Abstract
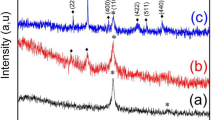
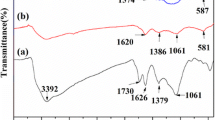
Magnetic composites have received increasing attention for electromagnetic wave absorption (EMA) applications. However, the practical EMA performance of the materials is severely hampered by mismatching impedance characteristics and finite electromagnetic attenuation capacity. Controlling the components and building the architecture fabrication is necessary to solve these issues. Herein, a series of Fe3O4, Fe3O4&Fe and Fe microspheres with flower-like hierarchical structures were constructed through a solvothermal method followed by an annealed process. This hierarchical structure and the synergy effect of dielectric dissipation and magnetic loss capacity offer Fe3O4 a perfect impedance matching, providing an excellent EMA performance of an effective absorption bandwidth (EAB) of 4.0 GHz and a reflection loss (RL) of 67.9 dB. Meanwhile, the coordination of the hierarchical structures and the multiple components endow Fe3O4&Fe composites with an EAB as wide as 5.7 GHz (9.0–14.7 GHz) and a RL as strong as 78.7 dB at 1.88 mm, which covers 75% X and 45% Ku bands. Such a remarkable lightweight and broad properties is due to the decent X band impedance matching and appropriate attenuation capacity. Therefore, this work highlights the significant of regulating the hierarchical structure and components to enhance the EMA performances.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liang, L., Gu, W., Wu, Y., Zhang, B., Wang, G., Yang, Y., Ji, G.: Heterointerface engineering in electromagnetic absorbers: new insights and opportunities. Adv. Mater. 34(4), 2106195 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202106195
Liang, L., Li, Q., Yan, X., Feng, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, H.-B., Zhou, X., Liu, C., Shen, C., Xie, X.: Multifunctional magnetic Ti3C2Tx MXene/graphene aerogel with superior electromagnetic wave absorption performance. ACS Nano 15(4), 6622–6632 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c09982
Lan, D., Gao, Z., Zhao, Z., Wu, G., Kou, K., Wu, H.: Double-shell hollow glass microspheres@Co2SiO4 for lightweight and efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 408, 127313 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127313
Li, X., You, W., Xu, C., Wang, L., Yang, L., Li, Y., Che, R.: 3D Seed-germination-like MXene with in situ growing CNTs/Ni heterojunction for enhanced microwave absorption via polarization and magnetization. Nano-Micro Lett. 13, 157 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-021-00680-w
Quan, B., Shi, W., Ong, S.J.H., Lu, X., Wang, P.L., Ji, G., Guo, Y., Zheng, L., Xu, Z.J.: Defect engineering in two common types of dielectric materials for electromagnetic absorption applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29(28), 1901236 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201901236
He, G., Duan, Y., Pang, H., Zhang, X.: Rational design of mesoporous MnO2 microwave absorber with tunable microwave frequency response. Appl. Surf. Sci. 490, 372–382 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.06.037
Zhou, C., Wu, C., Yan, M.: A versatile strategy towards magnetic/dielectric porous heterostructure with confinement effect for lightweight and broadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 370, 988–996 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.295
Liang, J., Chen, J., Shen, H., Hu, K., Zhao, B., Kong, J.: Hollow Porous bowl-like nitrogen-doped cobalt/carbon nanocomposites with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Mater. 33(5), 1789–1798 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.0c04734
Tian, W., Li, J., Liu, Y., Ali, R., Guo, Y., Deng, L., Mahmood, N., Jian, X.: Atomic-scale layer-by-layer deposition of FeSiAl@ZnO@Al2O3 hybrid with threshold anti-corrosion and ultra-high microwave absorption properties in low-frequency bands. Nano-Micro Lett. 13(1), 1–14 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-021-00678-4
Zhou, X., Jia, Z., Zhang, X., Wang, B., Wu, W., Liu, X., Xu, B., Wu, G.: Controllable synthesis of Ni/NiO@Porous carbon hybrid composites towards remarkable electromagnetic wave absorption and wide absorption bandwidth. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 87, 120–132 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2021.01.073
