Abstract
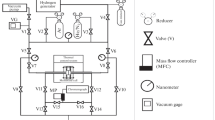
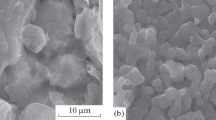
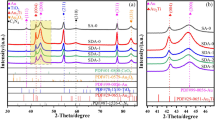
In this study, it was aimed to synthesize PdCu alloy membranes with firm, thin, and fcc phase structure (resistant to sulfur compounds), selectively permeable to hydrogen, using an electroless plating technique by creating an osmotic flux. First, coating studies were conducted without creating osmotic flux to determine the appropriate alloy formation temperature. Commercial porous borosilicate glass tubes were modified with alumina to form an interface that enhances the interaction between the coating and the support. The modified supports were cleaned and activated, then coated 3 times for 45 min in the Pd-based plating bath and then once for 15 min in the Cu-based plating bath. The coated supports were subjected to heat treatment at two different temperatures (550 and 650 °C) in a hydrogen environment for 8 h. Then, 650 °C, where the metals loaded on the surface were highly involved in the alloy structure and only the fcc phase was observed, was determined as the appropriate alloy temperature. Afterward, coating studies were conducted by creating osmotic flux with a 3 M sucrose solution, keeping the coating conditions and bath composition the same. From XRD analysis, fcc phase formation was observed in {111} {200} {220} planes in the membrane synthesized without osmotic flux, while alloy formation was detected in the {311} plane in addition to these planes in the membrane synthesized with osmotic flux. In this study, it has been shown that besides the temperature and time, the firmness of the metal layers formed before the heat treatment also affects the alloy formation in this plane. It was determined from SEM/EDS analyses that the membranes synthesized under the effect of osmotic flux were thinner, firmer, and homogeneous (⁓ 13.5 µm). Hydrogen transport parameters (T = 250 °C, ΔP = 101–304 kPa) were investigated in the synthesized membranes. In accordance with the literature, low hydrogen flux (0.04–0.09 mol/m2 s) and high selectivity values (αH2/N2:465–324) were determined in membranes synthesized with osmotic flux. Additionally, it was determined that this membrane remained stable in the hydrogen environment (T = 250 °C, ΔP = 203 kPa) for 96 h. The results of the study showed that conducting the electroless plating method with osmotic flux made positive contributions to the structure and hydrogen selectivity of the prepared alloy membranes.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iulianelli, A.; Manisco, M.; Bion, N.; Le Valant, A.; Epron, F.; Colpan, C.O: Sustainable H2 generation via steam reforming of biogas in membrane reactors: H2S effects on membrane performance and catalytic activity. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 46(57), 29183–29197 (2021)
Lundin, S.B.; Patki, N.S.; Zhang, Z.; Fuerst, T.F.; Wolden, C.A.; Way, J.D.: PdAu/YSZ composite hydrogen separation membranes with enhanced stability in the presence of CO. J. Membr. Sci. 611, 118371 (2020)
Liguori, S.; Kian, K.; Buggy, N.; Anzelmo, B.H.; Wilcox, J.: Opportunities and challenges of low-carbon hydrogen via metallic membranes. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 80, 100851 (2020)
Bellini, S.; Azzato, G.; Sun, Y.; Gallucci, F.; Caravella, A.: Metal membranes in hydrogen separation and purification. In: Basile, A., Spazzafumo, G. (eds.) Current Trends and Future Developments on (Bio-) Membranes. Elsevier (2020)
Li, H.; Caravella, A.; Xu, H.: Recent progress in Pd-based composite membranes. J. Mater. Chem. 37, 14069–14094 (2016)
Conde, J.J.; Marono, M.; Sanchez-Hervas, J.M.: Pd-based membranes for hydrogen separation: review of alloying elements and their influence on membrane properties. Sep. Purif. Rev. 46(2), 152–177 (2017)
Zhao, C.; Sun, B.; Jiang, J.; Xu, W.: H2 purification process with double layer bcc-PdCu alloy membrane at ambient temperature. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 45, 17540–17547 (2020)
