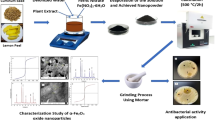
Abstract
Herein, the cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) magnetic nanoparticles-loaded date palm pollen (CFMNP-DPP) was synthesized using a one-step hydrothermal method, and its antibacterial capability was investigated. The CFMNP-DPP was completely characterized by various techniques such as powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), diffuse reflection spectroscopy (DRS), vibrating-sample magnetometer (VMS), and BET surface area analysis techniques confirmed the CoFe2O4 MNP was successfully stabilized on the palm pollen grains and resulted in porous, spherical ferrite magnetic particles with a size lower than 36 nm. Then, the antibacterial effect of prepared nanoparticles was studied against pathogenic bacteria Escherichia coli (E. coli), Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), and Klebsiella pneumoniae (K. pneumoniae). Overall, CFMNP-DPP concentrations of 10 to 70 µg/mL showed remarkable antibacterial activity. The maximum inhibition zone of the nanoparticles at 70 μg/mL for E. coli, S. aureus, and K. pneumoniae was 10, 12, and 12 mm, respectively. Consequently, CFMNP-DPP improved antibacterial activity in multidrug-resistant bacteria and can be used for medicinal applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ebrahiminezhad, A.; Zare-Hoseinabadi, A.; Sarmah, A.K.; Taghizadeh, S.; Ghasemi, Y.; Berenjian, A.: Plant-mediated synthesis and applications of iron nanoparticles. Mol. Biotechnol. 60, 154–168 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-017-0053-4
Kozma, G.; Rónavári, A.; Kónya, Z.; Kukovecz, A.: Environmentally benign synthesis methods of zero-valent iron nanoparticles. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 4, 291–297 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b01185
Dauthal, P.; Mukhopadhyay, M.: Noble metal nanoparticles: plant-mediated synthesis, mechanistic aspects of synthesis, and applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 55, 9557–9577 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.6b00861
Vijayaraghavan, K.; Nalini, S.K.: Biotemplates in the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Biotechnol. J. 5, 1098–1110 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201000167
Keat, C.L.; Aziz, A.; Eid, A.M.; Elmarzugi, N.A.: Biosynthesis of nanoparticles and silver nanoparticles. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2, 1–11 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-015-0076-2
Rajeshkumar, S.; Bharath, L.V.: Mechanism of plant-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles—a review on biomolecules involved, characterisation and antibacterial activity. Chem. Biol. Interact. 273, 219–227 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2017.06.019
Verma, S.K.; Jha, E.; Kumar Panda, P.; Thirumurugan, A.; Patro, S.; Parashar, S.K.S.; Suar, M.: Molecular insights to alkaline based bio-fabrication of silver nanoparticles for inverse cytotoxicity and enhanced antibacterial activity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 92, 807–818 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2018.07.037
Zheng, B.; Kong, T.; Jing, X.; Odoom-Wubah, T.; Li, X.; Sun, D.; Lu, F.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, Q.: Plant-mediated synthesis of platinum nanoparticles and its bioreductive mechanism. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 396, 138–145 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2013.01.021
Kumar, V.; Yadav, S.K.: Plant-mediated synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles and their applications. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 84, 151–157 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.2023
Nath, S.; Shyanti, R.K.; Pathak, B.: Plant-mediated synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles for antibacterial and anticancer applications. In: Green Nanoparticles. Springer, 2020, pp. 163–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-39246-8_7
Manjari, G.; Saran, S.; Arun, T.; Devipriya, S.P.; Vijaya Bhaskara Rao, A.: Facile Aglaia elaeagnoidea mediated synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles: antioxidant and catalysis properties. J. Clust. Sci. 28, 2041–2056 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-017-1199-8
