Abstract
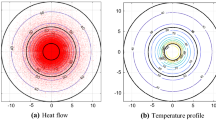
In solving the system of hyperbolic equations, highly accurate numerical methods which are easy to apply and have a shorter run time without causing numerical oscillations are more popular. In the present study, the space–time conservation element and solution element (CESE) method has been developed into two-dimensional spherical coordinates using polar elements. Then, the developed CESE method has been applied to investigate the propagation of a non-Fourier thermal waves in biological tissue. To evaluate the performance of the CESE method, the numerical results are compared to the existing semi-analytical results, and it is observed that the results are in good agreement. The experimental test is then conducted to measure the transient temperature behavior of the spherical Intralipid phantom irradiated by a near-infrared pulsed laser. A comparison of experimental and numerical results demonstrates the applicability of the dual phase lag model in the prediction of non-Fourier heat conduction in biological tissue. In addition, the contours of heat flux and temperature during and after laser irradiation are presented, and the propagation of thermal waves in the tissue is examined and discussed. The results indicate that the effects of the two-dimensional thermal wave appear after stopping the laser irradiation. Finally, the study of the effect of tissue type on wave progression in the tumor, muscle, and fat demonstrates that in the fat tissue, having the lowest thermal diffusivity, the thermal progression is less than the tumor and muscle. However, the temperature distribution in the fat tissue is greater than in the other tissues.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(c\) :
-
Specific heat of tissue
- \(c_{{\text{b}}}\) :
-
Specific heat of blood
- \({\varvec{F}}\) :
-
Flux vector in radial direction
- \({\varvec{G}}\) :
-
Flux vector in angular direction
- \({\varvec{H}}\) :
-
Space–time flux vector
- \(k\) :
-
Thermal conductivity
- \({\varvec{q}}\) :
-
Heat flux vector
- \({\varvec{q}}_{{\mathbf{r}}}\) :
-
Heat flux in radial direction
- \({\varvec{q}}_{{\varvec{\theta}}}\) :
-
Heat flux in angular direction
- \(q_{{\text{L}}}\) :
-
Laser intensity
- \(Q_{{\text{m}}}\) :
-
Metabolic heat generation
- \(Q_{{\text{r}}}\) :
-
Dimensionless heat flux in radial direction
- \(Q_{\theta }\) :
-
Dimensionless heat flux in angular direction
- \(r\) :
-
Coordinate variable in radial direction
- \({\varvec{r}}\) :
-
2-D position vector
- \(R\) :
-
Diffuse reflectance
- \({\varvec{S}}\) :
-
Source vector
- \(t\) :
-
Time
- \(T\) :
-
Temperature of tissue
- \(T_{{\text{b}}}\) :
-
Blood temperature
- \({\varvec{U}}\) :
-
Primary variable vector
- \(\zeta\) :
-
Dimensionless radius
- \(\eta\) :
-
Dimensionless time
- \(\theta\) :
-
Coordinate variable in angular direction
- \(\theta^{*}\) :
-
Dimensionless angle
- \(\rho\) :
-
Density of tissue
- \(\rho_{{\text{b}}}\) :
-
Density of blood
- \(\tau_{q}\) :
-
Phase lag time of heat flux
- \(\tau_{{\text{T}}}\) :
-
Phase lag time of temperature gradient
- \({\Phi }\) :
-
Dimensionless temperature
- \(\omega_{{\text{b}}}\) :
-
Blood perfusion rate
References
Dhar, P.; Paul, A.; Narasimhan, A.; Das, S.K.: Analytical prediction of sub–surface thermal history in translucent tissue phantoms during plasmonic photo–thermotherapy (PPTT). J. Therm. Biol. 62, 143–149 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtherbio.2016.06.023
Kumar, D.; Rai, K.: A study on thermal damage during hyperthermia treatment based on DPL model for multilayer tissues using finite element Legendre wavelet Galerkin approach. J. Therm. Biol. 62, 170–180 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtherbio.2016.06.020
Turkyilmazoglu, M.: Heat transfer from warm water to a moving foot in a footbath. Appl. Therm. Eng. 98, 280–287 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.12.027
Chang, S.C.: The method of space-time conservation element and solution element—a new approach for solving the Navier-Stokes and Euler equations. J. Comput. Phys. 119(2), 295–324 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1006/jcph.1995.1137
Poshti, A.G.T.; Khosravirad, A.; Ayani, M.B.: Analyses of non-Fourier heat conduction in 1-D spherical biological tissue based on dual-phase-lag bio-heat model using the conservation element/solution element (CE/SE) method: a numerical study. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 132, 105881 (2022)
Chang, S.C.; Wang, X.Y.; Chow, C.Y.: The method of space-time conservation element and solution element-applications to one-dimensional and two-dimensional time-marching flow problems. In: 12th Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference, p. 1754 (1995). https://doi.org/10.2514/6.1995-1754
Chang, S.C.; Wang, X.Y.; Chow, C.Y.: The space-time conservation element and solution element method: a new high-resolution and genuinely multidimensional paradigm for solving conservation laws. J. Comput. Phys. 156(1), 89–136 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1006/jcph.1999.6354
