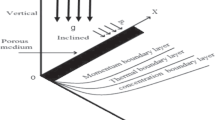
Abstract
The outcomes of partial slip on double-diffusive convection of Johnson–Segalman nanofluids in an asymmetric peristaltic path are presented in this research with the effect of inclined magnetic field. The mathematical formulation of Johnson–Segalman nanofluids is also discussed with double-diffusive convection and inclined magnetic field. To simplify extremely nonlinear partial differential equations, a lubricant approach is applied. The numerical calculations are obtained to the equations for the stream function, concentration, pressure gradient, temperature, velocity, nanoparticle volume fraction, and pressure rise. The impact of prominent hydro-mechanical parameters such as Brownian motion, thermophoresis, Soret, Dufour, and slip constraints on the axial velocity, trapping, volumetric fraction, pressure gradient, temperature, pressure rise, and concentration functions is evaluated graphically. It is noted that slip effect in the channel causes the fluid particles to stray, slowing the fluid velocity. Moreover, it has been noted that as thermophoretic effects and Brownian motion increase, nanoparticles rapidly move from the wall into the fluid, significantly raising temperature.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C :
-
Solutal concentration
- T :
-
Temperature
- G rF :
-
Grashof number of nanoparticles
- \(\Omega\) :
-
Nanoparticle volume fraction
- \(D_{B}\) :
-
Brownian diffusion coefficient
- Re:
-
Reynolds number
- \(D_{s}\) :
-
Solutal diffusively
- \(N_{t}\) :
-
Thermophoresis parameter
- \(\left( {\rho c} \right)_{f}\) :
-
Heat capacity of fluid
- \(N_{CT}\) :
-
Soret parameter
- \(G_{rc}\) :
-
Solutal Grashof number
- \(M\) :
-
Hartmann number
- Pr:
-
Prandtl number
- \(Le\) :
-
Lewis number
- \(N_{b}\) :
-
Brownian motion parameter
- \(D_{T}\) :
-
Thermophoretic diffusion coefficient
- \(G_{rt}\) :
-
Thermal Grashof number
- \(N_{TC}\) :
-
Dufour parameter
- \(Ln\) :
-
Nanofluid Lewis number
- \(\left( {\rho c} \right)_{p}\) :
-
Heat capacity of nanoparticle
- \(D_{TC}\) :
-
Dufour diffusively
- \(D_{CT}\) :
-
Soret diffusively
- \(u\) :
-
Axial velocity
- \(g\) :
-
Acceleration due to gravity
- \(d_{1} ,d_{3}\) :
-
Channel width
- \(k\) :
-
Thermal conductivity
- \(d_{2} , d_{4}\) :
-
Wave amplitudes
- \({\text{v}}\) :
-
Transverse velocity
- \(b\) :
-
Wave amplitude
- \(p\) :
-
Pressure
- \(t\) :
-
Time
- \(c\) :
-
Propagation of velocity
- \(\delta\) :
-
Wavelength
- \(\rho_{p}\) :
-
Nanoparticle mass density
- \(\gamma\) :
-
Solutal concentration
- \(\beta_{T}\) :
-
Volumetric coefficient of thermal expansion
- \(\omega_{3}\) :
-
Concentration slip parameter
- \(\omega_{1}\) :
-
Velocity slip parameter
- \(\delta\) :
-
Wave number
- \(\Psi\) :
-
Stream function
- \(\left( {\rho c} \right)_{p}\) :
-
Nanoparticle heat capacity
- \(\Gamma\) :
-
Magnetic field inclination angle
- \(\beta_{C}\) :
-
Volumetric coefficient of solutal expansion
- \(\omega_{4}\) :
-
Nanoparticles slip parameter
- \(\omega_{2}\) :
-
Temperature slip parameter
- \(\Theta\) :
-
Temperature
References
Bertuzzi, A.; Mancinelli, R.; Pescatori, M.; Salinari, S.; Ghista, D.N.: Models of gastrointestinal tract motility. In: Kline, J. (Ed.) Hand Book of Biomedical Engineering, pp. 637–654. Academic Press, London, UK (1988)
J. N. J. Lozano, Peristaltic flow with application to ureteral biomechanics, Ph.D. thesis, Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering, University of Notre Dame, Notre Dame, Ind, USA
Quillin, K.J.: Kinematic scaling of locomotion by hydrostatic animals: ontogeny of peristaltic crawling by the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris. J. Exp. Biol. 202, 661–674 (1999)
Saga, N.; Nakamura, T.: Development of a peristaltic crawling robot using magnetic fluid on the basis of the locomotion mechanism of the earthworm. Smart Mater. Struct. 13, 566–569 (2004)