Peters, T.A.; Stange, M.; Veenstra, P.; Nijmeijer, A.; Bredesen, R.: The performance of Pd–Ag alloy membrane films under exposure to trace amounts of H2S. J. Membr. Sci. 499, 105–115 (2016)
Nayebossadri, S.; Speight, J.D.; Book, D.: Hydrogen separation from blended natural gas and hydrogen by Pd-based membranes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 44(55), 29092–29099 (2019)
Tosques, J.; Guerreiro, B.H.; Martin, M.H.; Roue, L.; Guay, D.: Hydrogen solubility of bcc PdCu and PdCuAg alloys prepared by mechanical alloying. J. Alloy. Compd. 698, 725–730 (2017)
Chen, B.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Xu, T.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; Xu, H.: Long-term stability against H2S poisoning on Pd composite membranes by thin zeolite coatings. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 58(16), 6429–6437 (2019)
Tang, J.; Yamamoto, S.; Koitaya, T.; Yoshigoe, A.; Tokunaga, T.; Mukai, K.: Mass transport in the PdCu phase structures during hydrogen adsorption and absorption studied by XPS under hydrogen atmosphere. Appl. Surf. Sci. 480, 419–426 (2019)
Zhao, L.; Goldbach, A.; Xu, H.: Tailoring palladium alloy membranes for hydrogen separation from sulfur contaminated gas streams. J. Membr. Sci. 507, 55–62 (2016)
Acha, E.; van Delft, Y.C.; Cambra, J.F.; Arias, P.L.: Thin PdCu membrane for hydrogen purification from in-situ produced methane reforming complex mixtures containing H2S. Chem. Eng. Sci. 176, 429–438 (2018)
Endo, N.; Furukawa, Y.; Goshome, K.; Yaegashi, S.; Mashiko, K.; Tetsuhiko, M.: Characterization of mechanical strength and hydrogen permeability of a PdCu alloy film prepared by one-step electroplating for hydrogen separation and membrane reactors. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 44(16), 8290–8297 (2019)
Sumrunronnasak, S.; Tantayanon, S.; Kiatgamolchai, S.: Influence of layer compositions and annealing conditions on complete formation of ternary PdAgCu alloys prepared by sequential electroless and electroplating methods. Mater. Chem. Phys. 185(1), 98–103 (2017)
Wei, W.; Liua, L.C.; Gonga, H.R.; Songa, M.; Chang, M.L.; Chen, D.C.: Fundamental mechanism of BCC-FCC phase transition from a constructed PdCu potential through molecular dynamics simulation. Comput. Mater. Sci. 159, 440–447 (2019)
Liu, L.C.; Gong, H.R.; Zhou, S.F.; Gong, X.: Adsorption, diffusion, and permeation of hydrogen at PdCu surfaces. J. Membr. Sci. 588, 117206 (2019)
Marono, M.; Alessandro, G.D.; Morales, A.; Martinez-Diaz, D.; Alique, D.; Sanchez, J.M.: Influence of Si and Fe/Cr oxides as intermediate layers in the fabrication of supported Pd membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 234, 116091 (2020)
Plazaola, A.A.; Tanaka, D.A.P.; Annaland, M.V.S.; Gallucci, F.: Recent Advances in Pd-based membranes for membrane reactors. Molecules 22(1), 51 (2017)
Hawa, H.W.A.E.; Lundin, S.T.B.; Paglieri, S.N.; Harale, A.; Way, J.D.: The influence of heat treatment on the thermal stability of Pd composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 494, 113–120 (2015)
Contardi, I.; Cornaglia, L.; Tarditi, A.M.: Effect of the porous stainless steel substrate shape on the ZrO2 deposition by vacuum assisted dip-coating. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 42, 7986–7996 (2017)
Souleimanova, R.S.; Mukasyan, A.S.; Varma, A.: Pd membranes formed by electroless plating with osmosis: H2 permeation studies. AIChE 48(2), 262–268 (2002)
Li, A.; Liang, W.; Hughes, R.: Fabrication of dense palladium composite membranes for hydrogen separation. Catal. Today 56, 45–51 (2000)
Souleimanova, R.S.; Mukasyan, A.S.; Varma, A.: Pd-composite membranes prepared by electroless plating and osmosis: synthesis, characterization and properties. Sep. Purif. Technol. 25, 79–86 (2001)
