Abstract
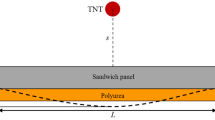
In order to balance the blast protective performance and lightweight property, sandwich panels with various geometries of core are being employed in the military armours and modern-day combat vehicles. Owing to the superior energy absorption capacity of auxetic-reentrant cellular structures, hybridizing auxetic cells with the regular hexagonal cells in the honeycomb core for the purpose of blast protection could be a promising method. Therefore, novel honeycomb cores with combined auxetic and hexagonal cells (AuxHex and Star-Reentrant) are designed for blast protection panel with an aim to enhance the blast performance by improving the energy absorption and minimizing the dynamic deflection of the back plate. Initially, the dynamic response of honeycomb sandwich panels with various regular geometrical cores is analysed and validated with the experimental results from the literature. Further, air blast analysis has been performed on AuxHex and Star-Reentrant honeycomb cored sandwich panel having same relative density as that of hexagonal honeycomb core under exactly same conditions. In addition to that, the study is extended for varying charges of TNT and at different stand-off distances. It has been revealed that the sandwich panel with AuxHex and Star-Reentrant core of same relative density as that of hexagonal honeycomb core absorbs 28% and 19.2% more amount of energy and experiences 17% and 8% less deflection, respectively, than those with regular hexagonal honeycomb core.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meyers, M.A.: Dynamic Behavior of Materials. Wiley, Hoboken (1994)
Li, B.; Liu, Y.; Tan, K.-T.: A novel meta-lattice sandwich structure for dynamic load mitigation. J. Sandwich Struct. Mater. 21(6), 1880–1905 (2019)
Chen, G.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, J.; Chen, C.; Cai, S.: Design and modelling of auxetic double arrowhead honeycomb core sandwich panels for performance improvement under air blast loading. J. Sandwich Struct. Mater. 23(8), 3574–3605 (2021)
Sahu, S.K.; Badgayan, N.D.; Samanta, S.; Rama Sreekanth, P.S.: Evaluation of cell parameter variation on energy absorption characteristic of thermoplastic honeycomb sandwich structure. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 46(12), 12487–12507 (2021)
Haq, A.U.; Reddy, N.S.K.: A brief review on various high energy absorbing materials. Mater. Today Proc. 38, 3198–3204 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.09.648
Kangda, M.Z.; Bakre, S.: Positive-phase blast effects on base-isolated structures. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 44(5), 4971–4992 (2019)
Imbalzano, G.; Tran, P.; Ngo, T.D.; Lee, P.V.: Three-dimensional modelling of auxetic sandwich panels for localised impact resistance. J. Sandwich Struct. Mater. 19(3), 291–316 (2017)
Garrido Silva, B.; Alves, F.; Sardinha, M.; Reis, L.; Leite, M.; Deus, A. M.; Vaz, M. F. Functionally graded cellular cores of sandwich panels fabricated by additive manufacturing. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Design Appl. 14644207221084611(2022)
Wang, T.; Qin, Q.; Wang, M.; Yu, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T.J.: Blast response of geometrically asymmetric metal honeycomb sandwich plate: experimental and theoretical investigations. Int. J. Impact Eng. 105, 24–38 (2017)
Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Hui, D.: Blast resistance and parametric study of sandwich structure consisting of honeycomb core filled with circular metallic tubes. Compos. B Eng. 145, 261–269 (2018)
Ashby, M.F.; Evans, T.; Fleck, N.A.; Hutchinson, J.W.; Wadley, H.N.G.; Gibson, L.J.: Metal Foams: A Design Guide. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2000)
Ling, X.; Zhang, Y.F.; Wang, Y.Q.: Dynamic response of buried fluid-conveying pipelines subjected to blast loading using shell theory. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 46(5), 4883–4893 (2021)
Tan, P.: Finite element simulation of the behaviours of laminated armour systems against blast wave and projectile dynamic impacts. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Design Appl. 227(1), 2–15 (2013)