Ansari, M.A.; Khan, H.M.; Alzohairy, M.A.; Jalal, M.; Ali, S.G.; Pal, R.; Musarrat, J.: Green synthesis of Al2O3 nanoparticles and their bactericidal potential against clinical isolates of multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 31, 153–164 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-014-1757-2
Jamdagni, P.; Rana, J.S.; Khatri, P.; Nehra, K.: Comparative account of antifungal activity of green and chemically synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles in combination with agricultural fungicides. Int. J. Nano Dimens. 9, 198–208 (2018)
Ogunyemi, S.O.; Abdallah, Y.; Zhang, M.; Fouad, H.; Hong, X.; Ibrahim, E.; Masum, M.M.I.; Hossain, A.; Mo, J.; Li, B.: Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using different plant extracts and their antibacterial activity against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 47, 341–352 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2018.1557671
Savale, A.; Ghotekar, S.; Pansambal, S.; Pardeshi, O.: Green synthesis of fluorescent CdO nanoparticles using Leucaena leucocephala L. extract and their biological activities. J. Bacteriol. Mycol. Open Access 5, 00148–00153 (2017)
Khatami, M.; Heli, H.; Mohammadzadeh Jahani, P.; Azizi, H.; Lima Nobre, M.A.: Copper/copper oxide nanoparticles synthesis using Stachys lavandulifolia and its antibacterial activity. IET Nanobiotechnol. 11, 709–713 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-nbt.2016.0189
Manjari, G.; Saran, S.; Arun, T.; Vijaya Bhaskara Rao, A.; Devipriya, S.P.: Catalytic and recyclability properties of phytogenic copper oxide nanoparticles derived from Aglaia elaeagnoidea flower extract. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 21, 610–618 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2017.02.004
Arumugam, A.; Karthikeyan, C.; Hameed, A.S.H.; Gopinath, K.; Gowri, S.; Karthika, V.: Synthesis of cerium oxide nanoparticles using Gloriosa superba L. leaf extract and their structural, optical and antibacterial properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 49, 408–415 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.01.042
Fardsadegh, B.; Jafarizadeh-Malmiri, H.: Aloe vera leaf extract mediated green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles and assessment of their in vitro antimicrobial activity against spoilage fungi and pathogenic bacteria strains. Green Process. Synth. 8, 399–407 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1515/gps-2019-0007
Gunti, L.; Dass, R.S.; Kalagatur, N.K.: Phytofabrication of selenium nanoparticles from Emblica officinalis fruit extract and exploring its biopotential applications: antioxidant, antimicrobial, and biocompatibility. Front. Microbiol. 10, 931–948 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00931
Babu, R.H.; Yugandhar, P.; Savithramma, N.: Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial studies of bio silica nanoparticles prepared from Cynodon dactylon L.: a green approach. Bull. Mater. Sci. 41, 1–8 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-018-1584-4
Jalill, R.D.A.; Nuaman, R.S.; Abd, A.N.: Biological synthesis of Titanium Dioxide nanoparticles by Curcuma longa plant extract and study its biological properties. World Sci. News 2, 204–222 (2016)
Subhapriya, S.; Gomathipriya, P.: Green synthesis of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles by Trigonella foenum-graecum extract and its antimicrobial properties. Microb. Pathog. 116, 215–220 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2018.01.027
Ahmad, W.; Jaiswal, K.K.; Soni, S.: Green synthesis of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles by using Mentha arvensis leaves extract and its antimicrobial properties. Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 50, 1032–1038 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/24701556.2020.1732419
Mahran, G.H.; Abdel-Wahab, S.M.; Attia, A.M.: A phytochemical study of date palm pollen. Planta. Med. 29, 171–175 (1976)
Shahriarinour, M.; Divsar, F.: Release kinetics and antibacterial property of curcumin-loaded date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) pollen. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07301-7
