al.: Effect of massive spalling on mechanical strength of solder joints in Pb-free solder reflowed on co-based surface finishes. J. Alloys Compd. 671, 100–108 (2016)
Gao, L.Y., Luo, Y.X., Wan, P., et al.: Theoretical and experimental investigations on mechanical properties of (Fe,Ni)Sn2 intermetallic compounds formed in SnAgCu/Fe-Ni solder joints. Mater. Charact. 178. (2021)
Hu, X., Xu, T., Keer, L.M., et al.: Microstructure evolution and shear fracture behavior of aged Sn3Ag0. 5Cu/Cu solder joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 673, 167–177 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This research received funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61176097). The authors express their gratitude to the Instrumental Analysis Center of Shanghai Jiao Tong University for providing access to a range of characterization equipment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yuexiao Liu: Methodologies, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Investigation, Visualization. Chongyang Li:Writing – review & editing. Peixin Chen: review & editing. Jinyang Liu: review & editing. Anmin Hu: Conceptualization, Supervision. Ming Li: Project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors state that they have no competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have influenced the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Li, C., Chen, P. et al. Effect of Co-W and Co-Fe-W Diffusion Barriers on the Reliability of the Solder/Cu Interface during Reflow Conditions. Electron. Mater. Lett. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-024-00491-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-024-00491-2