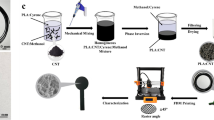
Abstract
Stable composites of water-dispersed graphene oxide (GO) and UV-cured acrylic resin, poly (ethylene glycol) diacrylate (PEGDA), were prepared to make printed conductive patterns using a digital light processing (DLP) three-dimensional (3D) printing method. The targeted structures were successfully printed by DLP 3D printing and the electrically conductive properties were obtained by reducing the insulating GO in the composites to reduced GO by chemical and thermal reduction processes. Three basic reduction procedures, pre-thermal, pre-chemical, and post-thermal reduction, were performed to introduce a high conductivity into a printed structure and the lowest resistance was achieved by the pre-thermal reduction in our study. The stability of the printed structures was also evaluated by monitoring the change in resistance with time. The strategy pursued by photopolymerization gives the outstanding features of printed structures for extensive applications in the manufacturing of electronic and sensing devices.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, H., Cao, X., Li, B., Zhou, X., Lu, G., Liusman, C., He, Q., Boey, F., Venkatraman, S.S., Zhang, H.: Single-layer graphene oxide sheet: a novel substrate for dip-pen nanolithography. Chem. Commun. 47, 10070–10072 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/c1cc12648b
Worsley, M.A., Pauzauskie, P.J., Olson, T.Y., Biener, J., Satcher, J.H., Baumann, T.F.: Synthesis of graphene aerogel with high electrical conductivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 14067–14069 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja1072299
Wu, Z.S., Ren, W., Gao, L., Zhao, J., Chen, Z., Liu, B., Tang, D., Yu, B., Jiang, C., Cheng, H.M.: Synthesis of graphene sheets with high electrical conductivity and good thermal stability by hydrogen arc discharge exfoliation. ACS Nano 3, 411–417 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn900020u
Lee, Y.R., Raghu, A.V., Jeong, H.M., Kim, B.K.: Properties of waterborne polyurethane/functionalized graphene sheet nanocomposites prepared by an in situ method. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 210, 1247–1254 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/macp.200900157
Xu, Y., Wang, Y., Liang, J., Huang, Y., Ma, Y., Wan, X., Chen, Y.: A hybrid material of graphene and poly (3,4-ethyldioxythiophene) with high conductivity, flexibility, and transparency. Nano Res. 2, 343–348 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-009-9032-9
Yoo, B.M., Shin, H.J., Yoon, H.W., Park, H.B.: Graphene and graphene oxide and their uses in barrier polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 131, 1–23 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.39628
Du, Y.C., Huang, L.J., Wang, Y.X., Yang, K., Tang, J.G., Wang, Y., Cheng, M.M., Zhang, Y., Kipper, M.J., Belfiore, L.A., Ranil, W.S.: Recent developments in graphene-based polymer composite membranes: preparation, mass transfer mechanism, and applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 136, 1–20 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.47761
Chen, C., Qiu, S., Cui, M., Qin, S., Yan, G., Zhao, H., Wang, L., Xue, Q.: Achieving high performance corrosion and wear resistant epoxy coatings via incorporation of noncovalent functionalized graphene. Carbon N. Y. 114, 356–366 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2016.12.044
Liang, Y., Wu, D., Feng, X., Müllen, K.: Dispersion of graphene sheets in organic solvent supported by ionic interactions. Adv. Mater. 21, 1679–1683 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200803160
Liu, K., Chen, L., Chen, Y., Wu, J., Zhang, W., Chen, F., Fu, Q., An, B.W., Kim, K., Kim, M., Kim, S.Y., Hur, S.H., Park, J.U.: Direct printing of reduced graphene oxide on planar or highly curved surfaces with high resolutions using electrohydrodynamics. J. Mater. Chem. 11, 8612–8617 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c1jm10717h
Liu, K., Chen, L., Chen, Y., Wu, J., Zhang, W., Chen, F., Fu, Q.: Preparation of polyester/reduced graphene oxide composites via in situ melt polycondensation and simultaneous thermo-reduction of graphene oxide. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 8612–8617 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/c1jm10717h
Gao, W., Alemany, L.B., Ci, L., Ajayan, P.M.: New insights into the structure and reduction of graphite oxide. Nat. Chem. 1, 403–408 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.281
Pei, S., Cheng, H.M.: The reduction of graphene oxide. Carbon N. Y. 50, 3210–3228 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2011.11.010
Stankovich, S., Dikin, D.A., Dommett, G.H.B., Kohlhaas, K.M., Zimney, E.J., Stach, E.A., Piner, R.D., Nguyen, S.B.T., Ruoff, R.S.: Graphene-based composite materials. Nature 442, 282–286 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04969
Tkachev, S.V., Buslaev, E.Y., Naumkin, A.V., Kotova, S.L., Laure, I.V., Gubin, S.P.: Reduced graphene oxide. Inorg. Mater. 48, 796–802 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168512080158
Ye, S., Feng, J.: A new insight into the in situ thermal reduction of graphene oxide dispersed in a polymer matrix. Polym. Chem. 4, 1765–1768 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3py00019b