Li, X., You, W., Zhang, R., Fang, J., Zeng, Q., Li, X., Xu, C., Wang, M., Che, R.: Synthesis of nonspherical hollow architecture with magnetic Fe core and Ni decorated tadpole-like shell as ultrabroad bandwidth microwave absorbers. Small 17(46), 2103351 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202103351
Liu, J., Liang, H., Wu, H.: Hierarchical flower-like Fe3O4/MoS2 composites for selective broadband electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Compos. A 130, 105760 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2019.105760
Meng, X., Lei, W., Yang, W., Liu, Y., Yu, Y.: Fe3O4 nanoparticles coated with ultra-thin carbon layer for polarization-controlled microwave absorption performance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 600, 382–389 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.05.055
Xu, J., Liu, Z., Li, Q., Wang, Y., Shah, T., Ahmad, M., Zhang, Q., Zhang, B.: Wrinkled Fe3O4@C magnetic composite microspheres: regulation of magnetic content and their microwave absorbing performance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 601, 397–410 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.05.153
Cui, C., Guo, R., Ren, E., Xiao, H., Zhou, M., Lai, X., Qin, Q., Jiang, S., Qin, W.: MXene-based rGO/Nb2CTx/Fe3O4 composite for high absorption of electromagnetic wave. Chem. Eng. J. 405, 126626 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126626
Ning, M., Lei, Z., Tan, G., Man, Q., Li, J., Li, R.-W.: Dumbbell-like Fe3O4@N-doped carbon@2H/1T-MoS2 with tailored magnetic and dielectric loss for efficient microwave absorbing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13(39), 47061–47071 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c13852
Zhou, X., Zhang, C., Zhang, M., Feng, A., Qu, S., Zhang, Y., Liu, X., Jia, Z., Wu, G.: Synthesis of Fe3O4/carbon foams composites with broadened bandwidth and excellent electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Compos. A 127, 105627 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2019.105627
Zeng, X., Jiang, G., Zhu, L., Wang, C., Chen, M., Yu, R.: Fe3O4 nanoflower-carbon nanotube composites for microwave shielding. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2(9), 5475–5482 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.9b01076
Chen, N., Jiang, J.-T., Guan, Z.-J., Yan, S.-J., Zhen, L., Xu, C.-Y.: Designing Co7Fe3@TiO2 core-shell nanospheres for electromagnetic wave absorption in S and C bands. Electron. Mater. Lett. 16(5), 413–423 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-020-00234-z
Cheng, Y., Li, Y., Ji, G., Quan, B., Liang, X., Zhao, Z., Cao, J., Du, Y.: Magnetic and electromagnetic properties of Fe3O4/Fe composites prepared by a simple one-step ball-milling. J. Alloys Compd. 708, 587–593 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.03.060
Xu, C., Wang, L., Li, X., Qian, X., Wu, Z., You, W., Pei, K., Qin, G., Zeng, Q., Yang, Z.: Hierarchical magnetic network constructed by CoFe nanoparticles suspended within “tubes on rods” matrix toward enhanced microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 13(1), 1–15 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-020-00572-5
Zhang, Y., Yang, Z., Li, M., Yang, L., Liu, J., Ha, Y., Wu, R.: Heterostructured CoFe@C@MnO2 nanocubes for efficient microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 382, 123039 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123039
Choi, M., Choi, D., Kim, J.: Magnetic permeability behaviors of FeCo micro hollow fiber composites. Electron. Mater. Lett. 11(5), 782–787 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-015-4500-8
Jang, M.-S., Chang, M.S., Kwon, Y.-T., Yang, S., Gwak, J., Kwon, S.J., Lee, J., Song, K., Park, C.R., Lee, S.B., et al.: High-throughput thermal plasma synthesis of FexCo1-x nano-chained particles with unusually high permeability and their electromagnetic wave absorption properties at high frequency (1–26 GHz). Nanoscale 13(27), 12004–12016 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NR01845K
Gao, N., Li, W.-P., Wang, W.-S., Liu, D.-P., Cui, Y.-M., Guo, L., Wang, G.-S.: Balancing dielectric loss and magnetic loss in Fe-NiS2/NiS/PVDF composites toward strong microwave reflection loss. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12(12), 14416–14424 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b23379
Li, Z., Lin, H., Ding, S., Ling, H., Wang, T., Miao, Z., Zhang, M., Meng, A., Li, Q.: Synthesis and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performances of Fe3O4@C decorated walnut shell-derived porous carbon. Carbon 167, 148–159 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.05.070