Zhang, Z.C.; Yu, S.J.; Chang, S.C.: A space-time conservation element and solution element method for solving the two-and three-dimensional unsteady Euler equations using quadrilateral and hexahedral meshes. J. Comput. Phys. 175(1), 168–199 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1006/jcph.2001.6934
Zhang, Z.C.; Yu, S.; Wang, X.Y.; Chang, S.C.; Himansu, A.; Jorgenson, P.: The CE/SE method for Navier-Stokes equations using unstructured meshes for flows at all speeds. In: 38th Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, p. 393 (2000). https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2000-393
Zhang, Z.C.; Yu, S.; He, H.; Chang, S.C.: Direct calculations of two-and three-dimensional detonations by an extended CE/SE method. In: 39th Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, p. 476 (2001). https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2001-476
Qamar, S.; Mudasser, S.: On the application of a variant CE/SE method for solving two-dimensional ideal MHD equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 60(6), 587–606 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apnum.2010.02.005
Chang, C.L.; Choudhari, M.M.: Hypersonic viscous flow over large roughness elements. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 25(1–4), 85–104 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00162-010-0191-9
Shen, H.; Wen, C.Y.; Saldívar Massimi, H.: Application of CE/SE method to study hypersonic non-equilibrium flows over spheres. In: 19th AIAA International Space Planes and Hypersonic Systems and Technologies Conference, p. 2509 (2014). https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2014-2509
Weng, C.; Gore, J.P.: A numerical study of two-and three-dimensional detonation dynamics of pulse detonation engine by the CE/SE method. Acta Mech. Sin. 21(1), 32–39 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-004-0004-8
Chou, Y.; Yang, R.J.: Two-dimensional dual-phase-lag thermal behavior in single-/multi-layer structures using CESE method. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 52(1), 239–249 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2008.06.025
Gang, W.; De-Liang, Z.; Kai-Xin, L.: An improved CE/SE scheme and its application to detonation propagation. Chin. Phys. Lett. 24(12), 3563 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1088/0256-307X/24/12/074
Wang, G.; Zhu, H.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, D.; Liu, K.: An improved CE/SE scheme and its application to dilute gas–particle flows. Comput. Phys. Commun. 182(8), 1589–1601 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpc.2011.04.004
Wang, G.; Zhang, D.; Liu, K.; Wang, J.: An improved CE/SE scheme for numerical simulation of gaseous and two-phase detonations. Comput. Fluids 39(1), 168–177 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compfluid.2009.07.010
Wang, J.; Liu, K.; Zhang, D.: An improved CE/SE scheme for multi-material elastic–plastic flows and its applications. Comput. Fluids 38(3), 544–551 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compfluid.2008.04.014
Noor, S.; Qamar, S.: Solution of a multi-dimensional batch crystallization model with fines dissolution using CE/SE method. Life Sci. J. 23, 337–341 (2014)
Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, J.: The improved space–time conservation element and solution element scheme for two-dimensional dam-break flow simulation. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 68(5), 605–624 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/fld.2525
Qamar, S.; Warnecke, G.: Application of space–time CE/SE method to shallow water magnetohydrodynamic equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 196(1), 132–149 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cam.2005.08.014
Jiang, C.; Feng, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, D.: AMR simulations of magnetohydrodynamic problems by the CESE method in curvilinear coordinates. Sol. Phys. 267(2), 463–491 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-010-9649-6
Paul, A.; Narasimhan, A.; Kahlen, F.J.; Das, S.K.: Temperature evolution in tissues embedded with large blood vessels during photo-thermal heating. J. Therm. Biol. 41, 77–87 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtherbio.2014.02.010
Sahoo, N.; Ghosh, S.; Narasimhan, A.; Das, S.K.: Investigation of non-Fourier effects in bio-tissues during laser assisted photothermal therapy. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 76, 208–220 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2013.08.014
Singh, G.; Anand, S.; Lall, B.; Srivastava, A.; Singh, V.: A low-cost portable wireless multi-frequency electrical impedance tomography system. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 44(3), 2305–2320 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3435-4
Li, C.; Miao, J.; Yang, K.; Guo, X.; Tu, J.; Huang, P., et al.: Fourier and non-Fourier bio-heat transfer models to predict ex vivo temperature response to focused ultrasound heating. J. Appl. Phys. 123(17), 174906 (2018)