Raslan, A., Saenz del Burgo, L., Ciriza, J., Luis Pedraz, J.: Graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide-based scaffolds in regenerative medicine. Int. J. Pharm. 580, 119226 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119226
Bonaccorso, F., Colombo, L., Yu, G., Stoller, M., Tozzini, V., Ferrari, A.C., Ruoff, R.S., Pellegrini, V.: Graphene, related two-dimensional crystals, and hybrid systems for energy conversion and storage. Science (80-) 347, 1246501 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1246501
Figueroa, N., Dong, H., El Saddik, A.: From sense to print: towards automatic 3D printing from 3D sensing devices. In: Proceedings of 2013 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, SMC 2013, pp. 4897–4904 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/SMC.2013.833
Rusling, J.F.: Developing microfluidic sensing devices using 3D printing. ACS Sens. 3, 522–526 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.8b00079
Leigh, S.J., Bradley, R.J., Purssell, C.P., Billson, D.R., Hutchins, D.A., Simple, A.: Low-cost conductive composite material for 3D printing of electronic sensors. PLoS ONE 7, 1–6 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0049365
Zhang, F., Tuck, C., Hague, R., He, Y., Saleh, E., Li, Y., Sturgess, C., Wildman, R.: Inkjet printing of polyimide insulators for the 3D printing of dielectric materials for microelectronic applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 133, 1–11 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.43361
Sangermano, M., Marchi, S., Valentini, L., Bon, S.B., Fabbri, P.: Transparent and conductive graphene oxide/poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate coatings obtained by photopolymerization. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 296, 401–407 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.201000372
Giardi, R., Porro, S., Chiolerio, A., Celasco, E., Sangermano, M.: Inkjet printed acrylic formulations based on UV-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. 48, 1249–1255 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-6866-4
Wu, L., Liu, L., Gao, B., Muñoz-Carpena, R., Zhang, M., Chen, H., Zhou, Z., Wang, H.: Aggregation kinetics of graphene oxides in aqueous solutions: experiments, mechanisms, and modeling. Langmuir 29, 15174–15181 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/la404134x
Maio, A., Fucarino, R., Khatibi, R., Rosselli, S., Bruno, M., Scaffaro, R.: A novel approach to prevent graphene oxide re-aggregation during the melt compounding with polymers. Compos. Sci. Technol. 119, 131–137 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2015.10.006
Mattevi, C., Eda, G., Agnoli, S., Miller, S., Mkhoyan, K.A., Celik, O., Mastrogiovanni, D., Granozzi, G., Carfunkel, E., Chhowalla, M.: Evolution of electrical, chemical, and structural properties of transparent and conducting chemically derived graphene thin films. Adv. Funct. Mater. 19, 2577–2583 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.200900166
Bourlinos, A.B., Gournis, D., Petridis, D., Szabó, T., Szeri, A., Dékány, I.: Graphite oxide: chemical reduction to graphite and surface modification with primary aliphatic amines and amino acids. Langmuir 19, 6050–6055 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1021/la026525h
Fabbri, P., Montecchi, M., Pasquali, L., Bittolo Bon, S., Sangermano, M., Valentini, L., Foix, D.: In situ graphene oxide reduction during UV-photopolymerization of graphene oxide/acrylic resins mixtures. Polymer (Guildf) 53, 6039–6044 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2012.10.045
Chiappone, A., Roppolo, I., Naretto, E., Fantino, E., Calignano, F., Sangermano, M., Pirri, F.: Study of graphene oxide-based 3D printable composites: effect of the in situ reduction. Compos. Part B Eng. 124, 9–15 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.05.049
Wei, Z., Hou, Y., Jiang, C., Liu, H., Chen, X., Zhang, A., Liu, Y.: Graphene enhanced electrical properties of polyethylene blends for high-voltage insulation. Electron. Mater. Lett. 15, 582–594 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-019-00158-3
Balasubramaniyan, R., Pham, V.H., Jang, J., Hur, S.H., Chung, J.S.: A one pot solution blending method for highly conductive poly (methyl methacrylate)-highly reduced graphene nanocomposites. Electron. Mater. Lett. 9, 837–839 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-013-6025-3
Shim, J., Lee, J., Lee, J.S., Son, D.I.: Thermally enhanced Boron Nitride nanotube/reduced Graphene Oxide paper and their application. Electron. Mater. Lett. 17, 500–506 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-021-00304-w
Choi, E., Kim, J., Cui, Y., Choi, K., Gao, Y., Han, S., Pyo, S.G.: Effect of the graphene oxide reduction temperature on supercapacitor performance. Electron. Mater. Lett. 13, 324–329 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-017-1603-4
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by research fund of the Chungnam National University. This work was also supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (NRF-2021R1I1A3052174).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, M.T.H., Kim, S.Y., Jeong, T.H. et al. Preparation and Stability of PEGDA/GO Conductive Materials by DLP 3D Printing. Electron. Mater. Lett. 18, 275–281 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-022-00338-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-022-00338-8