Sahu, S.K.; Rama Sreekanth, P.S.: Experimental investigation of in-plane compressive and damping behavior anisotropic graded honeycomb structure. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 47(12), 15741–15753 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-06771-z
Sur, A.; Darvekar, S.; Shah, M.: Recent advancements of micro-lattice structures: application, manufacturing methods, mechanical properties, topologies and challenges. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 46(12), 11587–11600 (2021)
Grujicic, M.; Yavari, R.; Snipes, J.S.; Ramaswami, S.: Use of aluminum foam core sandwich structures to improve the blast-mitigation performance of light tactical vehicle side-vent-channel solution. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Design Appl. 232(12), 993–1011 (2018)
Yao, S.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, P.; Cao, Y.; Ping, X.: Energy absorption characteristics of square frustum lattice structure. Compos. Struct. 275, 114492 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.114492
Cai, S.; Zhang, P.; Dai, W.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, J.: Multi-objective optimization for designing metallic corrugated core sandwich panels under air blast loading. J. Sandwich Struct. Mater. 23(4), 1192–1220 (2021)
Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xiao, D.; Wenwang, Wu.; Fang, D.: The Dynamic response of shallow sandwich arch with auxetic metallic honeycomb core under localized impulsive loading. Int. J. Impact Eng 137, 103442 (2020)
Cong, P.H.; Quyet, P.K.; Duc, N.D.: Effects of lattice stiffeners and blast load on nonlinear dynamic response and vibration of auxetic honeycomb plates. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 235(23), 7192–7211 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1177/0954406221992797
Wang, L.; Saito, K.; Gotou, Y.; Okabe, Y.: Design and fabrication of aluminum honeycomb structures based on origami technology. J. Sandwich Struct. Mater. 21(4), 1224–1242 (2019)
Omidvar, H.; Azari, K.K.; Mohammad Taheri, A.; Saghafi, A.A.: Impact and ballistic behavior optimization of kevlar–epoxy composites by taguchi method. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 38(5), 1161–1167 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-012-0381-4
Dharmasena, K.P.; Wadley, H.N.G.; Williams, K.; Xue, Z.; Hutchinson, J.W.: Response of metallic pyramidal lattice core sandwich panels to high intensity impulsive loading in air. Int. J. Impact Eng. 38(5), 275–289 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2010.10.002
Kang, K.-J.: Wire-woven cellular metals: the present and future. Prog. Mater Sci. 69, 213–307 (2015)
Huang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Scarpa, F.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J.: In-plane elasticity of a novel auxetic honeycomb design. Compos. B Eng. 110, 72–82 (2017)
Qi, C.; Pei, L.-Z.; Remennikov, A.; Yang, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.-S.; Liao, X.-W.: Parametric study and optimization of the protect system containing a re-entrant hexagon cored sandwich panel under blast impact. Compos. Struct. 252, 112711 (2020)
Lakes, R.: Foam structures with a negative Poisson’s ratio. Science 235(4792), 1038–1040 (1987)
Ingrole, A.; Hao, A.; Liang, R.: Design and modeling of auxetic and hybrid honeycomb structures for in-plane property enhancement. Mater. Des. 117, 72–83 (2017)
Yazdani Sarvestani, H.; Akbarzadeh, A.H.; Niknam, H.; Hermenean, K.: 3D printed architected polymeric sandwich panels: energy absorption and structural performance. Compos. Struct. 200, 886–909 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.04.002
Fu, M.-H.; Chen, Yu.; Ling-Ling, Hu.: A novel auxetic honeycomb with enhanced in-plane stiffness and buckling strength. Compos. Struct. 160, 574–585 (2017)
Del Broccolo, S.; Laurenzi, S.; Scarpa, F.: AUXHEX – A Kirigami inspired zero Poisson’s ratio cellular structure. Compos. Struct. 176, 433–441 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.05.050
Chen, G.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, P.; Cai, S.; Liu, J.: Blast resistance of metallic double arrowhead honeycomb sandwich panels with different core configurations under the paper tube-guided air blast loading. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 201, 106457 (2021)