Guo, Y.; Zou, H.; Wu, H.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.: Preparation of palladium membrane by bio-membrane assisted electroless plating for hydrogen separation. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 39(13), 7069–7076 (2014)
Conde, J.J.; Marono, M.; Sanchez-Hervas, J.M.: Pd-based membranes for hydrogen separation: review of alloying elements and their influence on membrane properties. Sep. Purif. Rev. 46(2), 152–177 (2017)
Lee, C.B.; Lee, S.W.; Park, J.S.; Ryi, S.K.; Lee, D.W.; Hwang, K.R.; Kim, S.H.: Ceramics used as intermetallic diffusion barriers in Pd-based composite membranes sputtered on porous nickel supports. J. Alloys Comput. 578, 425–430 (2013)
Chi, Y.H.; Yen, P.S.; Jeng, M.S.; Ko, S.T.; Lee, T.C.: Preparation of thin Pd membrane on porous stainless steel tubes modified by a two-step method. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 35, 6303–6310 (2010)
Chen, C.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, B.; Cheng, Z.: Sharp Cu@Sn nanocones on Cu foam for highly selective and efficient electrochemical reduction of CO2 to formate. Mater. Chem. A 6, 19621–19630 (2018)
Alique, D.; Martinez-Diaz, D.; Sanz, R.; Calles, J.A.: Review of supported Pd-based membranes preparation by electroless plating for ultra-pure hydrogen production. Membranes 8(1), 5 (2018)
Jia, H.; Wu, P.; Zeng, G.; Salas-Colera, E.; Serrano, A.; Castro, G.R.; Xu, H.; Sun, C.; Goldbach, A.: High-temperature stability of Pd alloy membranes containing Cu and Au. J. Membr. Sci. 544, 151–160 (2017)
Lee, Y.H.; Jang, Y.; Han, D.H.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, S.S.: Palladium-copper membrane prepared by electroless plating for hydrogen separation at low temperature. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 9(6), 106509 (2021)
Wang, T.; Dong, P.; Li, J.; You, Y.-W.: The factors affecting the diffusion properties of hydrogen in palladium copper alloys: Ab initio study. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 47, 27579–27589 (2022)
Islam, M.S.; Rahman, M.M.; Ilias, S.: Characterization of PdCu membranes fabricated by surfactant induced electroless plating (SIEP) for hydrogen separation. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 37, 3477–3490 (2012)
Westerwaal, R.J.; Bouman, E.A.; Haije, W.G.; Schreuders, H.; Dutta, S.; Wu, M.Y.; Boelsma, C.; Ngene, P.; Basak, S.; Dam, B.: The hydrogen permeability of PdCu based thin film membranes in relation to their structure: a combinatorial approach. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 40, 3932–3943 (2015)
Zhao, C.; Goldbach, A.; Xu, H.: Low-temperature stability of body-centered cubic PdCu membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 542, 60–67 (2017)
Zhang, K.; Way, J.D.: Palladium-copper membranes for hydrogen separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 186, 39–44 (2017)
Al-Mufachi, N.; Steinberger-Wilckens, R.: X-ray diffraction study on the effects of hydrogen on Pd60Cu40 wt% foil membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 454, 266–274 (2018)
Kian, K.; Woodall, C.M.; Wilcox, J.; Liguori, S.: Performance of Pd-based membranes and effects of various gas mixtures on H2 permeation. Environments 5, 138 (2018)
Liu, L.C.; Gong, H.R.; Zhou, S.F.: Hydrogen flux of BCC and FCC PdCuAg membranes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 44, 31160–31177 (2019)
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Gazi University Scientific Research Projects Unit for supporting our study with the Project Number 06/2017-16 and titled "Synthesis and Characterization of Palladium Alloy Membranes." The authors would like to thank Gazi University Academic Writing Application and Research Center for proofreading the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kilic, S., Dogan, M. & Cetinyokus, S. Effects of Osmotic Flux on PdCu Alloy Membrane Structure. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 8887–8899 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07522-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07522-w