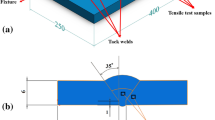
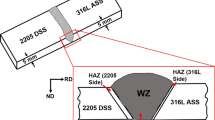
Abstract
The effect of weld chemistry (two types of electrodes (E2594 and E2595)) on the microstructure and texture development using electron back scattered diffraction and thermal stability during shielded metal arc welding of alloy 2507 have been studied. Base metal showed alternate bands of austenite (γ) and ferrite (δ) in almost equal fractions. Weldments were mainly comprised of 3 zones, namely base metal zone (BMZ), heat affected zone (HAZ), and weld metal zone (WMZ). After welding, ferritic solidification mode was found with diverse morphologies of austenite viz. grain boundary austenite, Widmanstatten austenite, and intergranular austenite and a decrease in the fraction of austenite in WMZ and HAZ. The texture intensity of δ was observed to be higher than that of γ. This implies a stronger texture for δ (a strong rotated cube texture \(\left( {\left\{ {001} \right\}\left\langle {110} \right\rangle } \right)\) along with minor α-fibre \(\left( {{\text{rolling}}\;{\text{direction}},\;{\text{RD}}//\left\langle {110} \right\rangle } \right)\) and γ-fibre \(\left( {{\text{normal}}\;{\text{direction}},\;{\text{ND}}//\left\langle {111} \right\rangle } \right)\)) than γ [Brass, Cu, Goss and S texture components (\(\left\{ {110} \right\}\left\langle {112} \right\rangle\), \(\left\{ {112} \right\}\left\langle {111} \right\rangle\), \(\left\{ {110} \right\}\left\langle {001} \right\rangle\) and \(\left\{ {123} \right\}\left\langle {634} \right\rangle\), respectively)] in the annealed state (BMZ). γ/δ grains showed the Kurdjumov–Sachs (K–S) orientation relationship. Kernel average misorientation (KAM) graphs/maps showed no significant change in BMZ but a substantial decrease in KAM values in δ than γ for both weldments. The peak temperature attained was sufficiently higher than the melting temperature of base/filler metal suggesting the proper melting and diffusion of molten metal throughout the thickness. The size of the melt pool widened for E2594 and was relatively small for E2595.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data also forms part of an ongoing study.
References
Maurya, A.K.; Pandey, C.; Chhibber, R.: Dissimilar welding of duplex stainless steel with Ni alloys: a review. Int. J. Press. Vessels Piping. 192, 104439 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpvp.2021.104439
Tavares, S.S.M.; Pardal, J.M.; Lima, L.D.; Bastos, I.N.; Nascimento, A.M.; de Souza, J.A.: Characterization of microstructure, chemical composition, corrosion resistance and toughness of a multipass weld joint of superduplex stainless steel UNS S32750. Mater. Charact. 58, 610–616 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2006.07.006
Kumar, A.; Londhe, S.; Dandekar, T.; Kamath, S.L.; Khatirkar, R.K.: Effect of cooling rate on the precipitation behavior of a Fe–Cr–Ni alloy. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 73, 1961–1973 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-020-02011-w
Dandekar, T.R.; Khatirkar, R.K.; Gupta, A.; Bibhanshu, N.; Bhadauria, A.; Suwas, S.: Strain rate sensitivity behaviour of Fe–21Cr–1.5Ni–5Mn alloy and its constitutive modelling. Mater. Chem. Phys. 271, 124948 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.124948
Arun, D.; Devendranath Ramkumar, K.; Vimala, R.: Multi-pass arc welding techniques of 12 mm thick super-duplex stainless steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 271, 126–143 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2019.03.031
Muthupandi, V.; Bala Srinivasan, P.; Seshadri, S.K.; Sundaresan, S.: Effect of weld metal chemistry and heat input on the structure and properties of duplex stainless steel welds. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 358, 9–16 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(03)00077-7
Dandekar, T.R.; Khatirkar, R.K.; Mahadule, D.; Chavhan, J.; Kumar, D.: Aging phenomenon in low molybdenum Fe–21Cr–5Mn–1.5Ni alloy: Microstructure evolution, texture development and corrosion behavior. Mater. Today Commun. 33, 104913 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.104913
Dandekar, T.R.; Kumar, A.; Khatirkar, R.K.; Singh, J.; Kumar, D.: Effect of isothermal aging at 750 °C on microstructure and mechanical properties of UNS S32101 lean duplex stainless steel. Mater. Today Commun. 29, 102753 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2021.102753