Kumar, S.; Vyavahare, S.; Teraiya, S.; Kootikuppala, J.; Bogala, H.: A state of the art review of additively manufactured auxetic structures. In: Dave, H.K.; Dixit, U.S.; Nedelcu, D. (Eds.) Recent Advances in Manufacturing Processes and Systems: Select Proceedings of RAM 2021, pp. 69–84. Springer Nature Singapore, Singapore (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-7787-8_6
Aryal, B.; Morozov, E. V.; Shankar, K. Effects of ballistic impact damage on mechanical behaviour of composite honeycomb sandwich panels. J. Sandwich Struct. Mater. 1099636220909743 (2020)
Rodriguez-Millan, M.; Garcia-Gonzalez, D.; Rusinek, A.; Arias, A.: Influence of stress state on the mechanical impact and deformation behaviors of aluminum alloys. Metals 8(7), 520 (2018)
Banerjee, A.; Dhar, S.; Acharyya, S.; Datta, D.; Nayak, N.: Determination of Johnson cook material and failure model constants and numerical modelling of Charpy impact test of armour steel. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 640, 200–209 (2015)
Ghazlan, A.; Ngo, T.; Le, V.T.; Nguyen, T.; Linforth, S.; Remennikov, A.; Whittaker, A.: A bio-mimetic cellular structure for mitigating the effects of impulsive loadings–a numerical study. J. Sandwich Struct. Mater. 23(6), 1929–1955 (2021)
Dharmasena, K.P.; Wadley, H.N.G.; Xue, Z.; Hutchinson, J.W.: Mechanical response of metallic honeycomb sandwich panel structures to high-intensity dynamic loading. Int. J. Impact Eng. 35(9), 1063–1074 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2007.06.008
Jin, X.; Wang, Z.; Ning, J.; Xiao, G.; Liu, E.; Shu, X.: Dynamic response of sandwich structures with graded auxetic honeycomb cores under blast loading. Compos. B Eng. 106, 206–217 (2016)
Wang, Y.; Yi, Yu.; Wang, C.; Zhou, G.; Karamoozian, A.; Zhao, W.: On the out-of-plane ballistic performances of hexagonal, reentrant, square, triangular and circular honeycomb panels. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 173, 105402 (2020)
Acosta, P.F.: Overview of UFC 3-340-02 structures to resist the effects of accidental explosions. Struct. Congr. 2011, 1454–1469 (2011)
Xu, M.; Ziran, Xu.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, H.; Bai, Y.; Fang, D.: Mechanical properties and energy absorption capability of AuxHex structure under in-plane compression: theoretical and experimental studies. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 159, 43–57 (2019)
Li, X.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Z.; Guiying, Wu.; Zhao, L.: Dynamic behavior of aluminum honeycomb sandwich panels under air blast: experiment and numerical analysis. Compos. Struct. 108, 1001–1008 (2014)
Roudbeneh, F.H.; Liaghat, G.; Sabouri, H.; Hadavinia, H.: Experimental investigation of impact loading on honeycomb sandwich panels filled with foam. Int. J. Crashworthiness 24(2), 199–210 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/13588265.2018.1426233
Yang, L.; Li, X.; Zi, F.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, Q.; Dong, Y.; Linzhi, Wu.: Dynamic response of graded PVC foam sandwich panel under air blast loads. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 29(25), 3694–3708 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/15376494.2021.1909190
Xue, Z.; Hutchinson, J.W.: Crush dynamics of square honeycomb sandwich cores. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng. 65(13), 2221–2245 (2006)
Wadley, H.N.G.; Børvik, T.; Olovsson, L.; Wetzel, J.J.; Dharmasena, K.P.; Hopperstad, O.S.; Deshpande, V.S.; Hutchinson, J.W.: Deformation and fracture of impulsively loaded sandwich panels. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 61(2), 674–699 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmps.2012.07.007
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ul Haq, A., Gunashekar, G. & Narala, S.K.R. The Dynamic Response of AuxHex and Star-Reentrant Honeycomb Cored Sandwich Panels Subject to Blast Loading. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 11755–11771 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07564-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07564-0