Qiu, T.; Tien, C.: Heat transfer mechanisms during short-pulse laser heating of metals. J. Heat Transf. 115(4), 835–841 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2911377
Maurer, M.; Thompson, H.: Non-Fourier effects at high heat flux. J. Heat Transf. 95(2), 284–286 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3450051
Cimmelli, V.A.; Frischmuth, K.: Hyperbolic heat conduction at cryogenic temperatures. Reniconti Del Circolo Matematico Di Palermo. 45, 137–145 (1996)
Turkyilmazoglu, M.: Heat transfer enhancement feature of the Non-Fourier Cattaneo-Christov heat flux model. J. Heat Transf. 143(9), 094501 (2021)
Jafarimoghaddam, A.; Turkyilmazoglu, M.; Pop, I.: Threshold for the generalized Non-Fourier heat flux model: Universal closed form analytic solution. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 123, 105204 (2021)
Antaki, P.J.: New interpretation of non-Fourier heat conduction in processed meat. J. Heat Transf. 127(2), 189–193 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1844540
Tzou, D.Y.: Macro-to Microscale Heat Transfer: The Lagging Behavior. Wiley, Chichester (2015)
Pennes, H.H.: Analysis of tissue and arterial blood temperatures in the resting human forearm. J. Appl. Physiol. 1(2), 93–122 (1948). https://doi.org/10.1152/jappl.1948.1.2.93
Liu, K.C.: Analysis for high-order effects in thermal lagging to thermal responses in biological tissue. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 81, 347–354 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2014.10.035
Yu, S.T.; Chang, S.C.; Yu, S.T.; Chang, S.C.: Treatments of stiff source terms in conservation laws by the method of space-time conservation element/solution element. In: 35th Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, p. 435 (1997). https://doi.org/10.2514/6.1997-435
Masoumi, S.; Ansari, M.A.; Mohajerani, E.; Genina, E.A.; Tuchin, V.V.: Combination of analytical and experimental optical clearing of rodent specimen for detecting beta-carotene: phantom study. J. Biomed. Opt. 23(9), 095002 (2018)
Vuylsteke, M.; Van Dorpe, J.; Roelens, J.; De Bo, T.; Mordon, S.: Endovenous laser treatment: a morphological study in an animal model. Phlebology 24(4), 166–175 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1258/phleb.2009.008070
Alemzadeh-Ansari, M.J.; Ansari, M.A.; Zakeri, M.; Haghjoo, M.: Influence of radiant exposure and repetition rate in infrared neural stimulation with near-infrared lasers. Lasers Med. Sci. 34(8), 1555–1566 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-019-02741-4
Ramadan, K.: Semi-analytical solutions for the dual phase lag heat conduction in multilayered media. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 48(1), 14–25 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2008.03.004
Zhou, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.: Dual-phase lag effects on thermal damage to biological tissues caused by laser irradiation. Comput. Biol. Med. 39(3), 286–293 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2009.01.002
Zhang, Y.: Generalized dual-phase lag bioheat equations based on nonequilibrium heat transfer in living biological tissues. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 52(21–22), 4829–4834 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2009.06.007
Kaminski, W.: Hyperbolic heat conduction equation for materials with a nonhomogeneous inner structure. J. Heat Transf. 112(3), 555–560 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2910422
Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.: An axisymmetric dual-phase-lag bioheat model for laser heating of living tissues. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 48(8), 1477–1485 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2008.12.012
Mitra, K.; Kumar, S.; Vedevarz, A.; Moallemi, M.: Experimental evidence of hyperbolic heat conduction in processed meat. J. Heat Transf. 117(3), 568–573 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2822615
Converse, M.; Bond, E.J.; Hagness, S.C.; Van Veen, B.D.: Ultrawide-band microwave space-time beamforming for hyperthermia treatment of breast cancer: a computational feasibility study. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 52(8), 1876–2189 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMTT.2004.832012
Xu, F.; Seffen, K.; Lu, T.: Non-Fourier analysis of skin biothermomechanics. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 51(9–10), 2237–2259 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2007.10.024
Acknowledgements
Author M.A.A. was supported by Grant No. 98029460 of Iranian National Science Foundation (INSF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Poshti, A.G.T., Ansari, M.A. & Ayani, M.B. The Developed Conservation Element and Solution Element Method in Two-Dimensional Spherical Coordinate and Its Application to the Analysis of Non-Fourier Heat Conduction. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 12371–12387 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07797-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07797-7