T. W. Latham, Fluid motion in a peristaltic pump, M.Sc. Thesis, MIT, Cambridge, 1966.
Jaffrin, M.Y.; Shapiro, A.H.: Peristaltic pumping. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 3, 13–37 (1971)
Burns, J.C.; Parkes, J.: Peristaltic motion. J. Fluid Mech. 29, 731–743 (1967)
Chow, T.S.: Peristaltic transport in a circular cylindrical pipe. J. Appl. Mech. 37, 901–906 (1970)
Mishra, M.; Rao, A.R.: Peristaltic transport of a Newtonian fluid in an asymmetric channel. Zeitschrift fur angewandte Mathematik and Physik 54, 532–550 (2004)
Shapiro, A.H.; Jaffrin, M.Y.; Weinberg, S.L.: Peristaltic pumping with long wavelengths at low Reynolds number. Cambridge University Press 37, 799–825 (1969)
Takabatake, S.; Ayukawa, K.: Numerical study of two-dimensional peristaltic flows. J. Fluid Mech. 122, 439–465 (1982)
Johnson, M.W., Jr.; Segalman, D.: A model for viscoelastic fluid behavior which allows non-affine deformation. J. Nonnewton. Fluid Mech. 2, 255–270 (1977)
Malkus, D.S.; Nohel, J.A.; Plohr, B.J.: Dynamics of shear flows of non-Newtonian fluids. J. Comput. Phys. 87, 464–497 (1990)
Vinogardov, G.V.; Malkin, A.Y.; Yanovskii, G.Y.; Borisenkova, E.K.; Yarlykov, B.V.; Brezhnava, G.V.: Viscoelastic properties and flow of narrow distribution polybutadienes and polyisopropenes. J. Polym. Sci. Part A-2 10, 1061–1084 (1972)
McLeish, T.C.B.; Ball, R.C.: A molecular approach to the spurt effect in polymer melt flow. J. Polym. Sci. (B) 24, 1765–1745 (1986)
Hayat, T.; Afsar, A.; Ali, N.: Peristaltic transport of a Johnson-Segalman fluid in an asymmetric channel. Math. Comput. Model. 47, 380–400 (2008)
Kraynik, A.M.; Schowalter, W.R.: Slip at the wall and extrudate roughness with aqueous solutions of polyvinyl alcohol and sodium borate. J. Rheol. 25, 95–114 (1981)
S. U. S. Choi, Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. In: Proceedings of the ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, San Francisco, CA, USA, (1995) 99–105 .
