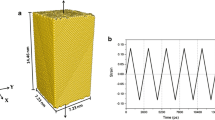
Abstract
In realistic applications, shape memory alloys are mostly under cyclic loading and, thus, fatigue failure is the major mode of failure in these components. Fatigue mainly starts from a nano- or micro-defect studying which is not feasible using experiments. Thus, Molecular Dynamics (MD) simulations are useful for obtaining understanding of the underlying mechanisms leading to failure of the part. In this study, MD simulations were performed on single crystal NiTi models containing a middle crack subjected to cyclic tensile loading in different crystallographic orientations (i.e., [100], [110] and [111]) at two austenitic temperatures. The orientation dependence of the fatigue behavior of NiTi was observed to be significant. The crack did not propagate significantly under [100] and [110] loading due to the stress-induced martensitic phase transformation at the crack tip. The formation of the martensite at the crack tip acted as a barrier to crack propagation. On the other hand, the crack grew significantly in the model loaded along [111] crystallographic orientation. The crack growth was accelerated when the crack met the {110}<111> slip system which is favorable for austenite with B2 crystal structure. In addition, the effect of temperature on the fatigue crack growth of NiTi was studied at 500 K and 550 K, both being above the austenite finish temperature. The results indicated a slower crack growth rate in NiTi at a higher temperature.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duerig, T.; Pelton, A.; Stöckel, D.: An overview of nitinol medical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 273, 149–160 (1999)
Lagoudas, D.C.: Shape Memory Alloys: Modeling and Engineering Applications. Springer, London (2008)
Ataollahi, S.; Mahtabi, M.J.: An interatomic potential for ternary NiTiHf shape memory alloys based on modified embedded atom method. Comput. Mater. Sci. 227, 112278 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2023.112278
Ataollahi, S.; Mahtabi, M.J.: A molecular dynamics study on the effect of precipitate on the phase transformation in NiTi. In: ReSEARCH Dialogues Conference Proceedings. (2021). https://scholar.utc.edu/research-dialogues/2021/posters/2.
Mahtabi, M.J.; Shamsaei, N.; Mitchell, M.R.; Fatigue of Nitinol: The state-of-the-art and ongoing challenges. J. Mech. Beh. Bio. Mat. 50, 228-254 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2015.06.010
Lado, L.; Ataollahi, S.; Yadollah, A.; Mahtabi, M.J.: Process-specific microstructure-sensitive modeling of fatigue in additively manufactured Ti-6Al-4V alloys. Solid Freeform Fabric. Symp. (SFF) 33, 801–810 (2022). https://doi.org/10.26153/tsw/44052
Mahtabi, M.; Yadollahi, A.; Stokes, R.; Morgan-Barnes, C.; Young, J.; Doude, H.; Bian, L.: Effect of powder reuse on microstructural and fatigue properties of Ti-6Al-4V fabricated via directed energy deposition. In 2022 International Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium. (2022)
Mahtabi, M.; Yadollahi, A.; Ataollahi, S.; Mahtabi, M.J.: Effect of build height on structural integrity of Ti-6Al-4V fabricated via laser powder bed fusion. Eng. Fail. Anal. 154, 107691 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2023.107691
Nishimura, K.; Miyazaki, N.: Molecular dynamics simulation of crack growth under cyclic loading. Comput. Mater. Sci. 31(3–4), 269–278 (2004)
Potirniche, G.; Horstemeyer, M.; Jelinek, B.; Wagner, G.: Fatigue damage in nickel and copper single crystals at nanoscale. Int. J. Fatigue 27(10–12), 1179–1185 (2005)
Potirniche, G.; Horstemeyer, M.; Gullett, P.; Jelinek, B.: Atomistic modelling of fatigue crack growth and dislocation structuring in FCC crystals. Proc. Royal Soc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 462(2076), 3707–3731 (2006)
Tang, T.; Kim, S.; Horstemeyer, M.: Fatigue crack growth in magnesium single crystals under cyclic loading: molecular dynamics simulation. Comput. Mater. Sci. 48(2), 426–439 (2010)
Ma, L.; Xiao, S.; Deng, H.; Hu, W.: Molecular dynamics simulation of fatigue crack propagation in bcc iron under cyclic loading. Int. J. Fatigue 68, 253–259 (2014)
Ding, J.; Wang, L.-S.; Song, K.; Liu, B.; Huang, X.: Molecular dynamics simulation of crack propagation in single-crystal aluminum plate with central cracks. J. Nanomater. 1, 17 (2017)
Chang, W.-J.; Fang, T.-H.: Influence of temperature on tensile and fatigue behavior of nanoscale copper using molecular dynamics simulation. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 64(8), 1279–1283 (2003)
You, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Moumni, Z.; Anlas, G.; Zhang, W.: Effect of the thermomechanical coupling on fatigue crack propagation in NiTi shape memory alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 685, 50–56 (2017)