Li, X., Qu, X., Xu, Z., Dong, W., Wang, F., Guo, W., Wang, H., Du, Y.: Fabrication of three-dimensional flower-like heterogeneous Fe3O4/Fe particles with tunable chemical composition and microwave absorption performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11(21), 19267–19276 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b01783
Liu, X., Hao, C., Jiang, H., Zeng, M., Yu, R.: Hierarchical NiCo2O4/Co3O4/NiO porous composite: a lightweight electromagnetic wave absorber with tunable absorbing performance. J. Mater. Chem. C 5(15), 3770–3778 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TC05167G
Wang, R., He, M., Zhou, Y., Nie, S., Wang, Y., Liu, W., He, Q., Wu, W., Bu, X., Yang, X.: Self-assembled 3D flower-like composites of heterobimetallic phosphides and carbon for temperature-tailored electromagnetic wave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11(41), 38361–38371 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b14873
Wang, J., Liu, L., Jiao, S., Ma, K., Lv, J., Yang, J.: Hierarchical carbon fiber@MXene@MoS2 core-sheath synergistic microstructure for tunable and efficient microwave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30(45), 2002595 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202002595
Zhao, Y., Zuo, X., Guo, Y., Huang, H., Zhang, H., Wang, T., Wen, N., Chen, H., Cong, T., Muhammad, J., et al.: Structural engineering of hierarchical aerogels comprised of multi-dimensional gradient carbon nanoarchitectures for highly efficient microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 13(1), 144 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-021-00667-7
Li, X., Dong, W., Zhang, C., Guo, W., Wang, C., Li, Y., Wang, H.: Leaf-Like Fe/C composite assembled by iron veins interpenetrated into amorphous carbon lamina for high-performance microwave absorption. Compos. A 140, 106202 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2020.106202
Xu, Z., Du, Y., Liu, D., Wang, Y., Ma, W., Wang, Y., Xu, P., Han, X.: Pea-like Fe/Fe3C nanoparticles embedded in nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes with tunable dielectric/magnetic loss and efficient electromagnetic absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11(4), 4268–4277 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b19201
Yang, Z., Xue, T., Yu, L., Ji, G., Xu, G., Xu, Z.J.: Nanocasting synthesis of Fe3O4@HTC nanocapsules and their superior electromagnetic properties. RSC Adv. 6(24), 20386–20391 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA01930G
Yang, P., Yu, M., Fu, J., Wang, L.: Synthesis and microwave absorption properties of hierarchical Fe micro-sphere assembly by nano-plates. J. Alloys Compd. 721, 449–455 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.05.296
Tong, G.-X., Wu, W.-H., Hu, Q., Yuan, J.-H., Qiao, R., Qian, H.-S.: Enhanced electromagnetic characteristics of porous iron particles made by a facile corrosion technique. Mater. Chem. Phys. 132(2–3), 563–569 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2011.11.070
Wu, H., Liu, J., Liang, H., Zang, D.: Sandwich-like Fe3O4/Fe3S4 composites for electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 393, 124743 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124743
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (Grant number 2021-BS-186, 2021-NLTS-12-01) and the Basic Research Project Educational Department of Liaoning Province (LQ2020002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NC: Conceptualization, Investigation, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing-original draft, Writing-review & editing. DL: Writing-review & editing, Data curation. X-YW: Investigation, Formal analysis. Z-JG: Data curation, Validation. J-TJ: Investigation, Formal analysis. K-JW: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Resources.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that we do not have any commercial or associative interest that represents a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, N., Li, D., Wang, XY. et al. Fabricating Fe3O4 and Fe3O4&Fe Flower-Like Microspheres for Electromagnetic Wave Absorbing in C and X Bands. Electron. Mater. Lett. 18, 370–380 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-022-00347-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-022-00347-7