S. Mosayebidorcheh, M. Hatami Analytical investigation of peristaltic nanofluid flow and heat transfer in an asymmetric wavy wall channel, International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,
Akram, S.; Afzal, Q.: Effects of thermal and concentration convection and induced magnetic field on peristaltic flow of Williamson nanofluid in inclined uniform channel. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 135, 857 (2020)
Ellahi, R.; Zeeshan, A.; Hussain, F.; Asadollahi, A.: Peristaltic blood flow of couple stress fluid suspended with nanoparticles under the influence of chemical reaction and activation energy. Symmetry 11, 276 (2019)
Akram, S.; Nadeem, S.: Influence of nanoparticles phenomena on the peristaltic flow of pseudoplastic fluid in an inclined asymmetric channel with different wave forms. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 36, 107–124 (2017)
Prakash, J.; Tripathi, D.; Triwari, A.K.; Sait, S.M.; Ellahi, R.: Peristaltic pumping of nanofluids through tapered channel in porous environment: Applications in blood flow. Symmetry 11, 868 (2019)
Kayani, S.M.; Hina, S.; Mustafa, M.: A new model and analysis for peristalsis of Carreau-Yasuda (CY) nanofluid subject to wall properties. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 45, 5179–5190 (2020)
Akbar, N.S.; Nadeem, S.: Endoscopic effects on the peristaltic flow of a nanofluid. Commun. Theor. Phys. 56, 761–768 (2011)
Bhatti, M.M.; Zeeshan, A.; Ellahi, R.: Simultaneous effects of coagulation and variable magnetic field on peristaltically induced motion of Jeffrey nanofluid containing gyrotactic microorganism. Microvasc. Res. 110, 32–42 (2017)
Qasim, M.; Ali, Z.; Wakif, A.; Boulahia, Z.: Numerical simulation of MHD peristaltic flow with variable electrical conductivity and Joule dissipation using generalized quadrature method. Commun. Theor. Phys. 71, 509–518 (2019)
Ali, F.; Sheikh, N.A.; Khan, I.; Saqib, M.: Magnetic field effect on blood flow of Casson fluid in axisymmetric cylindrical tube: a fractional model. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 423, 327–336 (2017)
Tripathi, D.; Beg, O.: A study on peristaltic flow of nanofluids: application in drug delivery systems. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 70, 61–70 (2014)
Sucharitha, G.; Vajravelu, K.; Lakshminarayana, P.: Magnetohydrodynamic nanofluid flow in a non-uniform aligned channel with Joule heating. J. Nanofluids 8, 1373 (2019)
Kothandapani, M.; Prakash, J.: Effects of thermal radiation parameter and magnetic field on the peristaltic motion of Williamson nanofluid in a tapered asymmetric channel. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 81, 234–245 (2015)
Reddy, M.G.; Makinde, O.D.: Magnetohydrodynamic peristaltic transport of Jeffrey nanofluid in an asymmetric channel. J. Mol. Liq. 223, 1242–1248 (2016)
Raza, M.; Ellahi, R.; Sait, S.M.; Sarafraz, M.M.; Shadloo, M.S.; Waheed, I.: Enhancement of heat transfer in peristaltic flow in a permeable channel under induced magnetic field using different CNTs. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 140, 1277–1291 (2019)
Akram, S.: Effects of nanofluid on peristaltic flow of a Carreau fluid model in an inclined magnetic field. Heat Transf. Asian Res. 43, 368–383 (2014)
Raza, M.; Ellahi, R.; Sait, S.M.; Sarfaraz, M.M.; Shadloo, M.S.; Waheed, I.: Enhancement of heat transfer in peristaltic flow in a permeable channel under induced magnetic field using different CNTs. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 140, 1277–1291 (2020)
Hussain, S.; Jamal, M.; Haddad, Z.; Arc, M.: Numerical modeling of magnetohydrodynamic thermosolutal free convection of power law fluids in a staggered porous enclosure. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 53, 102395 (2022)
Yldz, Ç.; Arc, M.; Karabay, H.: Effect of inclination angle on natural convection of nanofluids in a U-shaped cavity. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 5289–5294 (2019)