Yadaiah, N.; Bag, S.: Development of egg-configuration heat source model in numerical simulation of autogenous fusion welding process. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 86, 125–138 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2014.06.032
Criales, L.E.; Arısoy, Y.M.; Lane, B.; Moylan, S.; Donmez, A.; Özel, T.: Laser powder bed fusion of nickel alloy 625: experimental investigations of effects of process parameters on melt pool size and shape with spatter analysis. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf 121, 22–36 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2017.03.004
Kumar, B.; Bag, S.: Phase transformation effect in distortion and residual stress of thin-sheet laser welded Ti-alloy. Opt. Lasers Eng. 122, 209–224 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2019.06.008
Kumar, B.; Bag, S.; Mahadevan, S.; Paul, C.P.; Das, C.R.; Bindra, K.S.: On the interaction of microstructural morphology with residual stress in fiber laser welding of austenitic stainless steel. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 33, 158–175 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirpj.2021.03.009
Mondal, A.K.; Kumar, B.; Bag, S.; Nirsanametla, Y.; Biswas, P.: Development of avocado shape heat source model for finite element based heat transfer analysis of high-velocity arc welding process. Int. J. Thermal Sci. 166, 107005 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2021.107005
He, X.; Fuerschbach, P.W.; DebRoy, T.: Heat transfer and fluid flow during laser spot welding of 304 stainless steel. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 36, 1388–1398 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/36/12/306
Taylor, G.A.; Hughes, M.; Strusevich, N.; Pericleous, K.: Finite volume methods applied to the computational modelling of welding phenomena. Appl. Math. Model. 26, 311–322 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0307-904X(01)00063-4
Aguiar, I.V.; Escobar, D.P.; Santos, D.B.; Modenesi, P.J.: Microstructure characterization of a duplex stainless steel weld by electron backscattering diffraction and orientation imaging microscopy techniques. Matéria (Rio J) 20, 212–226 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-707620150001.0022
Norsok Standard M601-94. Welding and inspection of piping. Lysaker, Norway: Standards Norway; 2004. (n.d.)
Calliari, I.; Brunelli, K.; Dabalà, M.; Ramous, E.: Measuring secondary phases in duplex stainless steels. JOM. 61, 80–83 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-009-0016-8
Silva, D.D.S.; Simões, T.A.; Macedo, D.A.; Bueno, A.H.S.; Torres, S.M.; Gomes, R.M.: Microstructural influence of sigma phase on pitting corrosion behavior of duplex stainless steel/NaCl electrolyte couple. Mater. Chem. Phys. 259, 124056 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.124056
Chumbley, S.L.: Clean cast steel technology. Determination of transformation diagrams for duplex stainless steel (No. DOE/ID/14229-ISU-Final). Iowa State University, Ames, IA, USA (2005). https://doi.org/10.2172/850237
Freitas, G.C.L.D.; da Fonseca, G.S.; Moreira, L.P.; Leite, D.N.F.: Phase transformations of the duplex stainless steel UNS S31803 under non-isothermal conditions. J. Market. Res. 11, 1847–1851 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.02.008
Köse, C.; Topal, C.: Texture, microstructure and mechanical properties of laser beam welded AISI 2507 super duplex stainless steel. Mater. Chem. Phys. 289, 126490 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2022.126490
Badji, R.; Bacroix, B.; Bouabdallah, M.: Texture, microstructure and anisotropic properties in annealed 2205 duplex stainless steel welds. Mater. Charact. 62, 833–843 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2011.06.001
Sirohi, S.; Pandey, C.; Goyal, A.: Characterization of structure-property relationship of martensitic P91 and high alloy ferritic austenitic F69 steel. Int. J. Press. Vessels Piping 188, 104179 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpvp.2020.104179
Shamanian, M.; Kangazian, J.; Szpunar, J.A.: Insights into the microstructure evolution and crystallographic texture of API X-65 steel/UNS S32750 stainless steel dissimilar welds by EBSD analysis, Weld. World 65, 973–986 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-020-01062-3