Shahriarinour, M.; Divsar, F.; Youseftabar-Miri, L.; Banimahd Keivani, M.: Date palm pollen as a promising drug delivery system: release kinetic model and antimicrobial activity. Iran. J. Anal. Chem. 8, 90–98 (2021). https://doi.org/10.30473/ijac.2022.62531.1218
Hedayati, K.; Azarakhsh, S.; Ghanbari, D.: Synthesis and magnetic investigation of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles prepared via a simple chemical precipitation method. J. Nanostruct. 6, 127–131 (2016). https://doi.org/10.7508/jns.2016.02.004
Vinosha, P.A.; Mely, L.A.; Mary, G.I.N.; Mahalakshmi, K.; Das, S.J.: Study on cobalt ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation technique for photo-fenton application. Mech. Mater. Sci. Eng. J. 9, 1–7 (2017). https://doi.org/10.2412/mmse.36.49.466
Srinivasan, S.Y.; Paknikar, K.M.; Bodas, D.; Gajbhiye, V.: Applications of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles in biomedical nanotechnology. Nanomedicine 13, 1221–1238 (2018). https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm-2017-0379
Franco Jr., A.; Silva, F.C.: High temperature magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 172505–172509 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3422478
Ajroudi, L.; Villain, S.; Madigou, V.; Mliki, N.; Leroux, C.: Synthesis and microstructure of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Cryst. Growth 312, 2465–2471 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2010.05.024
Singh Yadav, R.; Havlica, J.; Masilko, J.; Kalina, L.; Wasserbauer, J.; Hajdúchová, M.; Enev, V.; Kuřitka, I.; Kožáková, Z.: Impact of Nd3+ in CoFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles on cation distribution, structural and magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 399, 109–117 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.09.055
Sumera, K.; Nasir, M.A.; Naveed, A.; Sadia, M.; Muhammad, A.H.; Nauman, N.; TenÃrio, M.K.L.; Noureddine, L.; Abdelhamid, E.: Aminodextran coated CoFe2O4 nanoparticles for combined magnetic resonance imaging and hyperthermia. Nanomaterials 10, 2182–2198 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112182
Darwish, A.M.G.; Khalifa, R.E.; El Sohaimy, S.A.: Functional properties of chia seed mucilage supplemented in low fat yoghurt. Alex. Sci. Exch. J. 39, 450–459 (2018). https://doi.org/10.21608/ASEJAIQJSAE.2018.13882
Yan, T.; Liu, H.; Gao, P.; Sun, M.; Wei, Q.; Xu, W.; Wang, X.; Du, B.: Facile synthesized highly active BiOI/Zn2GeO4 composites for the elimination of endocrine disrupter BPA under visible light irradiation. New J. Chem. 39, 3964–3972 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NJ02360A
Verma, S.K.; Jha, E.; Panda, P.K.; Thirumurugan, A.; Parashar, S.K.S.; Patro, S.; Suar, M.: Mechanistic insight into size dependent enhanced cytotoxicity of industrial antibacterial titanium oxide nanoparticles on colon cells because of reactive oxygen species quenching and neutral lipid alteration. ACS Omega 3, 1244–1262 (2018)
Verma, S.K.; Jha, E.; Sahoo, B.; Kumar Panda, P.; Thirumurugan, A.; Parashar, S.K.S.; Suar, M.: Mechanistic insight into the rapid one-step facile biofabrication of antibacterial silver nanoparticles from bacterial release and their biogenicity and concentration-dependent in vitro cytotoxicity to colon cells. RSC Adv. 7, 40034–40045 (2017)
Verma, S.K.; Jha, E.; Kumar Panda, P.; Das, J.K.; Thirumurugan, A.; Suar, M.; Parashar, S.K.S.: Molecular aspects of core-shell intrinsic defect induced enhanced antibacterial activity of ZnO nanocrystals. Nanomedicine 13, 1–26 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by Iran National Science Foundation Science (INSF, No:91002235). Also, we would like to thank the Research Council of the University of Islamic Azad University for providing a good contribution to all aspects of the project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shahriarinour, M., Divsar, F., Mehdipour, A. et al. Antibacterial Properties of Cobalt Ferrite Magnetic Nanoparticles Loaded on Date Palm Pollen Against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 7315–7322 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07811-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07811-y