Mahtabi, M.; Shamsaei, N.: Multiaxial fatigue modeling for nitinol shape memory alloys under in-phase loading. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 55, 236–249 (2016)
Zhao, T.; Kang, G.: Experimental study and life prediction on fatigue failure of NiTi shape memory alloy under multi-axial one-way shape memory cyclic loadings. Int. J. Fatigue 155, 106609 (2022)
Mahtabi, M.J.; Shamsaei, N.: Fatigue modeling for superelastic NiTi considering cyclic deformation and load ratio effects. Shape Memory Superel. 3(3), 250–263 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40830-017-0115-2
Thompson, A.P.; Aktulga, H.M.; Berger, R.; Bolintineanu, D.S.; Brown, W.M.; Crozier, P.S.; Int Veld, P.J.; Kohlmeyer, A.; Moore, S.G.; Nguyen, T.D.; Shan, R.; Stevens, M.J.; Tranchida, J.; Trott, C.; Plimpton, S.J.: Lammps - a flexible simulation tool for particle-based materials modeling at the atomic, meso, and continuum scales. Comput. Phys. Commun. 271, 108171 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpc.2021.108171
Stukowski, A.: Visualization and analysis of atomistic simulation data with ovito–the open visualization tool. Modell. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 18(1), 015012 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1088/0965-0393/18/1/015012
Hirel, P.: Atomsk: a tool for manipulating and converting atomic data files. Comput. Phys. Commun. 197, 212–219 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpc.2015.07.012
Ko, W.-S.; Grabowski, B.; Neugebauer, J.: Development and application of a Ni-Ti interatomic potential with high predictive accuracy of the martensitic phase transition. Phys. Rev. B 92(13), 134107 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.92.134107
Ataollahi, S.; Mahtabi, M.J.: Effects of precipitate on the phase transformation of single-crystal NiTi alloy under thermal and mechanical loads: a molecular dynamics study. Mater. Today Commun. 29, 102859 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2021.102859
Chandra, S.; Kumar, N.N.; Samal, M.K.; Chavan, V.M.; Patel, R.J.: Molecular dynamics simulations of crack growth behavior in Al in the presence of vacancies. Comput. Mater. Sci. 117, 518–526 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2016.02.032
Lu, M.; Wang, F.; Zeng, X.; Chen, W.; Zhang, J.: Cohesive zone modeling for crack propagation in polycrystalline NiTi alloys using molecular dynamics. Theoret. Appl. Fract. Mech. 105, 102402 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tafmec.2019.102402
Xie, G.; Wang, F.; Song, B.; Cheng, J.; Wang, J.; Zeng, X.: Grain size dependence of cracking performance in polycrystalline NiTi alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 884, 161132 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.161132
Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Gan, Y.; Han, X.; Liu, W.; Xin, H.: Micromechanism of partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide molecule agglomeration morphology and its impact on the stability of crude oil−water interfacial film. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 214, 110492 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2022.110492
Larsen, P.M.; Schmidt, S.; Schiøtz, J.: Robust structural identification via polyhedral template matching. Modell. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 24(5), 055007 (2016)
Sgambitterra, E.; Magaro, P.; Niccoli, F.; Furgiuele, F.; Maletta, C.: Fatigue crack growth in austenitic and martensitic NiTi: Modeling and experiments. Shape Memory Superel. 7(2), 250–261 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40830-021-00327-0
Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Sun, B.; Ponge, D.; Jiang, C.; Raabe, D.: The dual role of martensitic transformation in fatigue crack growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 119(9), e2110139119 (2022)
Okamoto, P.; Heuer, J.; Lam, N.; Ohnuki, S.; Matsukawa, Y.; Tozawa, K.; Stubbins, J.: Stress-induced amorphization at moving crack tips in NiTi. Appl. Phys. Lett. 73(4), 473–475 (1998)
Tozawa, K.; Haishi, Y.; Matsukawa, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Ohnuki, S.; Takahashi, H.: Nano-crystalline formation during stress-induced amorphization at crack tips in TiNi. Microscopy 48(5), 613–616 (1999)
Sgambitterra, E.; Maletta, C.; Magarò, P.; Renzo, D.; Furgiuele, F.; Sehitoglu, H.: Effects of temperature on fatigue crack propagation in pseudoelastic NiTi shape memory alloys. Shape Memory Superelast. 5(3), 278–291 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40830-019-00231-8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ataollahi, S., Mahtabi, M.J. An Investigation of the Growth of Fatigue Cracks in Single Crystal Superelastic NiTi Under High Strain Level Using Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Arab J Sci Eng (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-08460-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-08460-x