Ali, F.H.; Hamzah, H.K.; Egab, K.; Arc, M.; Shahsavar, A.: Non-Newtonian nanofluid natural convection in a U-shaped cavity under magnetic field. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 186, 105887 (2021)
Al-Amir, Q.R.; Hamzah, H.K.; Ali, F.H.; Bayraktar, S.; Arc, M.; Hatami, M.: Comparison study of vertical and horizontal elastic wall on vented square enclosure filled by nanofluid and hexagonal shape with MHD effect. Eur. Phys. J. Special Top. 231, 2623–2643 (2022)
Yldz, Ç.; Arc, M.; Karabay, H.; Bennacer, R.: Natural convection of nanofluid in a U-shaped enclosure emphasizing on the effect of cold rib dimensions. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 146, 801–811 (2021)
Garimella, S.V.; Simpson, J.E.: Effect of thermo solutal convection on directional solidification. Sadhana 26, 121–136 (2001)
Akbar, N.S.; Habib, M.B.: Peristaltic pumping with double diffusive natural convective nanofluid in a lopsided channel with accounting thermophoresis and Brownian moment. Microsyst. Technol. 25, 1217–1226 (2019)
Sharma, A.; Tripathi, D.; Sharma, R.K.; Tiwari, A.K.: Analysis of double diffusive convection in electroosmosis regulated peristaltic transport of nanofluids. Physica A 535, 122148 (2019)
Anwar Bég, O.; Tripathi, D.: Mathematica simulation of peristaltic pumping with double-diffusive convection in nanofluids a bio-nanoengineering model. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part N 225, 99–114 (2012)
Akram, S.; Afzal, Q.; Aly, E.H.: Half-breed effects of thermal and concentration convection of peristaltic pseudoplastic nanofluid in a tapered channel with induced magnetic field. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 22, 100775 (2020)
Alolaiyan, H.; Riaz, A.; Razaq, A.; Saleem, N.; Zeeshan, A.; Bhatti, M.M.: Effects of double diffusion convection on third grade nanofluid through a curved compliant peristaltic channel. Coatings 10(2), 154 (2020)
Asha, S.K.; Sunitha, G.: Thermal radiation and hall effects on peristaltic blood flow with double diffusion in the presence of nanoparticles. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 17, 100560 (2020)
Akram, S.; Athar, M.; Saeed, K.: Hybrid impact of thermal and concentration convection on peristaltic pumping of Prandtl nanofluids in non-uniform inclined channel and magnetic field. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 25, 100965 (2021)
Riaz, A.; Khan, S.U.D.; Zeeshan, A.; Khan, S.U.; Hassan, M.; Muhammad, T.: Thermal analysis of peristaltic flow of nanosized particles within a curved channel with second-order partial slip and porous medium. J. Thermal Anal. Calorim. 143, 1997–2009 (2021)
Ali, A.; Saleem, S.; Mumraiz, S.; Saleem, A.; Awais, M.; Khan Marwat, D.N.: Investigation on TiO2–Cu/H2O hybrid nanofluid with slip conditions in MHD peristaltic flow of Jeffrey material. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 143, 1985–1996 (2021)
Derek, C.; Tretheway, D.C.; Meinhart, C.D.: Apparent fluid slip at hydrophobic microchannel walls. Phys. Fluids 14, L9–L12 (2002)
Akram, S.; Razia, A.; Afzal, F.: Effects of velocity second slip model and induced magnetic field on peristaltic transport of non-Newtonian fluid in the presence of double-diffusivity convection in nanofluids. Arch. Appl. Mech. 90, 1583–1603 (2020)
Aly, E.H.; Ebaid, A.: Effect of the velocity second slip boundary condition on the peristaltic flow of nanofluids in an asymmetric channel: exact solution. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2014, 191876 (2014)
Hina, S.: MHD peristaltic transport of Eyring–Powell fluid with heat/mass transfer, wall properties and slip conditions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 404, 148–158 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Saeed, K., Akram, S. & Ahmad, A. Outcomes of Partial Slip on Double-Diffusive Convection on Peristaltic Waves of Johnson–Segalman Nanofluids Under the Impact of Inclined Magnetic Field. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 15865–15881 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07706-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07706-y