Dandekar, T.R.; Gupta, A.; Kumar, A.; Khatirkar, R.K.; Vadavadagi, B.: Shielded metal arc welding of UNS S32750 steel: microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion behaviour. Mater. Res. Express. 5, 106506 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aad99a
OIM, Analysis Version 7.2, TexSEM Laboratories Inc, Draper (2013)
Standard practice for preparation of metallographic specimens, E3–95, ASTM, PA, USA (1995)
Kumar, B.; Nagamani Jaya, B.: Thermal stability and residual stresses in additively manufactured single and multi-material systems. Metall. Mater. Trans. A (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-022-06928-3
Etter, A.L.; Baudin, T.; Mathon, M.H.; Swiatnicki, W.; Penelle, R.: Stored energy evolution in both phases of a duplex steel as a function of cold rolling reduction. Scr. Mater. 54, 683–688 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2005.10.034
Dandekar, T.R.; Khatirkar, R.K.; Kumar, A.; Bibhanshu, N.; Suwas, S.: Unidirectional cold rolling of Fe–21Cr–5Mn–1.5Ni alloy—microstructure, texture and magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 549, 169040 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2022.169040
Dandekar, T.R.; Kumar, A.; Khatirkar, R.K.; Mahadule, D.; Ayyappan, G.: Multistep cross rolling of UNS S32101 steel: microstructure, texture, and magnetic properties. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 30, 2916–2929 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05510-z
Taisne, A.; Décamps, B.; Priester, L.: Interface structure in ferritic/austenitic stainless steel bicrystals. MRS Proc. 652, Y8.14 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-652-Y8.14
Gerber, P.; Tarasiuk, J.; Chauveau, T.; Bacroix, B.: A quantitative analysis of the evolution of texture and stored energy during annealing of cold rolled copper. Acta Mater. 51, 6359–6371 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2003.08.039
Verlinden, B.; Driver, J.; Samajdar, I.; Doherty, R.D.: Thermo-mechanical processing of metallic materials. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2007)
Nowacki, J.; Łukojć, A.: Structure and properties of the heat-affected zone of duplex steels welded joints. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 164–165, 1074–1081 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2005.02.243
Chen, L.; Tan, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Jiang, Y.: Influence of cooling rate on microstructure evolution and pitting corrosion resistance in the simulated heat-affected zone of 2304 duplex stainless steels. Corros. Sci. 58, 168–174 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2012.01.018
Suwas, S.; Ray, R.K.: Crystallographic texture of materials. Springer, London (2014)
Herrera, C.; Ponge, D.; Raabe, D.: Characterization of the microstructure, crystallographic texture and segregation of an As-cast duplex stainless steel slab. Steel Res. Int. 79, 482–488 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.200806156
Wu, S.H.; Huang, J.C.; Wang, Y.N.: Evolution of microstructure and texture in Mg–Al–Zn alloys during electron-beam and gas tungsten arc welding. Metall. Mat. Trans. A 35, 2455–2469 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-006-0226-4
Hasan, F.; Jahanafrooz, A.; Lorimer, G.W.; Ridley, N.: The morphology, crystallography, and chemistry of phases in as-cast nickel–aluminum bronze. MTA 13, 1337–1345 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02642870
Vinoth Jebaraj, A.; Ajaykumar, L.; Deepak, C.R.; Aditya, K.V.V.: Weldability, machinability and surfacing of commercial duplex stainless steel AISI2205 for marine applications—a recent review. J. Adv. Res. 8, 183–199 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2017.01.002
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Director, IIT Bombay for providing the necessary facilities and constant encouragement to publish this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TRD: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Writing—Original draft, Visualization. BK: Methodology, Investigation, Visualization. RKK: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dandekar, T.R. Insights into the Microstructure and Texture Evolution Using Electron Backscattered Diffraction and Thermal Stability of Low Mn Fe–25Cr–6.5Ni–3.5Mo Alloy. Arab J Sci Eng 49, 1447–1459 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07881-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07881-y